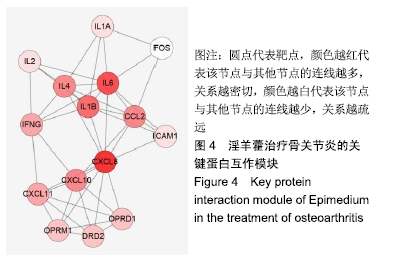
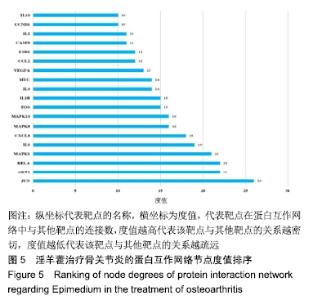
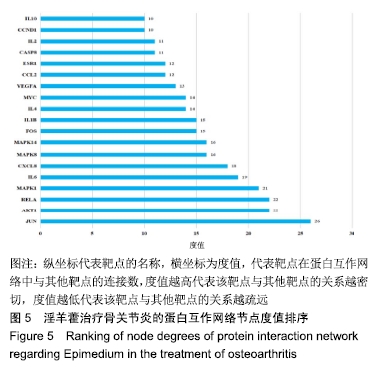
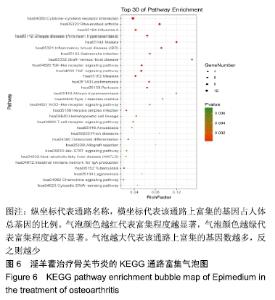
[1] SEMCIW AI, PIZZARI T, WOODLEY S, et al. Targeted gluteal exercise versus sham exercise on self-reported physical function for people with hip osteoarthritis (the GHOst trial - Gluteal exercise for Hip Osteoarthritis): a protocol for a randomised clinical trial. Trials. 2018;19(1):511.
[2] GU YT, CHEN J, MENG ZL, et al. Research progress on osteoarthritis treatment mechanisms. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;93:1246-1252.
[3] THOMAS AC, HUBBARD-TURNER T, WIKSTROM EA, et al. Epidemiology of Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis. J Athl Train. 2017;52(6):491-496.
[4] LI MH, XIAO R, LI JB, et al. Regenerative approaches for cartilage repair in the treatment of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(10):1577-1587.
[5] 黄威,尹宗生.炎症与骨关节炎软骨退变[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2019,27(5):448-452.
[6] HERMANN W, LAMBOVA S, MULLER-LADNER U. Current Treatment Options for Osteoarthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2018;14(2):108-116.
[7] 斯海波,梁明玮,程惊秋,等.软骨前体细胞及微小RNA-140在骨关节炎软骨损伤修复中的作用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2019, 33(5):650-656.
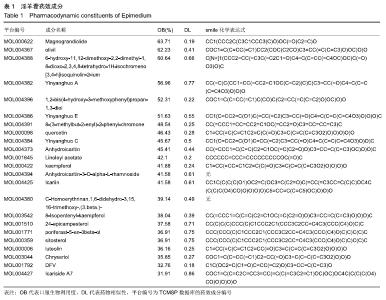
[8] 李睿,杨信信,张小辉,等.淫羊藿苷治疗骨性关节炎的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2018,24(8):1088-1092.
[9] 李安琪,刘益杰,冯伟,等.淫羊藿苷对IL-1β诱导的炎症性软骨细胞表型与代谢的影响[J].上海中医药杂志,2018,52(2):99-103.
[10] LI J, ZHAO P, LI Y, et al. Systems pharmacology-based dissection of mechanisms of Chinese medicinal formula Bufei Yishen as an effective treatment for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Sci Rep. 2015;5:15290.
[11] RU J, LI P, WANG J, et al. TCMSP: a database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines. J Cheminform. 2014;6:13.
[12] GFELLER D, GROSDIDIER A, WIRTH M, et al. SwissTargetPrediction: a web server for target prediction of bioactive small molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42(Web Server issue):W32-38.
[13] SZKLARCZYK D, MORRIS JH, COOK H, et al. The STRING database in 2017: quality-controlled protein-protein association networks, made broadly accessible. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45(D1):D362-D368.
[14] HUANG DA W, SHERMAN BT, LEMPICKI RA. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 2009;4(1):44-57.
[15] 石继祥,商培洋,周旭,等.补肾活血方调节淋巴回流对小鼠骨关节炎的影响[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2018,24(12):1699-1702.
[16] 李楠,林昌松,姜玉宝.补肾化瘀法治疗骨关节炎经验[J].中医杂志,2016,57(23):2047-2048.
[17] ZHOU X, JIANG L, FAN G, et al. Role of the ciRS-7/miR-7 axis in the regulation of proliferation, apoptosis and inflammation of chondrocytes induced by IL-1β. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;71:233-240.
[18] YANG H, WU D, LI H, et al. Downregulation of microRNA-448 inhibits IL-1β-induced cartilage degradation in human chondrocytes via upregulation of matrilin-3. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2018;23:7.
[19] 高堪达,王漱阳,王秋根.淫羊藿苷治疗小鼠骨关节炎后血清学及组织学改变的实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2017,31(8): 963-969.
[20] 周巧,刘健,忻凌,等.基于关联规则挖掘中药内外合治骨关节炎对免疫炎症指标的影响[J].中华中医药学刊,2017,35(8): 2070-2073.
[21] 宋思琦,吴丹,胡毓诗.白细胞介素-1受体拮抗蛋白对大鼠创伤性骨关节炎的治疗作用及机制研究[J].重庆医学,2019,48(6): 909-912,916.
[22] 秦丰伟,黄荷,焦锋,等.淫羊藿苷和骨髓间充质干细胞共育液对兔骨关节炎模型关节液中IL-1、TNF-α、IL-10、MMP-3表达的影响[J].实用医学杂志,2018,34(17):2876-2879.
[23] 刘益杰,陈世宣,赵仙丽,等.淫羊藿苷对白介素-1β诱导软骨细胞退变的保护作用[J].同济大学学报(医学版),2018,39(2):56-60.
[24] ZHAO Y, LI Y, QU R, et al. Cortistatin binds to TNF-α receptors and protects against osteoarthritis. EBioMedicine. 2019;41:556-570.
[25] 刘文.钙结合蛋白A12、白细胞介素-6、白细胞介素-8及血管内皮生长因子水平变化与骨关节炎患者病情程度的关系探讨[J].中国临床医生杂志,2019,47(4):454-456.
[26] 赵清,王婧,王来芳.IL-7R在膝关节骨关节炎滑膜中的表达及意义[J].中国现代医学杂志,2017,27(2):52-55.
[27] LINARDI RL, DODSON ME, MOSS KL, et al. The Effect of Autologous Protein Solution on the Inflammatory Cascade in Stimulated Equine Chondrocytes. Front Vet Sci. 2019;6:64.
[28] PISANI LP, ESTADELLA D, RIBEIRO DA. The Role of Toll Like Receptors (TLRs) in Oral Carcinogenesis. Anticancer Res. 2017;37(10):5389-5394.
[29] 刘新,黄文瑶,李卫国,等.TLR-4、IL-1与膝骨关节炎相关性的临床研究[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2013,7(4):481-485.
[30] ZUPAN J, KOMADINA R, MARC J. The relationship between osteoclastogenic and anti-osteoclastogenic pro-inflammatory cytokines differs in human osteoporotic and osteoarthritic bone tissues. J Biomed Sci. 2012;19:28.
|