Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (20): 3164-3169.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.20.009
Previous Articles Next Articles
Different dosages of retinoic acid to establish a rat model of osteoporosis: a stability evaluation
Sun Shi-dong1, Liang Qi-bin2, Fan Wei-zhi3, Zeng Zhan-peng1, Chen Bo-xing3
- 1Department of Traumatic Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Guangzhou Orthopedic Hospital, Guangzhou 510045, Guangdong Province, China; 3Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China
-
Revised:2017-05-27Online:2017-07-18Published:2017-07-28 -
Contact:Zeng Zhan-peng, Master, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Traumatic Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Sun Shi-dong, Master, Physician, Department of Traumatic Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the Science and Technology Program of Guangdong Province, No. 2014A020212593
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Sun Shi-dong, Liang Qi-bin, Fan Wei-zhi, Zeng Zhan-peng, Chen Bo-xing. Different dosages of retinoic acid to establish a rat model of osteoporosis: a stability evaluation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(20): 3164-3169.
share this article
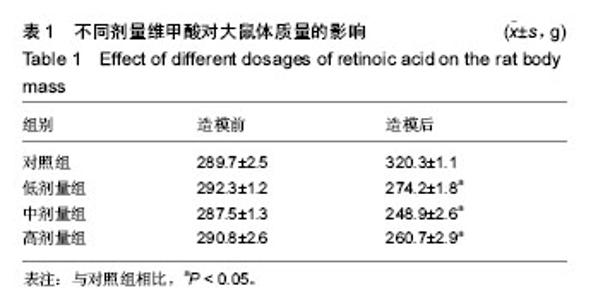
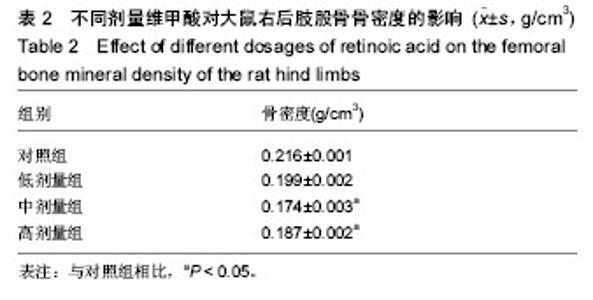
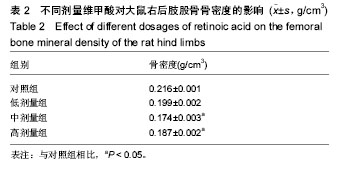
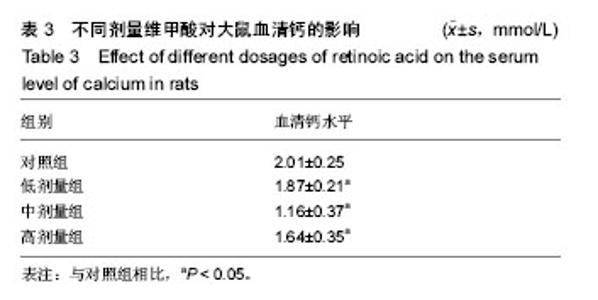
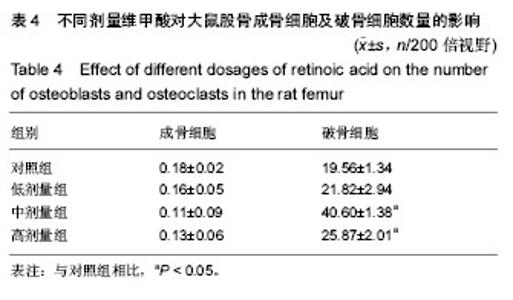
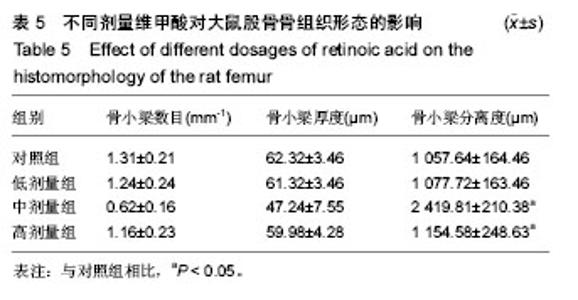
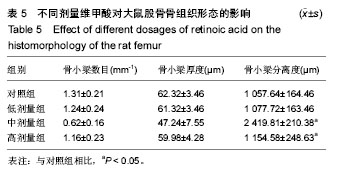
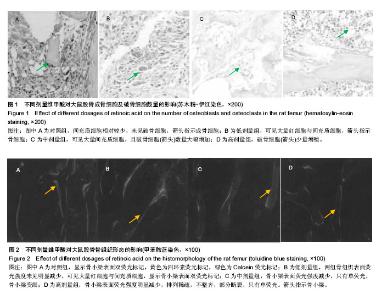
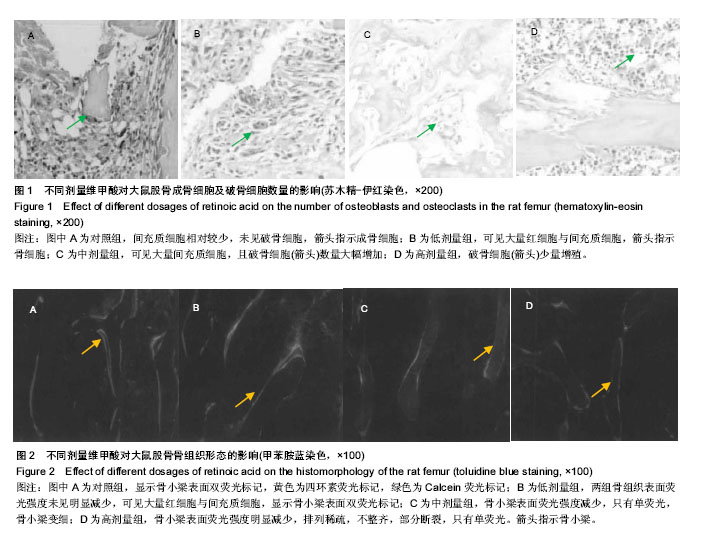
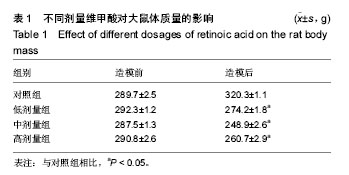
2.1 实验动物数量 观察分析80只建模大鼠,于造模结束时,共存活74只,实验期间未予补充样本量。其中6只死亡大鼠均来自高剂量组,组内存活14只,死亡原因初步考虑为维甲酸过量。 2.2 大体观察 对照组、低剂量组及中剂量组大鼠均精神活动良好,反应敏捷,毛发有光泽、柔顺,活动量正常。高剂量组大鼠造模3 d后发现大鼠精神一般,毛发粗糙,脾气暴躁;造模9 d后出现2只大鼠死亡,8只大鼠皮肤受损,将皮肤受损大鼠分笼喂养,造模9-14 d期间先后又有4只大鼠死亡,其余大鼠脾气火爆,打架频繁。 2.3 体质量 造模前4组体质量差异无显著性意义,造模14 d后低、中、高剂量组大鼠体质量均低于对照组(P < 0.05),其中中剂量组大鼠体质量下降最为明显,低、中、高剂量组大鼠体质量差异无显著性意义(表1)。"
| [1] Assessment of fracture risk and its application to screening for postmenopausal osteoporosis. Report of a WHO Study Group. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser. 1994;843:1-129. [2] Phetfong J, Sanvoranart T, Nartprayut K, et al. Osteoporosis: the current status of mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2016;21:12. [3] Tell-Lebanon O, Rotman-Pikielny P. Osteoporosis and diabetes - in which way are they related? Harefuah. 2016; 155(11):697-701.[4] Grover M, Bachrach LK. Osteoporosis in Children with Chronic Illnesses: Diagnosis, Monitoring, and Treatment. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2017. in press. [5] Kuo TR, Chen CH. Bone biomarker for the clinical assessment of osteoporosis: recent developments and future perspectives. Biomark Res. 2017;5:18.[6] Fukumoto S, Matsumoto T. Recent advances in the management of osteoporosis. F1000Res. 2017;6:625. [7] Soleyman-Jahi S, Yousefian A, Maheronnaghsh R, et al. Evidence-based prevention and treatment of osteoporosis after spinal cord injury: a systematic review. Eur Spine J. 2017. in press. [8] Schweser KM, Crist BD. Osteoporosis: a discussion on the past 5 years. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2017;10(2): 265-274. [9] Asadipooya K, Graves L, Greene LW. Transient osteoporosis of the hip: review of the literature. Osteoporos Int. 2017;28(6): 1805-1816. [10] Sözen T, Öz???k L, Ba?aran NÇ. An overview and management of osteoporosis. Eur J Rheumatol. 2017;4(1): 46-56.[11] Hanley DA, McClung MR, Davison KS, et al. Western Osteoporosis Alliance Clinical Practice Series: Evaluating the Balance of Benefits and Risks of Long-Term Osteoporosis Therapies. Am J Med. 2017;130(7):862.e1-862.e7.[12] 王秀玲.骨质疏松症几种相关基因的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2007,13(5):367-370.[13] 梁芝萍.骨质疏松患者与补钙[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2006, 15(14):1949.[14] 乔芳,常静.骨质疏松流行病学调查分析[J].中国实用医药,2012, 7(30):271-272.[15] 胡军,张华,牟青.骨质疏松症的流行病学趋势与防治进展[J].临床荟萃,2011,26(8):729-731.[16] 王伟,李春雯,史晓林.中国杭州骨质疏松性髋部骨折的流行病学研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2013,21(5):15-17.[17] 贺丽英,孙蕴,要文娟,等. 2010-2016年中国老年人骨质疏松症患病率Meta分析[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2016,22(12):1590-1596.[18] 孙宇强,王雪,关兴芳,等.维甲酸及其受体与肿瘤关系的研究进展[J].生命科学,2014,26(3):295-301.[19] 杨娟,张锡宝.维甲酸受体及其作用机制研究进展[J].皮肤性病诊疗学杂志,2014(5):423-426.[20] 贾经汉,邱新建,陈志坚.骨质疏松动物模型的研究进展[J].中国康复医学杂志,2007,22(8):765-768.[21] 王冰,徐又佳,郝彦明,等.去卵巢和激素致骨质疏松模型中骨密度与血清指标的比较[J].苏州大学学报:医学版,2008,28(1):10-13.[22] Allen SP, Maden M, Price JS. A role for retinoic acid in regulating the regeneration of deer antlers. Dev Biol. 2002; 251(2):409-23.[23] 徐洪璋,余斌.骨质疏松症动物模型研究现状[J].第一军医大学学报,2002,22(1):47-50.[24] 潘理平,曾茜.治疗骨质疏松症药物及其不良反应[J].药学实践杂志,2006,24(6):328-330.[25] 邵金莺,尹钟株,许哲.龙牡壮骨药对大鼠实验性骨质疏松的影响[J].中药药理与临床,1989(5):25-27.[26] Liao EY, Luo XH, Wang WB, et al. Effects of different nylestriol/levonorgestrel dosages on bone metabolism in female Sprague-Dawley rats with retinoic acid-induced osteoporosis. Endocr Res. 2003;29(1):23-42.[27] 胡彬,李青南,李朝阳,等.维甲酸致雌性大鼠骨代谢变化的实验研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,1997,3(3):12-14.[28] Oršoli? N, Golu?a E, Diki? D, et al. Role of flavonoids on oxidative stress and mineral contents in the retinoic acid-induced bone loss model of rat. Eur J Nutr. 2014;53(5): 1217-1227.[29] Ranhotra HS. The interplay between retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptors and human diseases. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2012;32(4):181-189.[30] 尚庆,刘宗超,鲁晓波.骨质疏松动物模型特点的综述[J].中国实用医药,2008,3(13):193-195.[31] 吕荣,徐新智,王军.介绍一种骨磨片荧光显微镜观察四环素的改进方法[J].临床与实验病理学杂志,2000,16(3):183.[32] 梁克玉,张全祥,魏玉玲.四环素标记、荧光显微镜观察中药对实验性骨折愈合的影响[C]//跨世纪骨伤杰出人才科技成果荟萃, 2004.[33] Mori T, Singtripop T, Kawashima S. Animal model of uterine adenomyosis: is prolactin a potent inducer of adenomyosis in mice? Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1991;165(1):232-234.[34] 刘钰瑜,崔燎,姚卫民,等.前列腺素衍生物对去卵巢大鼠骨质疏松的治疗作用[J].中国药理学通报,2009,25(10):1327-1330. [20] 夏维波,孟迅吾,邢小平,等.戊酸雌二醇对去卵巢大鼠骨质疏松的治疗作用[J].中华妇产科杂志,2001,36(10):606-609.[35] 许碧莲,崔燎,陈文双,等.维甲酸致大鼠骨质疏松模型探讨及丹参骨宝的预防作用[J].中国药理学通报,2010,26(4):539-543.[36] 成令忠.现代组织学[M].上海:上海科学技术文献出版社,2003.[37] 陈方,吴铁,崔燎.维甲酸致小鼠骨质疏松模型的量效关系及骨药理作用探讨[J].中国药理学通报,2002,18(6):681-684.[38] Lei YX, Zhao JJ, Hu AL, et al. Organic gallium improves tretinoin-induced osteoporosis in rats. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2007;27(9):1361-1364. [39] Zhao S, Niu F, Xu CY, et al. Diosgenin prevents bone loss on retinoic acid-induced osteoporosis in rats. Ir J Med Sci. 2016; 185(3):581-587. [40] Chen Q, Liu D, Xiong YM, et al. The Effects of Gallium Chloride on Apoptosis Osteoporosis Model of Rats Caused by Tretinoin Acid. Value Health. 2014;17(7):A771-772. [41] Xu G, Sun N, Zhao MJ, et al. Study on decoction's effect of different processed rhizomes of Cibotium barometz on retinoic acid induced male rats osteoporosis. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2014;39(6):1011-1015.[42] Yang J, Wu N, Peng J, et al. Prevention of retinoic acid-induced osteoporosis in mice by isoflavone-enriched soy protein. J Sci Food Agric. 2016;96(1):331-338. [43] Kang X, Li Z, Zhang WH, et al. Study on effect of combination of Epimedii Folium and Ligustri Lucidi Fructus on osteoporosis rats induced by retinoic acid. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2013;38(23):4124-4128. [44] Broulík PD, Raška I, Brouliková K. Prolonged overdose of all-trans retinoic acid enhances bone sensitivity in castrated mice. Nutrition. 2013;29(9):1166-1169. [45] Zhou Y, Liu Y, Gao Y. Effect of tanshitone on prevention and treatment of retinoic acid induced osteoporosis in mice. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2010;35(21):2923-2926. [46] Zhang H, Zhao Y, Li YQ, et al. Effects of deer tendons collagen on osteoporosis rats induced by retinoic acid. Zhong Yao Cai. 2010;33(3):411-414. [47] Li Y, Zhao Y, Sun X, et al. Prevention and therapeutic effects of sika deer velvet collagen hydrolysate on osteoporosis in rats by retinoic acid. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2010; 35(6):759-762. [48] Xu B, Cui L, Chen W, et al. Effects of DanShenGuBao on biomechanical properties and bone mineral density of femur induced by retinoic acid in rats. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2010;27(2):307-310. [49] Lei YX, Zhao JJ, Hu AL, et al. Organic gallium improves tretinoin-induced osteoporosis in rats. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2007;27(9):1361-1364. [50] Hotchkiss CE, Latendresse J, Ferguson SA. Oral treatment with retinoic acid decreases bone mass in rats. Comp Med. 2006;56(6):502-511. [51] Liao EY, Luo XH, Wang WB, et al. Effects of different nylestriol/levonorgestrel dosages on bone metabolism in female Sprague-Dawley rats with retinoic acid-induced osteoporosis. Endocr Res. 2003;29(1):23-42. [52] Wu B, Xu B, Huang TY. Effect of kanggusong in prevention and treatment of retinoic acid induced osteoporosis in rats. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 1996;16(1):32-36.[53] Wu B, Xu B, Huang TY, et al. A model of osteoporosis induced by retinoic acid in male Wistar rats. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 1996; 31(4):241-245.[54] Li N, Wang HM, Lin X, et al. Effect of Bugu Mixture on all-trans retinoic acid-induced apoptosis of bone marrow stromal cells. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 2004;2(5):367-371.[55] Wei M, Yang Z, Li P, et al. Anti-osteoporosis activity of naringin in the retinoic acid-induced osteoporosis model. Am J Chin Med. 2007;35(4):663-667.[56] Chen L, Chen LW, Chen H, et al. Skeletal biomechanical effectiveness of retinoic acid on induction of osteoporotic rats treated by alendronate and qianggu capsules. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2009;89(27):1930-1933.[57] Dai XX, Xiong YM, Guo X, et al. Dynamic effects of gallium chloride on osteoporotic rat model induced by tretinoin. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu. 2006;35(2):175-178.[58] Xu P, Hu WB, Guo X, et al. Therapeutic effect of dietary boron supplement on retinoic acid-induced osteoporosis in rats. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2006;26(12):1785-1788. [59] Xu P, Guo X, Zhang YG, et al. The effect of retinoic acid on induction of osteoporotic model rats and the possible mechanism. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2005; 36(2):229-232.[60] 吴波,徐冰,黄添友,等.维A酸致大鼠骨质疏松模型与机理研究[J].药学学报,1996,31(4):241-245.[61] 谈志龙,任海龙,白人骁,等.骨质疏松症与骨代谢生化测定指标[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2006,12(1):89-93.[62] 朱虎虎,孙炜,孙建新,等.维甲酸诱导雌性大鼠骨质疏松模型建立的效果观察[J].当代医学,2013,19(14):24-26. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Jiang Huanchang, Zhang Zhaofei, Liang De, Jiang Xiaobing, Yang Xiaodong, Liu Zhixiang. Comparison of advantages between unilateral multidirectional curved and straight vertebroplasty in the treatment of thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1407-1411. |
| [3] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhou Qian, Zhang Qiang, Chen Qiu. Human salivary components and osteoporosis/osteopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1439-1444. |
| [4] | Li Wei, Zhu Hanmin, Wang Xin, Gao Xue, Cui Jing, Liu Yuxin, Huang Shuming. Effect of Zuogui Wan on bone morphogenetic protein 2 signaling pathway in ovariectomized osteoporosis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1173-1179. |
| [5] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [6] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [7] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [8] | Gao Yujin, Peng Shuanglin, Ma Zhichao, Lu Shi, Cao Huayue, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. Osteogenic ability of adipose stem cells in diabetic osteoporosis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 999-1004. |
| [9] | Peng Kun. Improvement of the treatment effect of osteoporotic fractures: research status and strategy analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 980-984. |
| [10] | Shen Song, Xu Bin. Diffuse distribution of bone cement in percutaneous vertebroplasty reduces the incidence of refracture of adjacent vertebral bodies [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 499-503. |
| [11] | He Yunying, Li Lingjie, Zhang Shuqi, Li Yuzhou, Yang Sheng, Ji Ping. Method of constructing cell spheroids based on agarose and polyacrylic molds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| [12] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [13] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [14] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [15] | Shen Jiahua, Fu Yong. Application of graphene-based nanomaterials in stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 604-609. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||