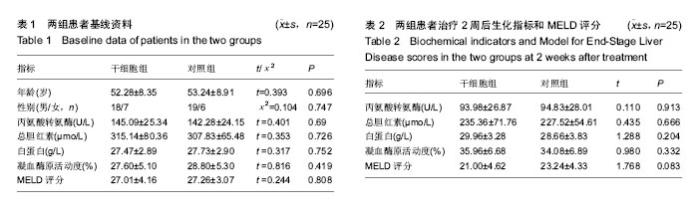
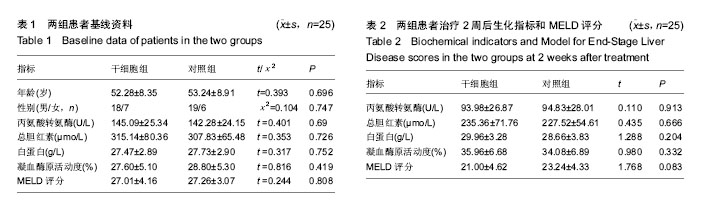
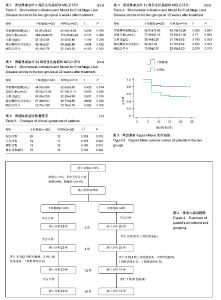
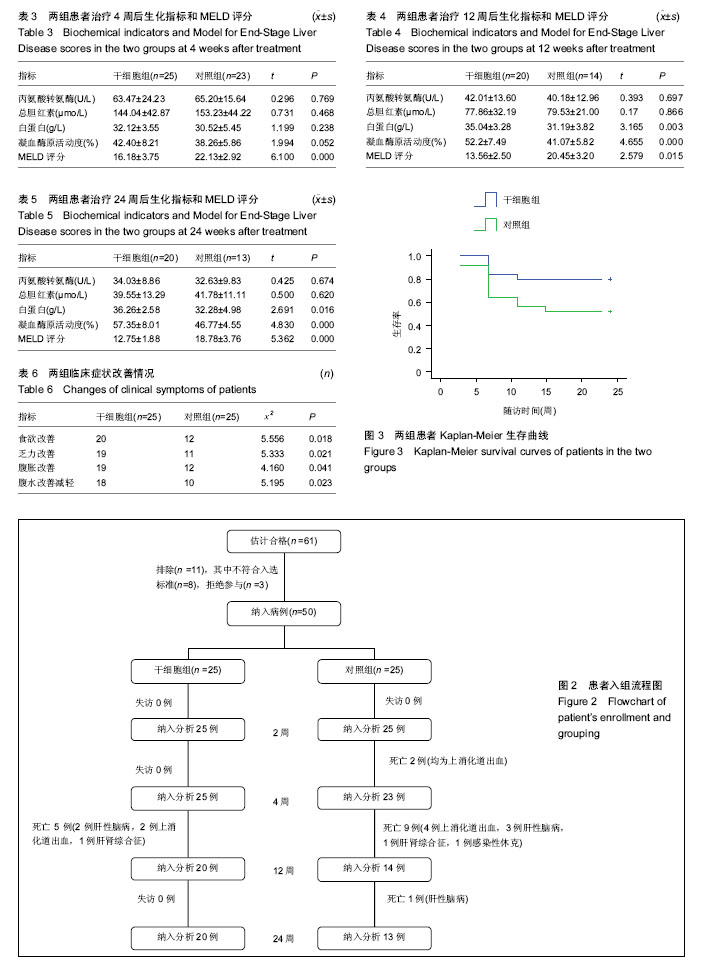
| [1] 中华医学会感染病学分会肝衰竭与人工肝学组. 肝衰竭诊治指南(2012年版)[J].实用器官移植电子杂志,2013,1(4):193- 202.[2] Xue HL, Zeng WZ, Wu XL, et al. Clinical therapeutic effects of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells transplantation in the treatment of end-stage liver disease. Transplant Proc. 2015;47(2):412-418.[3] Shin TH, Kim HS, Choi SW, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Inflammatory Skin Diseases: Clinical Potential and Mode of Action. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(2): E244.[4] Wang Z, Wang L, Su X, et al. Rational transplant timing and dose of mesenchymal stromal cells in patients with acute myocardial infarction: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):21.[5] Kanelidis A, Premer C, Lopez JG, et al. Route of Delivery Modulates the Efficacy of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Myocardial Infarction: A Meta-Analysis of Preclinical Studies and Clinical Trials.Circ Res. 2016: CIRCRESAHA. 116.309819. [6] Vickers ER, Karsten E, Flood J, et al. A preliminary report on stem cell therapy for neuropathic pain in humans. J Pain Res. 2014;7:255-263.[7] Ma XR, Tang YL, Xuan M, et al. Transplantation of autologous mesenchymal stem cells for end-stage liver cirrhosis: a meta-analysis based on seven controlled trials. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2015;2015:908275.[8] Peng L, Xie DY, Lin BL, et al. Autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in liver failure patients caused by hepatitis B: short-term and long-term outcomes. Hepatology. 2011 Sep 2;54(3):820-828.[9] 曲乃方,王者令,闫兆平,等. 38例慢性肝衰竭患者经干细胞治疗48周效果观察[J]. 中华细胞与干细胞杂志:电子版,2013,3(2): 73-77.[10] 姚豫桐,罗兰云,薛华,等. 自体外周血CD33+干细胞移植治疗晚期肝硬化100例的临床疗效分析[J].中华肝脏病杂志, 2014, 22(9):667-670. [11] 王全楚,张凌云,王东琳. 人脐带血间充质干细胞输注治疗慢性肝衰竭患者的近期疗效观察[J].胃肠病学和肝病学杂志, 2013, 22(1):22-24.[12] Kantarc?o?lu M, Demirci H, Avcu F, et al. Efficacy of autologous mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in patients with liver cirrhosis. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2015;26(3):244-250.[13] Deng Q, Cai T, Zhang S, et al. Autologous Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Transplantation Improves Portal Hemodynamics in Patients with Hepatitis B Virus-related Decompensated Cirrhosis. Hepat Mon. 2015;15(12):e32498.[14] Yu SJ, Chen LM, Lyu S, et al. Safety and efficacy of human umbilical cord derived-mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for treating patients with HBV-related decompensated cirrhosis. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2016;24(1):51-55. [15] 佟立新,张岁,闫宝勇,等. 人脐带间充质干细胞经外周静脉移植治疗失代偿期肝硬化的临床疗效[J]. 世界华人消化杂志, 2015, 23(15):2457-2462.[16] 曾芝雨,李东良,方坚,等. 脐带间充质干细胞联合骨髓干细胞移植治疗失代偿期肝硬化:1年随访对照[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(10): 1533-1538.[17] 李元元, 徐若男, 施明, 等. 人脐带间充质干细胞治疗慢加急性肝衰竭患者的初步临床观察[J]. 中华细胞与干细胞杂志:电子版, 2015, 5(1):36-40.[18] 刘波,董静,张骏飞,等.人脐带间充质干细胞治疗慢加急性肝衰竭患者近期疗效与安全性分析[J]. 实用肝脏病杂志, 2013, 16(1): 29-31.[19] Karahuseyinoglu S, Cinar O, Kilic E, et al. Biology of stem cells in human umbilical cord stroma: in situ and in vitro surveys. Stem Cells. 2007;25(2):319-331.[20] Zhou C, Yang B, Tian Y, et al. Immunomodulatory effect of human umbilical cord Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells on lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 2011;272(1):33-38.[21] Feng T, Zhang J, Zeng G, et al. Therapeutic potential of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in mice with acute hepatic failure. Int J Artif Organs. 2015;38(5):271-276.[22] Yang JF, Cao HC, Pan QL, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells from the human umbilical cord ameliorate fulminant hepatic failure and increase survival in mice. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2015;14(2):186-193.[23] Shi M, Zhang Z, Xu R, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cell transfusion is safe and improves liver function in acute-on-chronic liver failure patients. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2012;1(10):725-731.[24] Liu WH, Song FQ, Ren LN, et al. The multiple functional roles of mesenchymal stem cells in participating in treating liver diseases. J Cell Mol Med. 2015;19(3):511-520.[25] Yovchev MI, Xue Y, Shafritz DA, et al. Repopulation of the fibrotic/cirrhotic rat liver by transplanted hepatic stem/progenitor cells and mature hepatocytes. Hepatology. 2014;59(1):284-295.[26] Herrera MB, Fonsato V, Bruno S, et al. Human liver stem cells improve liver injury in a model of fulminant liver failure. Hepatology. 2013;57(1):311-319.[27] Chai NL, Zhang XB, Chen SW, et al. Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviate liver fibrosis in rats. World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22(26):6036-6048.[28] Li T, Yan Y, Wang B, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate liver fibrosis. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(6):845-854.[29] Eom YW, Shim KY, Baik SK. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for liver fibrosis. Korean J Intern Med. 2015;30(5):580-589.[30] Hirata M, Ishigami M, Matsushita Y, et al. Multifaceted Therapeutic Benefits of Factors Derived From Dental Pulp Stem Cells for Mouse Liver Fibrosis. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016;5(10):1416-1424.[31] Meier RP, Mahou R, Morel P, et al. Microencapsulated human mesenchymal stem cells decrease liver fibrosis in mice. J Hepatol. 2015;62(3):634-641.[32] Li Q, Zhou X, Shi Y, et al. In vivo tracking and comparison of the therapeutic effects of MSCs and HSCs for liver injury. PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e62363.[33] Li T, Zhu J, Ma K, et al. Autologous bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation promotes liver regeneration after portal vein embolization in cirrhotic rats. J Surg Res. 2013;184(2):1161-1173. [34] Xue G, Han X, Ma X, et al. Effect of Microenvironment on Differentiation of Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells into Hepatocytes In Vitro and In Vivo. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:8916534.[35] Al Ghrbawy NM, Afify RA, Dyaa N, et al. Differentiation of Bone Marrow: Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells into Hepatocyte-like Cells. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus. 2016;32(3):276-283.[36] Yang L, Wang Y, Wang X, et al. Effect of allogeneic umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in a rat model of hepatic cirrhosis. J Tradit Chin Med. 2015;35(1):63-68.[37] 黄湛镰,高志良.肝衰竭的三重打击及治疗策略[J].内科急危重症杂志, 2014, 20(3):154-156.[38] Zhang Y, Cai W, Huang Q, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells alleviate bacteria-induced liver injury in mice by inducing regulatory dendritic cells. Hepatology. 2014;59(2):671-682.[39] Higashimoto M, Sakai Y, Takamura M, et al. Adipose tissue derived stromal stem cell therapy in murine ConA-derived hepatitis is dependent on myeloid-lineage and CD4+ T-cell suppression. Eur J Immunol. 2013;43(11):2956-2968.[40] Sharma RR, Pollock K, Hubel A, et al. Mesenchymal stem or stromal cells: a review of clinical applications and manufacturing practices.Transfusion. 2014;54(5):1418-1437. |