Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (21): 3394-3400.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2607
Previous Articles Next Articles
Molecular signaling pathways in the occurrence and development of osteoarthritis
Liao Jianzhao1, Zhang Xiaoyun2, Zhang Xuan3
- 1Graduate School, 2School of Bone Injury, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 3Department of Traumatology and Hand Surgery, Ruikang Hospital, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2019-10-08Revised:2019-10-11Accepted:2019-11-07Online:2020-07-28Published:2020-04-18 -
Contact:Zhang Xuan, MD, Attending physician, Department of Traumatology and Hand Surgery, Ruikang Hospital, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China Zhang Xiaoyun, Master, Attending physician, School of Bone Injury, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Liao Jianzhao, Master candidate, Graduate School, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81760796 and 81960803; the Basic Ability Improvement Project of Young Teachers in Guangxi Universities, No. 2019KY0352; the 2019 School-Level Scientific Research Project of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2019QN027; the First-Class Subject of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2019XK029; the Doctoral Introduction Research Foundation Project of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine in 2017, No. B170045
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liao Jianzhao, Zhang Xiaoyun, Zhang Xuan. Molecular signaling pathways in the occurrence and development of osteoarthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(21): 3394-3400.
share this article
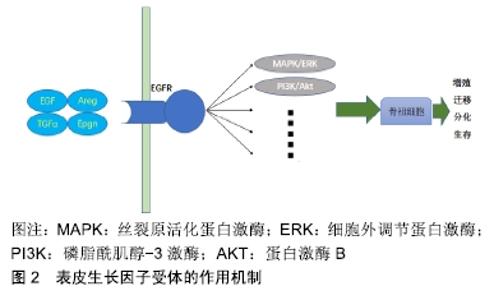
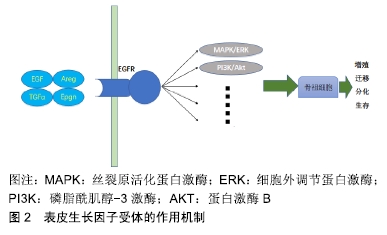
2.1 表皮生长因子受体信号通路在骨性关节炎中的作用 表皮生长因子受体是一种糖蛋白,属于酪氨酸激酶型受体,可通过与配体(包括表皮生长因子、转化生长因子α、Areg等)结合,启动多条信号通路[丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase,MAPK)/细胞外调节蛋白激酶、磷脂酰肌醇-3激酶/蛋白激酶B(protein kinase B,AKT)等]刺激骨祖细胞的增殖、生存、分化和迁移[5],见图2[6]。目前,大多数研究骨性关节炎中表皮生长因子受体信号通路作用的学者一致认为,与其他生长因子信号通路一样,表皮生长因子受体对关节软骨具有双重作用:一方面,它通过刺激骨细胞的增殖发挥合成代谢的作用;另一方面,通过抑制Sox9的表达发挥分解代谢的作用;此外表皮生长因子受体还能刺激基质金属蛋白酶等基质降解蛋白酶的表达促进基质降解[6]。 "
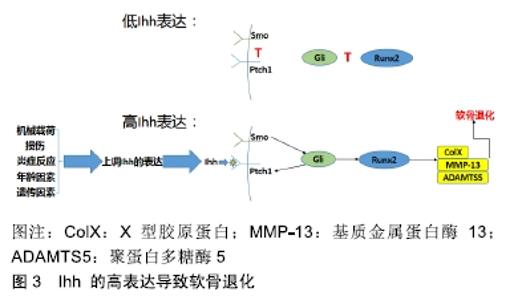
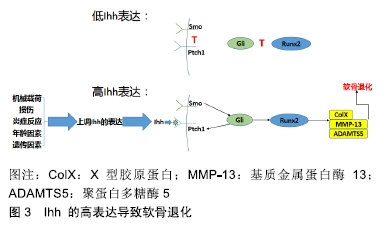
2.1.1 表皮生长因子受体信号通路在维持关节软骨正常功能中发挥重要作用 JIA等[7]的研究在明确条件性的基因敲除小鼠模型对整体骨代谢没有影响的前提下,通过对表皮生长因子受体缺陷的条件性的基因敲除小鼠的观察,发现表皮生长因子受体信号的缺失会导致关节软骨出现异常发育的情况;通过对关节滑液分泌情况的观察发现,表皮生长因子受体信号通过调控Prg4进而调节滑液的分泌;对比条件性的基因敲除和非条件性的基因敲除小鼠的软骨表面硬度发现,表皮生长因子受体信号调控关节软骨的力学特性;研究数据还表明表皮生长因子受体信号是获得足够数量的浅表软骨细胞所必需的,通过保持软骨细胞的增殖能力,促进其生存,并维持它们的浅表特性。 2.1.2 抑制表皮生长因子受体信号通路能促进软骨细胞外基质的降解 基质金属蛋白酶能够分解软骨细胞外基质,如蛋白聚糖和胶原蛋白等,导致骨性关节炎的发生和促进骨性关节炎的发展[8]。ZHANG等[9]对内侧半月板失稳小鼠模型的研究中发现,表皮生长因子受体活性的降低会加快软骨细胞凋亡速度、促进软骨细胞外基质降解,这与蛋白酶(聚蛋白多糖酶5和基质金属蛋白酶13)和缺氧诱导因子2α的上调是一致的。CHEN等[10]在研究双向调节蛋白在骨性关节炎发病机制的作用中发现,双向调节蛋白通过激活表皮生长因子受体信号通路诱导基质金属蛋白酶13表达上调,从而促进细胞外基质降解;同时通过表皮生长因子受体小干扰RNA和药物抑制剂阻断表皮生长因子受体的表达发现,表皮生长因子受体受体参与双向调节蛋白介导的基质金属蛋白酶13的上调:双向调节蛋白通过表皮生长因子受体的作用,激活基质金属蛋白酶13启动子上的磷脂酰肌醇-3激酶、Akt,最终激活核因子κB,从而破坏关节软骨;HUANG等[11]的研究也得出了类似的结论。 这些研究结果均提示,表皮生长因子受体在维持正常的关节软骨功能中发挥着重要功能,同时在骨性关节炎发生、发展的过程中也发挥着保护关节软骨的重要作用,并提示该受体是骨性关节炎治疗的潜在靶点。由此认为,针对表皮生长因子受体的靶向治疗药物是骨性关节炎治疗研究的新方向,其确切的疗效和作用机制需要更深入的研究。 2.2 Ihh信号通路在骨性关节炎中的作用 哺乳动物中存在3个Hedgehog的同源基因:SonicHedgehog(SHH)、Indian Hedgehog(IHH)和Desert Hedgehog(DHH),分别编码Shh、Ihh和Dhh蛋白,其中Ihh是软骨细胞中主要的HH配体,在胚胎发育过程中由前肥大软骨细胞表达[12-13],在软骨内骨化中发挥着重要作用[14];Ihh通过与Patched-1(PTCH1)受体结合,后者解除其对Smoothened(SMO)的抑制作用,再作用于胶质瘤相关癌基因蛋白(glioma-associated oncogene1,Gli)家族,上调下游靶基因(包括Gli1,人蛋白质修补同系物(Human Protein patched homolog, PTCH)和Hedgehog相互作用蛋白(Hedgehog-interacting protein, HHIP)[13,15],进而产生Runt相关转录因子2,介导聚蛋白多糖酶5、基质金属蛋白酶13等的表达,最终导致软骨细胞肥大[13,16],见图3。 "

2.2.1 Ihh在骨性关节炎发展过程中表达增加 WEI等[17]的研究表明,Ihh在健康关节软骨中呈现低表达状态,但在骨性关节炎发展过程中Ihh表达明显增加。LIN等[13]对小鼠和人类软骨外植体的研究中发现,Ihh信号在骨性关节炎中均被激活,并且在遗传修饰小鼠中发现了Ihh活化水平与骨关节炎严重程度呈现正相关。ZHANG等[12]在研究关节滑液的Ihh浓度与膝关节软骨损伤严重程度是否存在相关性时发现,Ihh的表达随着肥大软骨细胞标记物X型胶原蛋白的增加迅速上调。上述研究均说明,Ihh通过上调已知导致软骨变性的基因表达和诱导软骨细胞肥大促进骨性关节炎的发生和发展。 2.2.2 Ihh的抑制缓解骨性关节炎的进展 ZHOU等[18]对Ihh基因缺失小鼠的研究发现,Ihh的缺失可以下调X型胶原蛋白和基质金属蛋白酶13的表达。XU等[19]和KIM等[16]的研究中,也得出了类似的结果,Ihh水平的上升伴随着软骨细胞大小的增加、软骨厚度的减少、以及基质金属蛋白酶13、X型胶原和聚蛋白多糖酶5等的上调,而Ihh敲除小鼠的软骨细胞增殖和肥大现象则显著减少。这表明阻断Ihh信号是保护关节软骨、缓解骨性关节炎进展的一种手段。 据此,对Ihh在治疗上的研究提供了更多的思路。通过药理学或遗传性抑制Ihh信号传导能够降低骨性关节炎的严重程度[13],达到预防或早期干预骨性关节炎的目的。但是ZHOU等[18]认为在较大的动物中不可能敲除Ihh,在人类骨性关节炎治疗中Ihh基因的敲除也不是一个选项,而Ihh信号的化学抑制剂会导致严重的不良反应,故提出通过局部传递小干扰RNA来实现Ihh的高效敲除可能是一种更有效的策略;在ZHANG等[20]和PIGNATELLO等[21]的研究中,几项Ⅰ-Ⅲ期临床试验也表明基于RNA干扰的治疗作为沉默特定基因,用于治疗人类疾病是一种潜在的有效手段;但LIN等[13]则认为,Ihh阻断剂的毒性和不良反应主要与发育和生长有关,由于骨关节炎主要发生在成熟个体中,因此药物的作用不会成为一个问题。 2.3 核因子κB信号通路在骨性关节炎中的作用 核因子κB是一种蛋白复合物,几乎存在于所有动物细胞类型中,可控制DNA的转录、细胞因子的产生和细胞稳态。核因子κB信号通路的调节介导多种细胞功能的基因转录,包括细胞增殖、分化、凋亡和炎症反应等[22],见图4。在骨关节炎中,受应激相关因子、趋化因子、细胞外基质降解产物和促炎性细胞因子等的刺激后触发一系列基因的表达。在骨性关节炎发生、发展环节中,核因子κB通路分别在关节软骨、滑膜和软骨下骨三个部位发挥作用[23],其中对关节软骨的破坏是关键环节。 "
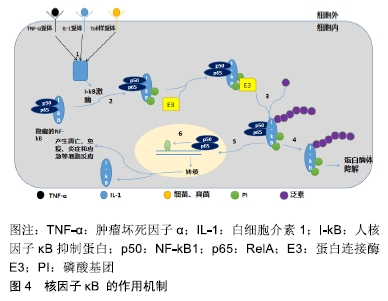

2.3.1 核因子κB在关节软骨中起促进分解的作用 在骨性关节炎中,核因子κB转录因子诱导多种降解酶的分泌,包括基质金属蛋白酶中的基质金属蛋白酶1,2,3,7,8,9,13等[24],进而减少胶原蛋白和蛋白多糖的合成,并且在正反馈环中增强核因子κB的活化[25],最终核因子κB通过诱导一氧化氮、环氧合酶2、一氧化氮合酶和前列腺素E2的产生,进而促进关节损伤、软骨炎症、细胞凋亡和软骨细胞分解代谢[26]。随着骨性关节炎的进展,核因子κB信号传导继续增强,而活化的核因子κB介导细胞因子(核因子κ B受体活化因子配体、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α等)、趋化因子(白细胞介素8、趋化因子C-C 基元配体5等)、前列腺素E2、 基质金属蛋白酶1-13、聚蛋白多糖酶4、聚蛋白多糖酶5和血管生成因子等的合成,引起进一步的软骨退化、新血管生成和滑膜炎症(滑膜炎)[27]。 2.3.2 抑制核因子κB能延缓骨性关节炎的进展并对关节软骨起保护作用 ZHANG等[28]在评估降钙素在治疗骨性关节炎中的作用及其分子机制的研究中发现,降钙素显著降低了核因子κB途径的关键蛋白(如人核因子κB抑制蛋白α)的表达。ZHAO等[29]在研究柚皮苷对骨性关节炎软骨保护的作用机制则发现,小鼠前交叉韧带切断模型的核因子κB2水平明显上调,而这种现象在柚皮苷治疗组中明显减弱,这说明了抑制核因子κB信号通路对软骨和软骨细胞具有保护作用。BUHRMAN等[30]和ZHUANG等[31]的研究还发现,抑制核因子κB途径可以抑制细胞的炎症反应。 目前研究表明,无论是中药柚皮苷、丹参,还是化学药物降钙素、生长激素释放肽、巴西苏木素和锦葵色素等[28-29,32-35],它们对骨性关节炎的治疗作用均可通过抑制核因子κB信号通路实现,通过抑制核因子κB信号通路调节软骨细胞的炎症反应和分解代谢等。同时为临床治疗提供的新的思路和研究方向:靶向干扰/抑核因子κB信号通路传导能保护软骨细胞、延缓骨性关节炎的进展,并且在骨性关节炎的治疗中发挥正向的作用。 2.4 Notch信号通路在骨性关节炎中的作用 Notch信号传导是一种进化上的保守途径,影响细胞正常形态发生的多个过程,包括多能祖细胞的分化、细胞增殖、细胞边界的形成和细胞凋亡等过程。NOTCH途径被认为是软骨细胞外基质中分解代谢和合成代谢分子的潜在调节因子[36-38]。哺乳动物有4种Notch受体(Notch1-4)和5种Notch配体(Delta-like 1,3,4,Jagged1和Jagged2)。Notch蛋白由相邻细胞的Notch配体与受体相互作用产生,再经过3次剪切,由胞内段(Notch intracellular domain,NICD)释放入胞质,并进入细胞核与细胞核内蛋白效应器(CBFl/Suppresor of Hairless/Lag,CSL)结合,形成NICD/CSL转录激活复合体,从而激活HES、HEY、HERP等碱性螺旋-环-螺旋蛋白转录抑制因子家族的靶基因,发挥生物学作用[39]。 2.4.1 生理性的Notch信号传导是维持关节软骨功能所必需的 曹俊杰等[40]的研究表明Notch信号参与骨形态发生蛋白4诱导的间充质干细胞成骨分化;LIU等[41]的研究表明,关节软骨细胞中的功能重组信号序列结合蛋白依赖性Notch信号传导是维持关节和关节软骨所必需的;LIU等[42]通过体外和体内实验证明了Notch信号传导能够调节合成代谢所需基因的表达,并得出Notch的瞬时活化会增强软骨基质的合成并维持生理条件下的关节功能的结论。 2.4.2 Notch信号传导的持续激活导致软骨退化和骨关节炎 Notch在机体中发挥着双向的调节功能,既发挥着重要的生理性作用,是维持软骨和关节关键调节因子[41],又发挥着病理性作用,其持续激活会加速软骨退化和骨性关节炎的进展[43]。LIU等[42]对Notch信号在骨性关节炎中作用机制的研究证明持续的Notch信号传导抑制软骨的形成并促进软骨纤维化和降解。LUO等[44]在研究Notch信号通路在颞下颌关节骨性关节炎中的作用时发现,Notch信号通路的早期阻断可以延迟骨性关节炎进展期的软骨破坏。HOSAKA等[39]的研究也发现类似的结果,说明关节软骨中持续的Notch信号传导导致早期和进行性骨关节炎样病变,并且在骨骼发育后通过核转录抑制因子抑制Notch信号传导的实验中,发现骨性关节炎小鼠模型中的骨性关节炎发展被抑制。而SASSI等[45]的研究发现在骨性关节炎软骨细胞中阻断Notch信号传导不仅导致骨性关节炎标记物(Coll、基质蛋白酶13、内皮型一氧化氮合酶)的消退,而且还导致健康软骨标记物(Colli和聚集蛋白聚糖)的恢复。 综上所述,靶向Notch信号通路调节是一种治疗骨性关节炎的新手段,但目前没有足够的研究阐释Notch信号通路调节剂治疗骨性关节炎的作用机制,需要进一步研究其瞬时激活和持续表达的调节方式,加之以更多的实验室及临床证据证明其可行性。 2.5 其他相关信号通路 2.5.1 p38MAPK信号通路在骨性关节炎中的作用 MAPK是一组丝氨酸-苏氨酸蛋白激酶,被细胞外刺激因素(如细胞应激、细胞因子、神经递质、激素及细胞黏附等)激活[46],通过3层蛋白激酶级联系统,进入细胞核刺激细胞核并激活相应的基因,从而调节细胞增殖、分化和凋亡[47]。 LI等[48]研究表明p38MAPK信号通路的激活与骨性关节炎中软骨的胶原蛋白降解、软骨细胞凋亡及炎症过程相关。SUN等[49]的研究发现抑制p38MAPK信号通路可以抑制促炎性细胞因子的表达,并改善炎症反应诱导的细胞损伤、并减少软骨细胞凋亡。 2.5.2 Hippo-Yes相关蛋白(Yes-associated protein,YAP)信号通路在骨性关节炎中的作用 YAP可在细胞内起连接和转录共激活作用[50];Hippo信号通路由一系列保守激酶组成,主要通过调控细胞增殖和凋亡控制器官大小[51]。该通路的核心是由哺乳动物STE20样激酶1/2、Salvador同系物1、LATS1/2和MOB激酶激活因子1A/B组成的激酶级联。当Hippo信号被激活时,通过巨噬细胞刺激和LATS激酶的一系列磷酸化事件最终导致通路的关键效应因子YAP/TAZ磷酸化,随后与靶向转录增强的关联域或其他转录因子相互作用,调控下游信号级联,从而控制细胞增殖、凋亡、分化和成熟[52]。 GONG等[53]的研究在人骨性关节炎软骨和手术诱导的骨性关节炎动物模型中均发现YAP水平的上调,并通过一系列研究表明,抑制YAP表达能逆转白细胞介素1β诱导的软骨细胞凋亡和软骨细胞外基质的降解;Deng等[54]的研究发现YAP的表达与骨性关节炎的发病机制高度相关,软骨细胞中YAP的激活能抑制骨性关节炎的进展、保护关节软骨,同时还能够通过抑制IKKα/β的活化抑制核因子κB途径进而起到保护关节软骨的作用。 "

| [1] 中华医学会骨科学分会关节外科学组.骨关节炎诊疗指南[J].中华骨科杂志,2018,38(12):705-715. [2] ZHANG JF, SONG LH, WEI JN, et al. Prevalence of and risk factors for the occurrence of symptomatic osteoarthritis in rural regions of Shanxi Province, China. Int J Rheum Dis. 2016;19(8):781-789. [3] HUNTER DJ, BIERMA-ZEINSTRA S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2019;393(10182):1745-1759. [4] JOINER DM, LESS KD, VAN WIEREN EM, et al. Accelerated and increased joint damage in young mice with global inactivation of mitogen-inducible gene 6 after ligament and meniscus injury. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(2):R81. [5] ZHU J, SICLARI VA, LIU F, et al. Amphiregulin-EGFR signaling mediates the migration of bone marrow mesenchymal progenitors toward PTH-stimulated osteoblasts and osteocytes. PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e50099. [6] QIN L, BEIER F. EGFR Signaling: Friend or Foe for Cartilage? JBMR Plus. 2019;3(2):e10177. [7] JIA H, MA X, TONG W, et al. EGFR signaling is critical for maintaining the superficial layer of articular cartilage and preventing osteoarthritis initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(50):14360-14365. [8] LI H, FENG F, BINGHAM CO 3RD, et al. Matrix metalloproteinases and inhibitors in cartilage tissue engineering. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2012;6(2):144-154. [9] ZHANG X, ZHU J, LIU F, et al. Reduced EGFR signaling enhances cartilage destruction in a mouse osteoarthritis model. Bone Res. 2014;2:14015. [10] CHEN YT, HOU CH, HOU SM, et al. The effects of amphiregulin induced MMP-13 production in human osteoarthritis synovial fibroblast. Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014:759028. [11] HUANG CY, LIN HJ, CHEN HS, et al. Thrombin promotes matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression through the PKCδ c-Src/EGFR/PI3K/Akt/AP-1 signaling pathway in human chondrocytes. Mediators Inflamm. 2013;2013:326041. [12] ZHANG C, WEI X, CHEN C, et al. Indian hedgehog in synovial fluid is a novel marker for early cartilage lesions in human knee joint. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(5):7250-7265. [13] LIN AC, SEETO BL, BARTOSZKO JM, et al. Modulating hedgehog signaling can attenuate the severity of osteoarthritis. Nat Med. 2009;15(12):1421-1425. [14] WORTHLEY DL, CHURCHILL M, COMPTON JT, et al. Gremlin 1 identifies a skeletal stem cell with bone, cartilage, and reticular stromal potential. Cell. 2015;160(1-2):269-284. [15] HUANG J, ZHAO L, CHEN D. Growth factor signalling in osteoarthritis. Growth Factors. 2018;36(5-6):187-195. [16] KIM EJ, CHO SW, SHIN JO, et al. Ihh and Runx2/Runx3 signaling interact to coordinate early chondrogenesis: a mouse model. PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e55296. [17] WEI F, ZHOU J, WEI X, et al. Activation of Indian hedgehog promotes chondrocyte hypertrophy and upregulation of MMP-13 in human osteoarthritic cartilage. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2012;20(7):755-763. [18] ZHOU J, CHEN Q, LANSKE B, et al. Disrupting the Indian hedgehog signaling pathway in vivo attenuates surgically induced osteoarthritis progression in Col2a1-CreERT2; Ihhfl/fl mice. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(1):R11. [19] XU T, XU G, GU Z, et al. Hedgehog signal expression in articular cartilage of rat temporomandibular joint and association with adjuvant-induced osteoarthritis. J Oral Pathol Med. 2017;46(4):284-291. [20] ZHANG G, GUO B, WU H, et al. A delivery system targeting bone formation surfaces to facilitate RNAi-based anabolic therapy. Nat Med. 2012;18(2):307-314. [21] PIGNATELLO R, SARPIETRO MG, CASTELLI F. Synthesis and biological evaluation of a new polymeric conjugate and nanocarrier with osteotropic properties. J Funct Biomater. 2012;3(1):79-99. [22] ZHENG C, YIN Q, WU H. Structural studies of NF-κB signaling. Cell Res. 2011;21(1):183-195. [23] RIGOGLOU S, PAPAVASSILIOU AG. The NF-κB signalling pathway in osteoarthritis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013;45(11): 2580-2584. [24] GOLDRING MB, MARCU KB. Cartilage homeostasis in health and rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11(3): 224. [25] KAPOOR M, MARTEL-PELLETIER J, LAJEUNESSE D, et al. Role of proinflammatory cytokines in the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7(1):33-42. [26] MARCU KB, OTERO M, OLIVOTTO E, et al. NF-kappaB signaling: multiple angles to target OA. Curr Drug Targets. 2010;11(5):599-613. [27] KRASNOKUTSKY S, ATTUR M, PALMER G, et al. Current concepts in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2008;16 Suppl 3:S1-3. [28] ZHANG LB, MAN ZT, LI W, et al. Calcitonin protects chondrocytes from lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis and inflammatory response through MAPK/Wnt/NF-κB pathways. Mol Immunol. 2017;87:249-257. [29] ZHAO Y, LI Z, WANG W, et al. Naringin Protects Against Cartilage Destruction in Osteoarthritis Through Repression of NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Inflammation. 2016;39(1):385-392. [30] BUHRMANN C, MOBASHERI A, BUSCH F, et al. Curcumin modulates nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB)-mediated inflammation in human tenocytes in vitro: role of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(32):28556-28566. [31] ZHUANG Z, YE G, HUANG B. Kaempferol Alleviates the Interleukin-1β-Induced Inflammation in Rat Osteoarthritis Chondrocytes via Suppression of NF-κB. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23:3925-3931. [32] XU X, LV H, LI X, et al. Danshen attenuates osteoarthritis-related cartilage degeneration through inhibition of NF-κB signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro. Biochem Cell Biol. 2017;95(6):644-651. [33] QU R, CHEN X, WANG W, et al. Ghrelin protects against osteoarthritis through interplay with Akt and NF-κB signaling pathways. FASEB J. 2018;32(2):1044-1058. [34] WEINMANN D, MUELLER M, WALZER SM, et al. Brazilin blocks catabolic processes in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes via inhibition of NFKB1/p50. J Orthop Res. 2018;36(9):2431-2438. [35] DAI T, SHI K, CHEN G, et al. Malvidin attenuates pain and inflammation in rats with osteoarthritis by suppressing NF-κB signaling pathway. Inflamm Res. 2017;66(12):1075-1084. [36] DONG Y, JESSE AM, KOHN A, at el. RBPjk-dependent Notch signaling regulates mesenchymal progenitor cell proliferation and differentiation during skeletal development. Development. 2010;137(9):1461-1471. [37] KOHN A, DONG Y, MIRANDO AJ, et al. Cartilage-specific RBPjk-dependent and -independent Notch signals regu-late cartilage and bone development. Development. 2010;137(9):1198-1212. [38] MEAD TJ, YUTZEY KE. Notch pathway regulation of chondrocyte differentiation and proliferation during appendicular and axial skeleton development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(34):14420-14425. [39] HOSAKA Y, SAITO T, SUGITA S, et al. Notch signaling in chondrocytes modulates endochondral ossification and osteoarthritis development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(5):1875-1880. [40] 曹俊杰,李爱芳,卫亚琳,等.Notch信号参与BMP4诱导的间充质干细胞成骨分化及其机制的初步探讨[J].中国生物工程杂志, 2017,37(4):48-55. [41] LIU Z, REN Y, MIRANDO AJ, et al. Notch signaling in postnatal joint chondrocytes, but not subchondral osteoblasts, is required for articular cartilage and joint maintenance. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(4):740-751. [42] LIU Z, CHEN J, MIRANDO AJ, et al. A dual role for NOTCH signaling in joint cartilage maintenance and osteoarthritis. Sci Signal. 2015;8(386):ra71. [43] ZHENG Y, LIU C, NI L, et al. Cell type-specific effects of Notch signaling activation on intervertebral discs: Implications for intervertebral disc degeneration. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(7):5431-5440. [44] LUO X, JIANG Y, BI R, et al. Inhibition of notch signaling pathway temporally postpones the cartilage degradation progress of temporomandibular joint arthritis in mice. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2018;46(7):1132-1138. [45] SASSI N, GADGADI N, LAADHAR L, et al. Notch signaling is involved in human articular chondrocytes de-differentiation during osteoarthritis. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2014; 34(1):48-57. [46] WANG J, CHEN H, CAO P, et al. Inflammatory cytokines induce caveolin-1/β-catenin signalling in rat nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis through the p38 MAPK pathway. Cell Prolif. 2016;49(3):362-372. [47] SUGIURA R, SATOH R, ISHIWATA S, et al. Role of RNA-Binding Proteins in MAPK Signal Transduction Pathway. J Signal Transduct. 2011;2011:109746. [48] LI Z, MENG D, LI G, et al. Celecoxib Combined with Diacerein Effectively Alleviates Osteoarthritis in Rats via Regulating JNK and p38MAPK Signaling Pathways. Inflammation. 2015; 38(4):1563-1572. [49] SUN HY, HU KZ, YIN ZS. Inhibition of the p38-MAPK signaling pathway suppresses the apoptosis and expression of proinflammatory cytokines in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Cytokine. 2017;90:135-143. [50] LIN KC, PARK HW, GUAN KL. Regulation of the Hippo Pathway Transcription Factor TEAD. Trends Biochem Sci. 2017;42(11):862-872. [51] HEALLEN T, MORIKAWA Y, LEACH J, et al. Hippo signaling impedes adult heart regeneration. Development. 2013; 140(23): 4683-4690. [52] YU FX, ZHAO B, GUAN KL. Hippo Pathway in Organ Size Control, Tissue Homeostasis, and Cancer. Cell. 2015;163(4): 811-828. [53] GONG Y, LI SJ, LIU R, et al. Inhibition of YAP with siRNA prevents cartilage degradation and ameliorates osteoarthritis development. J Mol Med (Berl). 2019;97(1):103-114. [54] DENG Y, LU J, LI W, et al. Reciprocal inhibition of YAP/TAZ and NF-κB regulates osteoarthritic cartilage degradation. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):4564. |
| [1] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [2] | Peng Zhihao, Feng Zongquan, Zou Yonggen, Niu Guoqing, Wu Feng. Relationship of lower limb force line and the progression of lateral compartment arthritis after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with mobile bearing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1368-1374. |
| [3] | Liu Xiangxiang, Huang Yunmei, Chen Wenlie, Lin Ruhui, Lu Xiaodong, Li Zuanfang, Xu Yaye, Huang Meiya, Li Xihai. Ultrastructural changes of the white zone cells of the meniscus in a rat model of early osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1237-1242. |
| [4] | Liu Xin, Yan Feihua, Hong Kunhao. Delaying cartilage degeneration by regulating the expression of aquaporins in rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 668-673. |
| [5] | Ma Zetao, Zeng Hui, Wang Deli, Weng Jian, Feng Song. MicroRNA-138-5p regulates chondrocyte proliferation and autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 674-678. |
| [6] | Cao Xuhan, Bai Zixing, Sun Chengyi, Yang Yanjun, Sun Weidong. Mechanism of “Ruxiang-Moyao” herbal pair in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 746-753. |
| [7] | Li Yonghua, Feng Qiang, Tan Renting, Huang Shifu, Qiu Jinlong, Yin Heng. Molecular mechanism of Eucommia ulmoides active ingredients treating synovitis of knee osteoarthritis: an analysis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 765-771. |
| [8] | Song Shan, Hu Fangyuan, Qiao Jun, Wang Jia, Zhang Shengxiao, Li Xiaofeng. An insight into biomarkers of osteoarthritis synovium based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 785-790. |
| [9] | Deng Zhenhan, Huang Yong, Xiao Lulu, Chen Yulin, Zhu Weimin, Lu Wei, Wang Daping. Role and application of bone morphogenetic proteins in articular cartilage regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 798-806. |
| [10] | Lü Jiaxing, Bai Leipeng, Yang Zhaoxin, Miao Yuesong, Jin Yu, Li Zhehong, Sun Guangpu, Xu Ying, Zhang Qingzhu. Evaluation of internal fixation with proximal femoral nail antirotation in elderly knee osteoarthritis patients with femoral intertrochanteric fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 391-396. |
| [11] | Zheng Li, Li Dadi, Hu Weifan, Tang Jinlong, Zhao Fengchao. Risk assessment of contralateral knee arthroplasty after unilateral total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 374-379. |
| [12] | Lu Yuyun, Huang Mei, Shi Xinlei, Chen Baoyan. Bibliometric and visualization analysis of breast cancer stem cell literature from 2011 to 2020 based on Web of Science database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4001-4008. |
| [13] | Liu Jinfu, Zeng Ping, Nong Jiao, Fan Siqi, Feng Chengqin, Huang Jiaxing. Integrative analysis of biomarkers and therapeutic targets in synovium of patients with osteoarthritis by multiple microarrays [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3690-3696. |
| [14] | Chen Feng, Zhang Xiaoyun, Chen Yueping, Liao Jianzhao, Li Jiajun, Song Shilei, Lai Yu. Molecular mechanism of anhydroicaritin in the treatment of osteoarthritis: an analysis based on network pharmacology and bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3704-3710. |
| [15] | Yang Wei, Chen Zehua, Yi Zhiyong, Huang Xudong, Han Qingmin, Zhang Ronghua. Effectiveness of intra-articular injection of hyaluronic acid versus placebo in the treatment of early and mid-stage knee osteoarthritis: a Meta-analysis based on randomized, double-blind, controlled, clinical trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3760-3766. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||