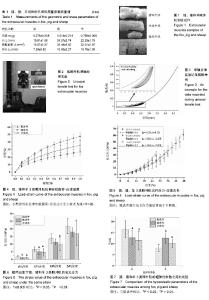
| [1] 陈维毅,李晓娜,高志鹏.眼力学研究进展[J]. 医用生物力学, 2016, 31(4): 340-346.[2] 麦光焕.眼外肌功能亢进与不足程度的分级方法[J].中华眼科杂志,2005, 41(7):663-666.[3] 李丽,戴兵,贾延磊,等.下斜肌转位术治疗垂直性斜视手术前后立体视功能分析[J]. 中医临床研究, 2013(5):109-110.[4] 封利霞. 眼外肌Pulley的研究进展[J]. 国际眼科纵览, 2002, 26(6):321-325.[5] 郑荣昌,赵堪兴,孙春华,等. 妊娠晚期胎儿眼外肌Pulley系统发育特征[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2007,11(45):9146-9148.[6] 孙春华.不同种属哺乳动物眼外肌周围结缔组织结构及功能的初步研究[D]. 天津医科大学, 2007.[7] 钱学翰,赵堪兴,李云生,等. Pulley与经典眼外肌相关结缔组织解剖结构关系的研究[J]. 解剖学研究, 2004, 26(3):195-198.[8] Quaia C,Ying HS, Nichols AM, et al The Viscoelastic Properties ofPassive Eye Muscle in Primates.Ⅰ: Static Forces and Step Responses. PloS One.2009; 4: e4850.[9] Yoo L,Reed J,Shin A,et al.Characterization of Ocular Tissues UsingMicroindentation and Hertzian Viscoelastic Models. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52(6):3475-3482.[10] Shin A, Yoo L, Chaudburi Z, et al.Independent Passive MechanicalBehavior of Bovine Extraocular Muscle Compartments.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.2012; 53: 8414-8423.[11] Shin KS. Biomechanics of Compartmentalized Mechanical Properties of Extraocular Muscle and Tendon. Dissertations & Theses - Gradworks, 2014.[12] Al-Hinnawi MF, Barbenel J, Al-Qurainy I A, et al. Quantitative mechanical assessment of the extraocular muscles. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 1991;205(2):101-108.[13] Vijayaraghavan A, Demer J L. A Ring-sling Computational Model of Active Rectus Muscle Pulleys Supports Active Pulley Hypothesis (APH). Arvo Meeting Abstracts.2005;46(5).[14] Asmussen G, Gaunitz U. Mechanical properties of the isolated inferior oblique muscle of the rabbit. Pflügers Archiv.1981; 392(2):183-190.[15] Frueh BR, Hayes A, Lynch GS,et al. Contractile properties andtemperature sensitivity of the extraocular muscles, the levator and superior rectus, ofthe rabbit. J Physiol.1994; 452(2): 327-336.[16] Croes SA, von Bartheld CS.Measurement of contractile force of skeletal andextraocular muscles: Effects of blood supply, muscle size and in situ or in vitropreparation. JNeurosci Meth.2007; 166: 53-65. [17] Kelleher JE, Siegmund T, Chan RW, et al.Optical measurements of vocal fold tensile properties: Implications for phonatory mechanics.J Biomech.2011; 44(9):1729-1734.[18] Calvo B,Ramírez A,Alonso A,et al.Passive nonlinear elastic behaviour of skeletal muscle: experimental results and model formulation.J Biomech.2010; 43(2):318-325.[19] Rashid B, Destrade M, Gilchrist MD. Mechanical characterization of brain tissue in simple shear at dynamic strain rates. J MechBehav Biomed Mater.2013; 28: 71-85.[20] Moerman KM, Simms CK, Nagel T.Control of tension–compression asymmetry in Ogden hyperelasticity with application to soft tissue modelling. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater.2016; 56 218-228.[21] 高志鹏. 眼外肌力学行为及相关的眼球运动建模研究[D]. 太原理工大学, 2014.[22] 郭红梅,高志鹏,陈维毅. 离体狐眼外肌被动行为的超弹性分析[J]. 医用生物力学, 2017, 32(1):27-31.[23] 张晓翔,赵玉婷,高志鹏,等. 猪眼外直肌生物力学性能的实验研究[J].太原理工大学学报, 2017, 48(2):250-253.[24] Calvo B, Ramírez A, Alonso A, et al. Passive nonlinear elastic behaviour of skeletal muscle: experimental results and model formulation.J Biomech.2010; 43(2):318-325.[25] Collins CC, Carlson MR, Scott AB,et al. Extraocular muscle forces in normal human subjects Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1981; 20: 652-664.[26] Schutte S, van den Bedem SP, van Keulen F, et al.A finite-element analysis model of orbital biomechanics. Vision Res.2006;46(11):1724-1731.[27] Kennedy E,Duma S.The effects of the extraocular muscles on eye impact force-deflection and globe rupture response.J Biomech.2008; 41: 3297-3302.[28] 高志鹏,陈维毅. 滑车组织在眼球内旋运动时维持眼外肌力学优势的模拟研究[J]. 医用生物力学,2014,29(6):498-503.[29] Hassan MA,Hamdi M,Noma A. The nonlinear elastic and viscoelastic passive properties of left ventricular papillary muscle of a Guinea pig heart. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 2012;5:99-109.[30] Paersch C, Trimmer BA, Dorfmann A. A constitutive model for active-passive transition of muscle fibers.Int J Nonlin Mech. 2012; 47: 377-387.[31] Dorfmann A, Trimmer BA, Woods WA. A constitutive model for muscle properties in a soft-bodied arthropod.J Roy Soc. 2007; 4:257-269.[32] 熊祝华,杨德品. 连续体力学概论[M].长沙: 湖南大学出版社, 1986.[33] 李永胜,陈维毅. 骨骼肌收缩的本构模型: I被动行为[J]. 力学进展2010; 40: 63-678.[34] Mcloon LK,Christiansen SP. Extraocular Muscles: Extraocular Muscle Anatomy. Encyclopedia of the Eye.2010:89-98. |