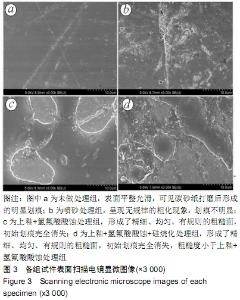
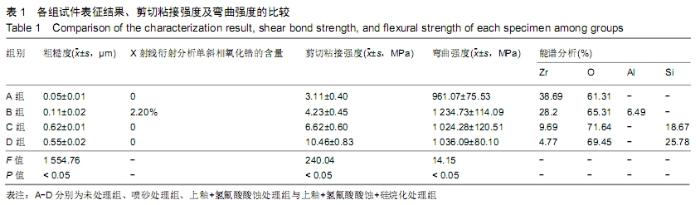
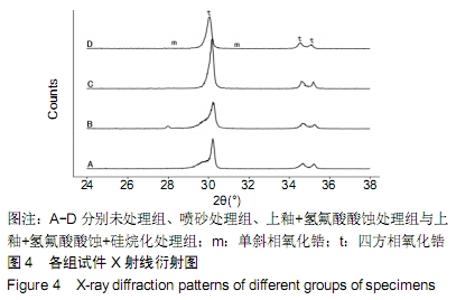
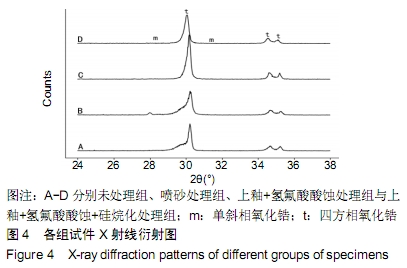
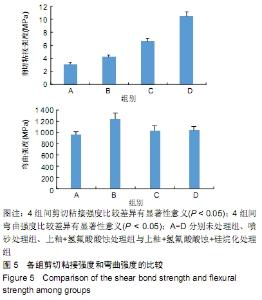
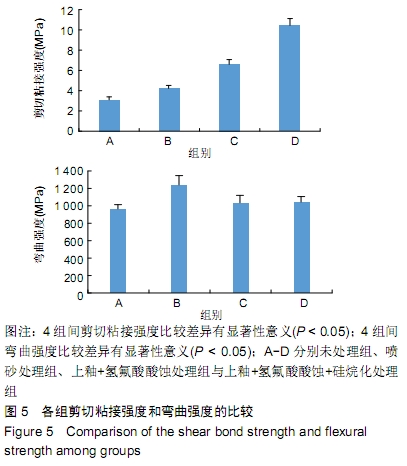
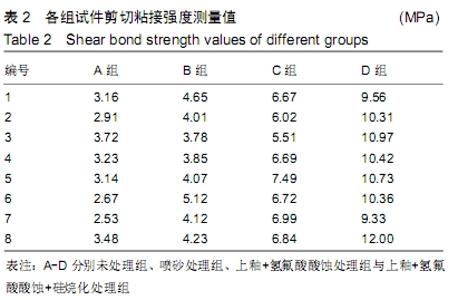
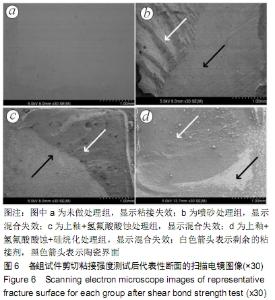
[1] 王继德,邓久鹏,沈宝莲,等.三种表面粗化方式与氧化锆陶瓷粘接性及抗折强度:谁更有优势?[J].中国组织工程研究, 2018,22(26): 102-107.
[2] ARAÚJO AMM, JANUÁRIO ABD, MOURA DMD, et al.Can the application of multi-mode adhesive be a substitute to silicatized/ silanized Y-TZP ceramics? Braz Dent J. 2018;29(3): 275-281.
[3] BIELEN V, INOKOSHI M, MUNCK JD, et al. Bonding effectiveness to differently sandblasted dental zirconia. J Adhes Dent. 2015;17(3):235-242.
[4] WANDSCHER VF, PROCHNOW C, RIPPE MP, et al. Retentive strength of Y-TZP crowns: comparison of different silica coating methods on the intaglio surfaces.Oper Dent. 2017;42(5): E121-E133.
[5] CAMPOS TMB, RAMOS NC, MACHADO JPB, et al. A new silica-infiltrated Y-TZP obtained by the sol-gel method.J Dent. 2016;48:55-61.
[6] 王瑜,龚玲,计艳,等.溶胶-凝胶法制备硅涂层提高牙科高强度陶瓷与复合树脂的粘接强度[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2012,28(1):30-33.
[7] 陈超,姜婷.表面融附玻璃陶瓷对氧化锆与树脂粘接强度的影响[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2011,46(z1):99-103.
[8] GUAZZATO M, ALBAKRY M, QUACH L, et al. Influence of surface and heat treatments on the flexural strength of a glass-infiltrated alumina/zirconia-reinforced dental ceramic.Dent Mater. 2005; 21:454-463.
[9] LIU L, LIU S, SONG X, et al. Effect of Nd: YAG laser irradiation on surface properties and bond strength of zirconia ceramics Lasers. Med Sci.2015;30(2):627-634.
[10] RONA N, YENISEY M, KUCUKTURK G, et al. Effect of electrical discharge machining on dental Y-TZP ceramic-resin bonding. J Prosthodont Res. 2016;61(2):158-167.
[11] KIRMALI O, AKIN H, KAPDAN A. Evaluation of the surface roughness of zirconia ceramics after different surface treatments. Acta Odontol Scand. 2014;72(6):432-439.
[12] RIPPE M, AMARAL R, OLIVEIRA F, et al. Evaluation of tensile retention of Y-TZP crowns cemented on resin composite cores: effect of the cement and Y-TZP surface conditioning. Oper Dent. 2015;40(1):E1-E10.
[13] SAKER S, IBRAHIM F, OZCAN M, et al. Effect of different surface treatments on adhesion of in-ceram zirconia to enamel and dentin substrates. J Adhes Dent. 2013;15(4):369-376.
[14] ANTUNES MCF, MIRANDA JS, CARVALHO RLA, et al. Can low-fusing glass application affect the marginal misfit and bond strength of Y-TZP crowns? Braz Oral Res. 2018; 32:E34-E43.
[15] BRITISH STANDARDS INSTITUTION. Dentistry-Ceramic materials: ISO6872. London: BSI standards Publication,2015:1-40.
[16] 李新,苏乃川,廖运茂,等.不同条件的表面喷砂对牙科氧化锆材料表面丧失的影响[J].口腔医学,2017,37(1):28-32.
[17] CHEUNG G, BOTELHO M, MATINLINNA J. Effect of surface treatments of zirconia ceramics on the bond strength to resin cement.J Adhes Dent.2014;16(1):49-56.
[18] GARVIE RC, NICHOLSON PS. Phase analysis in zirconia systems. Journal of the American Ceramic Society.1972; 55(6):303-305.
[19] ANAND S, EBENEZAR R, ANAND N, et al. Microshear bond strength evaluation of surface pretreated zirconia ceramics bonded to dentin.Eur J Dent.2015;9(2):224-227.
[20] PASSOS SP, LINKE B, MAJOR PW, et al. The effect of air-abrasion and heat treatment on the fracture behavior of Y-TZP. Dent Mater. 2015;31(9):1011-1021.
[21] MARIA MAR, BISINOTO GV, MASSAO SM, et al. Improving adhesion between luting cement and zirconia-based ceramic with an alternative surface treatment. Braz Oral Res. 2015;29(1):1-7.
[22] OKADA M, INOUE K, IRIE M, et al. Resin adhesion strengths to zirconia ceramics after primer treatment with silane coupling monomer or oligomer. Dent Mater J. 2017;36(5):600-605.
[23] CAMPOS F, VALANDRO LF, FEITOSA SA, et al. Adhesive cementation promotes higher fatigue resistance to zirconia crowns. Oper Dent. 2016;42(2):215-224.
[24] NTALA P, CHEN X, NIGGLI J, et al. Development and testing of multi-phase glazes for adhesive bonding to zirconia substrates. J Dent. 2010;38(10):773-781.
[25] CENK C, MUTLU O, GUL L, et al. Comparison of alternative adhesive cementation concepts for zirconia ceramic: glaze layer vs zirconia primer. J Adhes Dent. 2012;14:75-82.
[26] PEAMPRING C, AKSORNMUANG J, SANOHKAN S. In vitro fracture resistance of composite-resin-veneered zirconia crowns. J Conserv Dent. 2017;20(4):225-229.
[27] JAIN T, PORWAL A, BABU S, et al. Effect of different surface treatments on biaxial flexural strength of yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2018;19(3):318-323.
[28] RAMOS-TONELLO CM, TREVIZO BF, RODRIGUES RF, et al. Pre-sintered Y-TZP sandblasting: effect on surface roughness, phase transformation, and Y-TZP/veneer bond strength. J Appl Oral Sci. 2017;25(6):666-673.
[29] PRASAD HA, PASHA N, HILAL M, et al. To evaluate effect of airborne particle abrasion using different abrasives particles and compare two commercial available zirconia on flexural strength on heat treatment. Int J Biomed Sci. 2017;13(2):93-112.
[30] BAGHERI H, HOOSHMAND T, AGHAJANI F. Effect of ceramic surface treatments after machine grinding on the biaxial flexural strength of different CAD/CAM dental ceramics. J Dent. 2015; 12(9):621-629.
[31] KOSMAC T, OBLAK C, JEVNIKAR P, et al. Strength and reliability of surface treated Y-TZP dental ceramics. J Biomed Mater Res. 2000;53(4):304-313.
[32] AURÉLIO IL, DORNELES LS, MAY LG. Extended glaze firing on ceramics for hard machining: Crack healing, residual stresses, optical and microstructural aspects. Dent Mater. 2017;33(2):226-240.
[33] AMARAL M, CESAR PF, BOTTINO MA,et al. Fatigue behavior of Y-TZP ceramic after surface treatments. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2016;57:149-156.
[34] KUMCHAI H, JUNTAVEE P, SUN AF, et al. Effect of glazing on flexural strength of full-contour zirconia.Int J Dent. 2018;2018: 8793481.
|