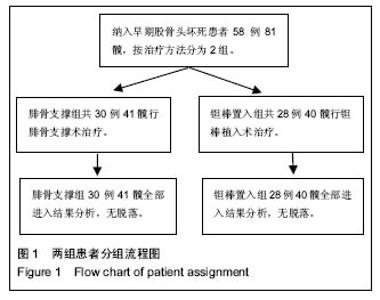
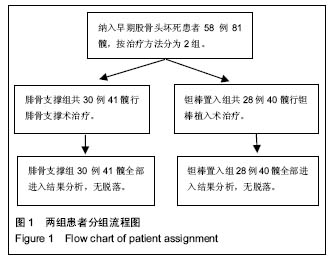
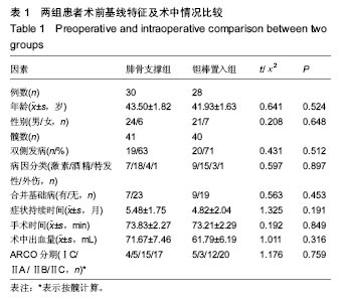
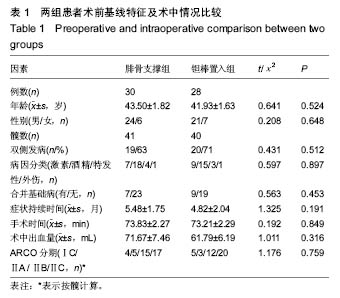
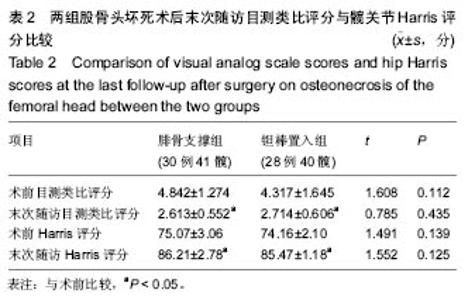
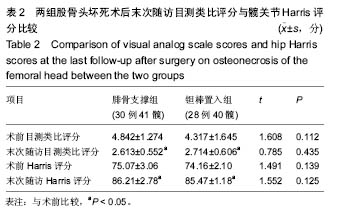
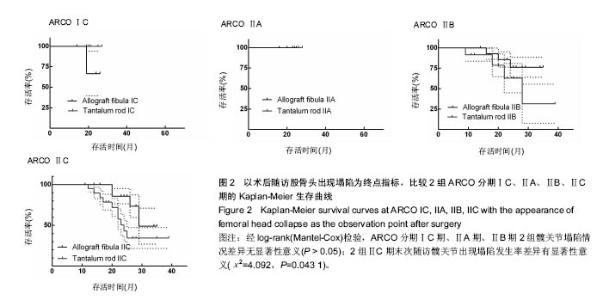
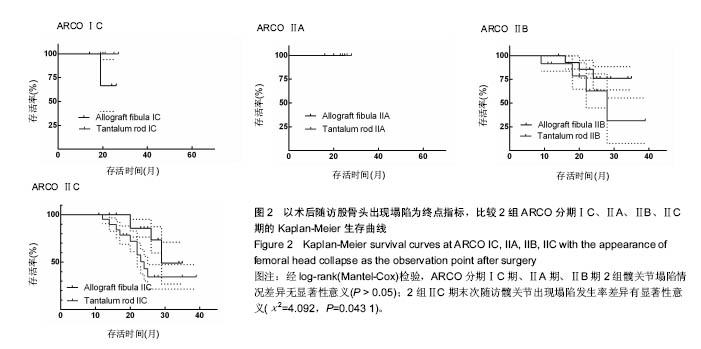
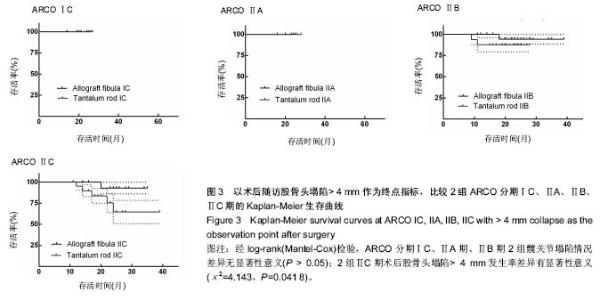
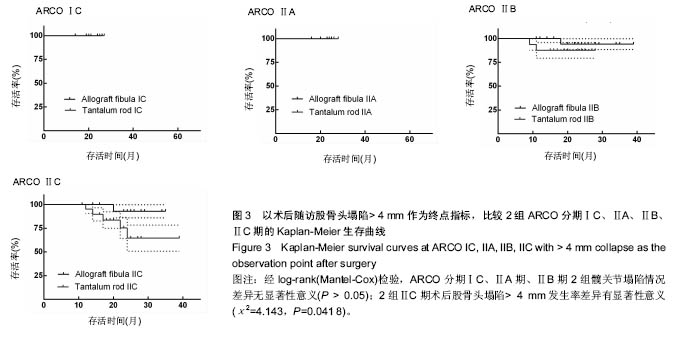
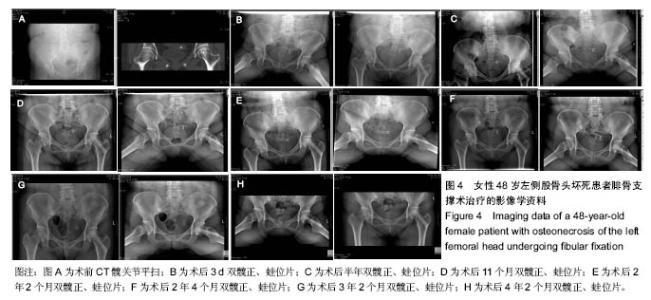
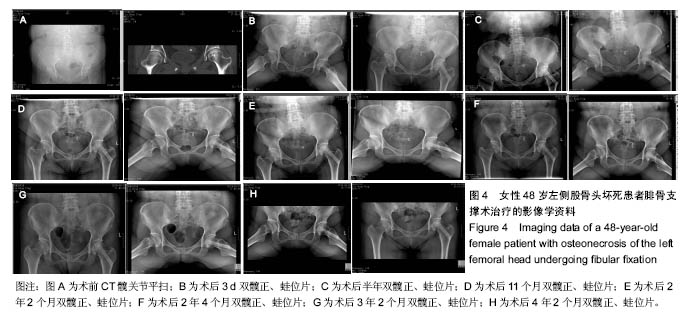
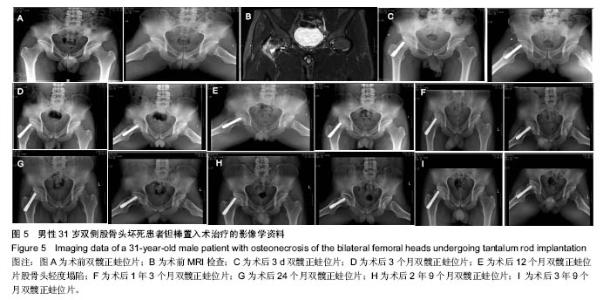
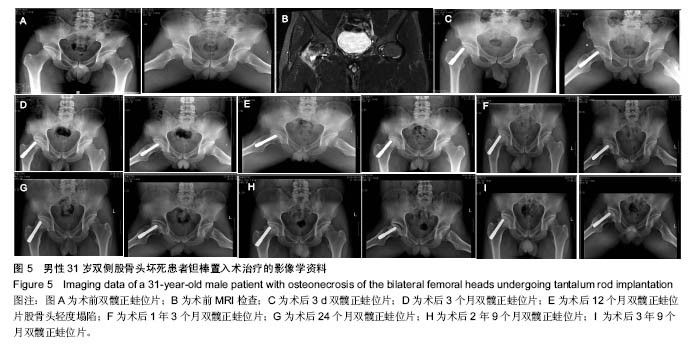
| [1]Fukushima W, Yamamoto T, Takahashi S, et al. The effect of alcohol intake and the use of oral corticosteroids on the risk of idiopathic osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a case-control study in Japan. Bone Joint J. 2013;95-b(3):320-325.[2]Varitimidis SE, Dimitroulias AP, Karachalios TS, et al. Outcome after tantalum rod implantation for treatment of femoral head osteonecrosis: 26 hips followed for an average of 3 years. Acta Orthopaedica. 2009;80(1):20-25.[3]毛子木,尹崑,王宇泽,等. 钽棒置入治疗股骨头坏死的疗效分析及预后模型建立[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(47):7043- 7050.[4]谭旭仪,高菲菲,高书图,等. 多孔钽棒配合股骨头坏死愈胶囊治疗激素性股骨头坏死临床观察[J]. 中国中西医结合杂志, 2016, 36(1):40-43.[5]吴敏,官建中,肖玉周,等. 髓芯减压钽棒植入治疗成人早期股骨头坏死的疗效观察[J]. 中华全科医学, 2016,14(8):1259-1261+ 1292.[6]刘书勇,马晓燕. 多孔钽棒置入联合髓芯减压对早期股骨头坏死的近期疗效[J]. 临床医学,2016,36(7):58-59.[7]唐立明,葛辉,庞智晖,等. 同种异体腓骨移植术治疗股骨头坏死的临床与计算生物力学研究[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2016,10(2):169-176.[8]苏来提•肖合热提,盛加根. 探讨髓芯减压+同种异体骨打压植骨治疗早期股骨头坏死的临床疗效[J]. 临床医学研究与实践, 2016,18:11-13.[9]柳海平,柴喜平.钻孔减压、植骨合中药治疗早中期股骨头缺血坏死30例[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志,2015,23(6):49-50.[10]孙明曜,王俊博,曾羿,等. 腓骨移植治疗不同股骨头坏死面积患者的随访研究[J]. 华西医学,2015,30(8):1430-1434.[11]李子荣. 股骨头坏死临床诊疗规范[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志. 2015,9(1):1-6.[12]Sugano N, Atsumi T, Ohzono K, et al. The 2001 revised criteria for diagnosis, classification, and staging of idiopathic osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Orthop Sci. 2002;7(5): 601-605.[13]庞智晖, 何伟, 张庆文, 等. 中药辅助改良减压植骨内稳定术治疗围塌陷期激素性股骨头坏死[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志, 2009, 17(1):30-33.[14]陈镇秋,何伟,魏秋实,等. 钽棒植入治疗围塌陷期股骨头坏死的疗效[J]. 广东医学,2012,33(14):2076-2078.[15]Kim YM, Lee SH, Lee FY, et al. Morphologic and biomechanical study of avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Orthopedics. 1991;14(10):1111-1116.[16]徐佩君,盛加根,徐镇,等.不断股直肌起点髋前侧入路行吻合血管游离腓骨治疗股骨头坏死的解剖学研究[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2014,8(5):13-15.[17]Mont MA, Hungerford DS. Non-traumatic avascular necrosis of the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995;77(3): 459-474.[18]唐立明, 葛辉, 庞智晖,等. 同种异体腓骨移植术治疗股骨头坏死的临床与计算生物力学研究[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2016,10(2):169-176.[19]田雷, 王坤正, 党晓谦, 等. 吻合血管游离腓骨移植治疗股骨头坏死的中期及远期疗效评估[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2012,6(6):879-887.[20]Liu Y, Su X, Zhou S, et al. A modified porous tantalum implant technique for osteonecrosis of the femoral head: survivorship analysis and prognostic factors for radiographic progression and conversion to total hip arthroplasty. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(2):1918-1930.[21]Zhao D, Liu B, Wang B, et al. Autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells associated with tantalum rod implantation and vascularized iliac grafting for the treatment of end-stage osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Biomed Res Int. 2015; 2015(3):240506.[22]Vargas JR, Seelman SJ. Micro-alloyed porous metal having optimized chemical composition and method of manufacturing the same: US, US8734514[P]. 2014.[23]Zardiackas LD, Parsell DE, Dillon LD, et al. Structure, metallurgy, and mechanical properties of a porous tantalum foam. J Biomed Mat Res. 2001;58(2):180.[24]Ünal MB, Cansu E, Parmaks?zo?lu F, et al. Treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head with free vascularized fibular grafting: Results of 7.6-year follow-up Acta Orthopaedica Et Traumatologica Turcica.2016;50(3):323.[25]唐立明,葛辉,庞智晖,等. 同种异体腓骨移植术治疗股骨头坏死的临床与计算生物力学研究[J].中华关节外科杂志电子版, 2016, 10(2):47-53.[26]林志炯,苏培基,伍中庆,等.股骨头髓芯减压加异体腓骨移植术治疗股骨头缺血性坏死[J].中国骨伤,2009,22(8):628-630.[27]Taso AK,Roberson JR,Christie MJ. Biomechanical and clinical evaluations of a porous tantalum implant for the treatment of early - stage osteonecrosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005; 87(S2): 22-27.[28]Nadeau M,Sguin C,Theodoropoulos JS.Short term clinical outcome of a porous tantalum implant for the treatment of advanced osteonecrosis of the femoral head.Mcgill J Med. 2007;10(1): 4-10.[29]王华锋, 王静成. 骨小梁金属(多孔钽)棒植入治疗早期股骨头坏死的研究进展[J]. 临床骨科杂志, 2010,13(5):563-565. |