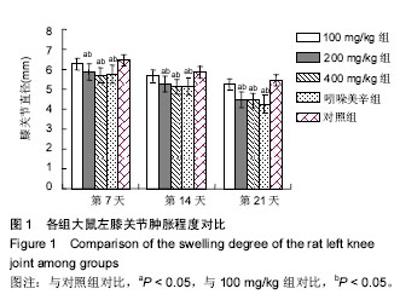
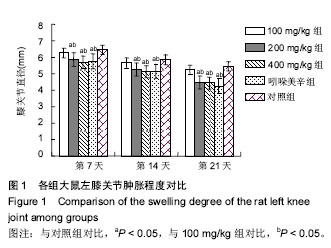
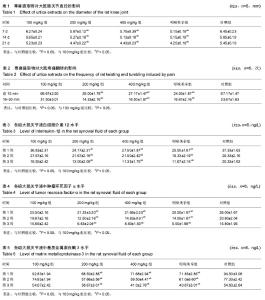
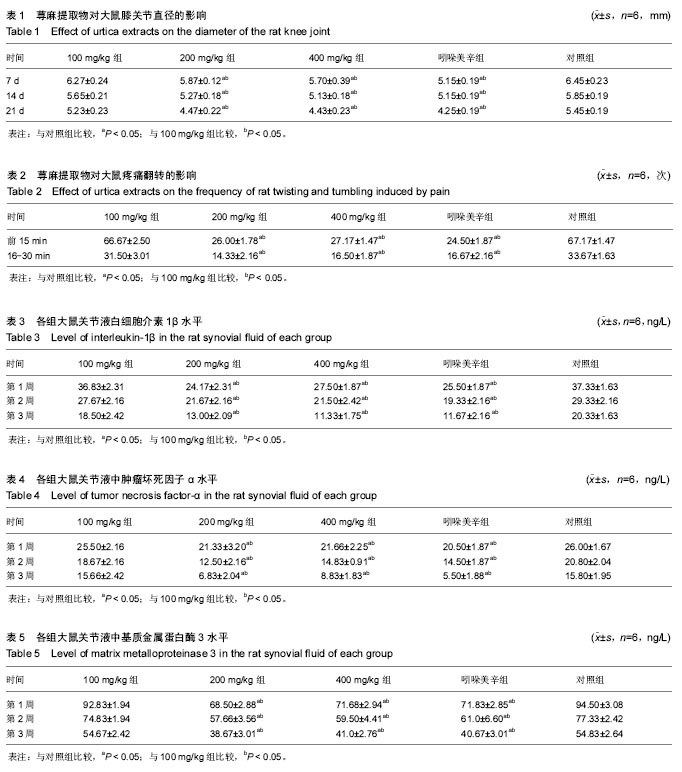
| [1] 王梦月,刘瑛,卫莹芳,等. 川产荨麻药理作用的初步研究[J]. 中国民族民间医药杂志, 2001,51:229-231[2] 王梦月,卫莹芳,史炎,等. 三种活麻水煎液药理作用探索[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2001, 12(8):673-674[3] 王梦月,卫莹芳,李晓波. 荨麻抗风湿活性部位的化学成分研究[J]. 中草药,2006,37(9):1300-1303[4] 王梦月,卫莹芳,史焱. 荨麻多糖药理作用初步研究[J]. 中药材, 2001,24(9):666-667[5] 敖特根白音,李运起,韩艳华,等. 国内外麻叶荨麻的研究进展[J]. 中国野生植物资源, 2015,34(1):32-36[6] 张嫚丽.麻叶荨麻化学成分及抗炎药理活性初步研究[D].河北医科大学, 2004.[7] 李喆: 麻叶荨麻叶化学成分、多糖含量测定及抗炎活性的研究[J]. 河北医科大学, 2008.[8] Randall C, Meethan K, Randall H, et al. Nettle sting of Urtica dioica for joint pain — an exploratory study of this complementary therapy. Complement Ther Med. 1999;7(3): 126-131.[9] 李妍.荨麻多糖提取分离、结构分析及功能的研究[D].中国人民解放军军事医学科学院, 2005.[10] 李婉. 浅谈非甾体抗炎药的不良反应及其预防[J]. 中国保健营养,2017,27(10):56-57[11] 李冬,张光武,刘家帮,等. 非甾体抗炎药辅助关节镜治疗膝骨关节炎的临床疗效分析[J]. 临床药物治疗杂志, 2015, 13(4): 54-57[12] LUU THI THANH THUY , 王梦月. 荨麻属药用植物的研究进展[J].中国民族民间医药, 2015,12:16-24.[13] 王燕雲,刁治民,曹霞,等. 药用植物荨麻经济价值及应用潜力[J]. 青海草业,2015,24(2):25-34[14] 李晓红,赵永娜,李顺英,等. 滇产粗根荨麻不同提取部位的镇痛抗炎作用研究[J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 2008,20(2):343-345.[15] 刘敏, 陈阳斌. 依托考昔治疗骨关节炎研究进展[J]. 现代仪器与医疗, 2016, 22(4):1-3[16] 肖壮,唐涛,孙先润,等. 骨关节炎治疗药物的研究进展[J].中国药房,2016,27(35):5037-5040[17] 石劲敏,李瑞. 手性非甾体抗炎新药依托度酸[J]. 中国临床药学杂志,2000,9(5):321-324.[18] van Ryn J, Pairet M.Selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors: pharmacology, clinical effects and therapeutic potential. Expert Opin Investig Drugs.1997;6(5):609-614.[19] 薛静,伍骥,郑超. 基于循证医学指导下的骨关节炎治疗建议[J]. 中华关节外科杂志,电子版:2013,7(3):2083-2086.[20] 任硕. 膝骨关节炎治疗方案的优化选择[J]. 山东中医药大学, 2010.[21] Hochberg MC, Altman RD, April KT,et al.American college of Rheumatology 2012 recomnlendations for the use of nonpharmacologic and phamacologictherapies in osteoarthritis of the hand,hip,and knee. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012;64(4):465-474.[22] Wu MX, Li XH, Lin MN, et al.clinical study on the treatment of Knee osteoarthritis of Shen-Sui insufficiency syndrometype by electmacupuncture. Chin J Integr Med.2010;16(24): 291-297.[23] 崔殿波,李薇,王莹,等. 狭叶荨麻提取物抗炎镇痛药理作用研究[J]. 中医药学报, 2014,42(4):61-63.[24] 王亚丽,秦民坚,戴岳,等.狭叶荨麻根、茎、叶的抗炎镇痛作用[J].现代中药研究与实践, 2005,19(3):42-43,46. |