Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (13): 2100-2107.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.13.022
Previous Articles Next Articles
Human amniotic epithelial cells: culture technology optimization and biological characteristics
Liu Chao, Xu Zhi-guo, Wang Shao-hong, Cheng Hong-ling, Yang Xu-wei, Gong Bo, Liu Yang, Xu Chun-yan
- Umbilical Cord Blood Hematopoietic Stem Cell Bank of Zhejiang Province, Eastern Union Stem Cell & Gene Engineering Co., Ltd., Huzhou 313000, Zhejiang Province, China
-
Revised:2016-12-05Online:2017-05-08Published:2017-06-09 -
Contact:Xu Zhi-guo, Deputy senior engineer, Umbilical Cord Blood Hematopoietic Stem Cell Bank of Zhejiang Province, Eastern Union Stem Cell & Gene Engineering Co., Ltd., Huzhou 313000, Zhejiang Province, China -
About author:Liu Chao, Master, Intermediate engineer, Umbilical Cord Blood Hematopoietic Stem Cell Bank of Zhejiang Province, Eastern Union Stem Cell & Gene Engineering Co., Ltd., Huzhou 313000, Zhejiang Province, China -
Supported by:Online Technology Market Transaction Industrialization Project of Zhejiang Province, No. 2012jssc02
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Chao, Xu Zhi-guo, Wang Shao-hong, Cheng Hong-ling, Yang Xu-wei, Gong Bo, Liu Yang, Xu Chun-yan. Human amniotic epithelial cells: culture technology optimization and biological characteristics[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(13): 2100-2107.
share this article
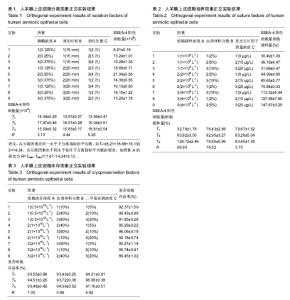
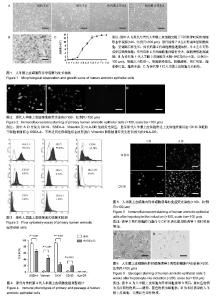
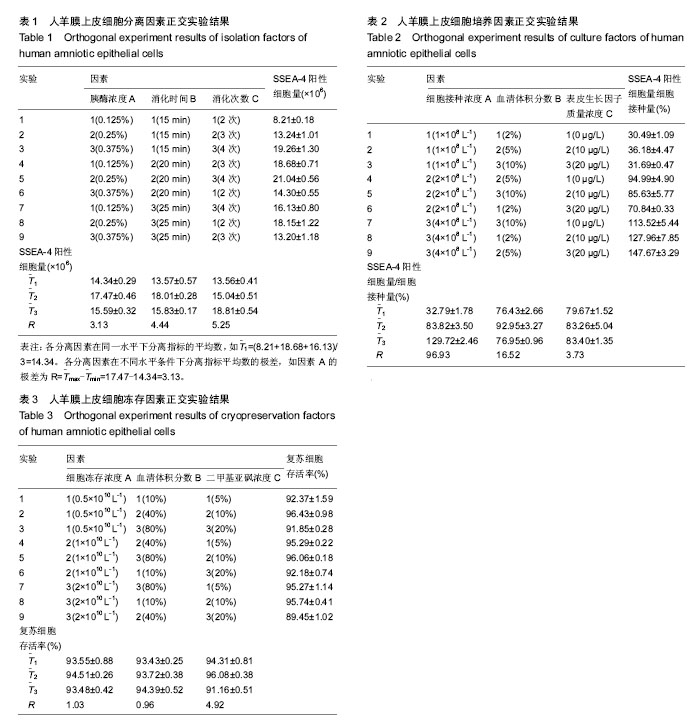
2.1 hAECs的分离 极差法分析分离因素正交实验结果,由表1数据得到分离指标——“SSEA-4阳性细胞量”极差最大的因素是消化次数,即消化次数对SSEA-4阳性细胞量影响最大。各因素影响大小排序:消化次数(C)>消化时间(B)>胰酶浓度(A)。比较各因素不同水平的 值,获得优化的分离因素组合为A2B2C3,即胰酶浓度0.25%,消化时间20 min,分4次消化。 2.2 hAECs的培养 极差法分析培养因素正交实验结果,由表2得到培养指标——“SSEA-4阳性细胞量/细胞接种量”极差最大的因素是细胞接种浓度,即细胞接种浓度对SSEA-4阳性细胞量/细胞接种量影响最大。各因素影响大小排序:细胞接种浓度(A)>血清体积分数(C)>表皮生长因子质量浓度(B)。比较各因素不同水平的T(_)值发现,表皮生长因子质量浓度的最高 值(T(_)3与第二T(_)值(T(_)2数值接近,但表皮生长因子质量浓度水平2仅为水平3的一半,从方案经济性考虑,表皮生长因子质量浓度应选择水平2(10 μg/L)更为适宜,故优化的培养因素组合为A3B2C2,即细胞接种浓度4×108 L-1,血清体积分数为5%,表皮生长因子质量浓度10 μg/L。)) 2.3 hAECs的冻存 极差法分析冻存因素正交实验结果,由表3得到,细胞冻存浓度与血清体积分数的极差相近,表明两者对冻存指标——“复苏细胞存活率”的影响程度相近。二甲基亚砜浓度的极差最大,表明二甲基亚砜浓度对复苏细胞存活率影响最大。各因素影响大小排序:二甲基亚砜浓度(C)>细胞冻存密度(A)>血清体积分数(B)。通过各因素不同水平的值比较,得到优化的冻存因素组合为A2B3C2,即细胞冻存浓度1×1010 L-1,血清体积分数为80%,二甲基亚砜浓度10%。 2.4 hAECs形态学观察与生长曲线 体外原代培养的hAECs在光镜下呈典型上皮细胞形态。细胞接种后二三天内贴壁生长,刚贴壁的细胞呈圆形,折光性较强。完全贴壁后细胞胞质展开,呈不规则多角形,折光性减弱。原代hAECs 7 d左右形成单层贴壁细胞,呈铺路石样生长。传代后第2代细胞增殖速度加快,5 d左右可形成单层贴壁细胞。hAECs培养4代后细胞胞体略有变大,细胞增殖速度减缓(图1A)。苏木精-伊红染色后观察,传代第1代细胞大小较均一,细胞核染蓝色,核膜清晰,核仁明显,胞浆染红色,胞质丰富(图1B)。 传代第1代hAECs接种于培养瓶后,0-2 d为细胞生长潜伏期,以细胞贴壁过程为主。3-5 d生长曲线曲率最大,为hAECs快速增殖的指数生长期;6 d后生长速度减缓,细胞基本长满培养瓶底,进入平顶期。传代第1代培养细胞符合典型的细胞生长曲线(图1C)。 2.5 免疫荧光染色检测结果 免疫荧光染色显示,原代hAECs表达上皮细胞表面标志CK19和胚胎干细胞表面标志SSEA-4,不表达间充质细胞标志波形蛋白Vimentin和移植排斥发生密切相关的HLA-DR(图2)。表明hAECs免疫原性低,用于细胞治疗不易发生移植排斥现象。 2.6 hAECs流式细胞术检测结果 流式细胞仪检测原代hAECs强阳性表达SSEA-4,阳性表达间充质干细胞相关标志物CD73,弱阳性表达CD90,CD105和SSEA-1阳性表达量很低,造血细胞表面标志物CD34、CD45几乎不表达,同样不表达HLA-DR(图3)。 实验通过对原代与传代第4代hAECs(DMEM/F12+体积分数5%胎牛血清)相关免疫表型流式检测发现,传代第4代hAECs的SSEA-4和CK19表达较原代显著减少(P < 0.000 1),Vimentin和CD105表达P4较原代细胞显著增多(P < 0.000 1),原代与传代第4代hAECs均不表达HLA-DR (图4)。 SSEA-4是细胞全能性表达标志物,CK19是上皮细胞特异性表达标志物,Vimentin和CD105是间充质细胞的特异性表达标志物。实验结果表明,hAECs经过培养传代后,细胞在“分化全能性”上有所减弱。上皮细胞与间充质细胞标志物的变化表明,hAECs培养过程符合上皮间充质转化的特征表现。然而,培养过程中与免疫排斥密切相关的HLA-DR始终不表达,表明hAECs能始终保持免疫原性低的特性,有利于降低细胞治疗过程中排斥反应的发生概率。 2.7 hAECs诱导后的免疫荧光染色与糖原染色 成熟肝细胞高表达白蛋白与CK18。诱导后细胞免疫荧光染色显示,诱导3周后hAECs的白蛋白与CK18表达量均较诱导1周明显增加(图5)。 hAECs诱导3周后经糖原PAS染色显示,紫红色物质为反应阳性物质——糖原,蓝色物质为细胞核(图6)。显示hAECs经实验诱导方案诱导后,成功获得具有一定合成功能的肝样细胞。"
| [1] Marongiu F,Gramignoli R,Dorko K,et al.Hepatic Differentiation of Amniotic Epithelial Cells.Hepatology. 2011;53(5): 1719-1729. [2] Niknejad H,Yazdanpanah G.Opposing effect of amniotic membrane on angiogenesis originating from amniotic epithelial cells.Ira J Med Hypotheses Ideas.2014;8(1):39-41.[3] Toshio M,Fabio M,Ewa E,et al.Isolation of amniotic epithelial stem cells.Curr Protoc Stem Cell Biol.2010;Chapter 1:Unit 1E.3.[4] Sean M,Sharina R,Rutu A,et al.Amnion Epithelial Cell Isolation and Characterization for Clinical Use.Curr Protoc Stem Cell Biol.2010;Chapter 1:1E.6.1-1E.6.25.[5] Gita P,Vijesh V,Yang TJ,et al.Changes in culture expanded human amniotic epithelial cells: implications for potential therapeutic applications.PlOs One.2011; 6(11):e26136- e26136.[6] Adinolfi M,Akle CA,Mccoll I,et al.Expression of HLA antigens, beta 2-microglobulin and enzymes by human amniotic epithelial cells.Nature.1982;295(5847):325-327.[7] Satoko Y,Kunihiko T,Yasuharu U,et al.Differentiation of adult hepatic stem-like cells into pancreatic endocrine cells.Cell Transplant.2005;14(9):647-653.[8] Tomoharu T,Isamu I,Shigeo S.Establishment and characterization of a pluripotent stem cell line derived from human amniotic membranes and initiation of germ layers in vitro.Human Cell.2004;17(3):125-130.[9] 程金华,朱化彬,孙秀柱,等.冷冻保护剂和胎牛血清对牛成纤维细胞冷冻效果的影响[J]. 中国畜牧杂志,2006,42(21):12-14.[10] 杨银芬,考桂兰,侯先志,等.不同细胞密度冻存对奶牛乳腺上皮细胞的影响[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2010,32(4):626-629.[11] 郭海平,郭冠萍,郝鹏.BHK21细胞冻存密度与复苏后活力的关系分析[J].畜牧与饲料科学, 2010,31(3):6-7.[12] 陈露萍,王璞,汤海亮,等.不同冻存液对人诱导性多能干细胞冻存与复苏效果的影响[J]. 中国临床神经科学,2012,20(5):494-499.[13] 杨东斌,宋来君,杨波,等.不同人羊膜间充质干细胞冻存液冻存细胞效果比较[J].郑州大学学报:医学版,2009,44(3):568-572.[14] 金玲,陈剑,吴静,等.人羊膜上皮细胞的分离、纯化及其生物学特性研究[J].广东医学, 2010,31(16):2055-2057.[15] Paolo C,Chiara M,Pasquale V.Amniotic membrane transplantation in human immunodeficiency virus-positive children.Arch Ophthalmol.2008;126(6):866-867.[16] 方宁,宋秀军,张路,等.人羊膜上皮细胞的分离、培养及鉴定[J].遵义医学院学报,2009, 32(2):121-124.[17] Tabatabaei M,Mosaffa N,Nikoo S,et al.Isolation and partial characterization of human amniotic epithelial cells: the effect of trypsin.Avicenna J Med Biotechnol.2014;6(1):10-20.[18] Liu X,Zhou Q,Zhang X,et al.In vitro culture and molecular characterization of human amniotic epithelial cells.Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi.2014;30(12):1318-1321.[19] Yang TJ,Vijesh V,Han L Y,et al.Immunogenicity and immunomodulatory properties of hepatocyte-like cells derived from human amniotic epithelial cells.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2012;8(1):91-99.[20] Miki T,Wong W,Zhou E,et al.Biological impact of xeno-free chemically defined cryopreservation medium on amniotic epithelial cells.Stem Cell Res Ther.2016;7(1):8.[21] 李云剑,林樾,燕辛,等.培养基血清浓度对人表皮干细胞增殖分化的影响[J].现代生物医学进展,2010,10(20):3831-3833.[22] Koike C,Zhou K,Takeda Y,et al.Characterization of amniotic stem cells.Cell Reprogram.2014;16(4):298-305.[23] Roy R,Kukucka M,Messroghli D,et al. Epithelial-to- mesenchymal transition enhances the cardioprotective capacity of human amniotic epithelial cells.Cell Transplant. 2013;24(6):985-1002.[24] Elwan MA,Ishii T,Sakuragawa N.Characterization of dopamine D-2 receptor gene expression and binding sites in human placenta amniotic epithelial cells.Placenta.2003; 24(6): 658-663.[25] Marcus AJ,Coyne TM,Black IB,et al.Fate of amnion-derived stem cells transplanted to the fetal rat brain: migration, survival and differentiation.J Cell Mol Med.2008;12(4): 1256-1264.[26] Wang JP.Phenotypic identification and differentiation potential analysis of two kinds of human amniotic cells.Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi.2012;20(1): 146-53.[27] Tan Jean L,Chan Siow T,Lo Camden Y,et al.Amnion cell-mediated immune modulation following bleomycin challenge: controlling the regulatory T cell response.Stem Cell Res Ther.2015;6:8.[28] García-López G,García-Castro IL,Avila-González D,et al.Human Amniotic Epithelium (HAE) as a Possible Source of Stem Cells(SC).Gaceta Medica De Mexico.2015;151(1): 66-74.[29] Toshio M.Amnion-derived stem cells: In quest of clinical applications.Stem Cell Res Ther.2011;2(3):1-11.[30] Drews K,Jozefczuk J,Prigione A,et al.Human induced pluripotent stem cells-from mechanisms to clinical applications. J Mol Med.2012;90(7):735-745.[31] 耿娟娟,崔勇,邱书奇.羊膜上皮细胞的体外培养及干细胞特性研究[J].实用医学杂志, 2012,28(2):172-174.[32] Okere B,Alviano F,Costa R,et al.In vitro differentiation of human amniotic epithelial cells into insulin-producing 3D spheroids.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2015;28(3): 390-402.[33] Kim S,Kim HS,Lee E,et al.In vivo hepatic differentiation potential of human cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells.Int J Mol Med.2011;27(5):701-706.[34] Forte G,Minieri M,Cossa P,et al.Hepatocyte growth factor effects on mesenchymal stem cells: proliferation, migration, and differentiation.Stem Cells.2006; 24(1):23-33.[35] Kang NH,Hwang KA,Kim SU,et al.Potential antitumor therapeutic strategies of human amniotic membrane and amniotic fluid-derived stem cells.Cancer Gene Ther. 2012; 19(8):517-522.[36] Lai D,Wang Y,Sun J ,et al.Derivation and characterization of human embryonic stem cells on human amnion epithelial cells.Sci Rep.2015;5:10014.[37] Tan JL,Chan ST,Wallace EM,et al.Human amnion epithelial cells mediate lung repair by directly modulating macrophage recruitment and polarization. Cell Transplant.2014;23(3): 319-328.[38] Carbone A,Paracchini V,Castellani S,et al.Human amnion-derived cells: prospects for the treatment of lung diseases.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther.2014;9(4):297-305.[39] Hassan N,Ghasem Y.Anticancer effects of human amniotic membrane and its epithelial cells.Med Hypotheses. 2014; 82(4):488-489.[40] McDonald CA,Payne NL,Sun G,et al.Immunosuppressive potential of human amnion epithelial cells in the treatment of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.J Neuroinflammation. 2015;12:112.[41] Grzywocz Z,Pius-Sadowska E,Klos P,et al.Growth factors and their receptors derived from human amniotic cells in vitro.Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2014;52(3):163-170. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [3] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [4] | He Yunying, Li Lingjie, Zhang Shuqi, Li Yuzhou, Yang Sheng, Ji Ping. Method of constructing cell spheroids based on agarose and polyacrylic molds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| [5] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [6] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [7] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [8] | Shen Jiahua, Fu Yong. Application of graphene-based nanomaterials in stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 604-609. |
| [9] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [10] | Li Hui, Chen Lianglong. Application and characteristics of bone graft materials in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 626-630. |
| [11] | Gao Cangjian, Yang Zhen, Liu Shuyun, Li Hao, Fu Liwei, Zhao Tianyuan, Chen Wei, Liao Zhiyao, Li Pinxue, Sui Xiang, Guo Quanyi. Electrospinning for rotator cuff repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 637-642. |
| [12] | Guan Jian, Jia Yanfei, Zhang Baoxin , Zhao Guozhong. Application of 4D bioprinting in tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 446-455. |
| [13] | Liu Jiali, Suo Hairui, Yang Han, Wang Ling, Xu Mingen. Influence of lay-down angles on mechanical properties of three-dimensional printed polycaprolactone scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2612-2617. |
| [14] | Huang Bo, Chen Mingxue, Peng Liqing, Luo Xujiang, Li Huo, Wang Hao, Tian Qinyu, Lu Xiaobo, Liu Shuyun, Guo Quanyi . Fabrication and biocompatibility of injectable gelatin-methacryloyl/cartilage-derived matrix particles composite hydrogel scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2600-2606. |
| [15] | Fang Xiaoyang, Tang Tian, Wang Nan, Qian Yuzhang, Xie Lin. Repair and regenerative therapies of the annulus fibrosus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1582-1587. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||