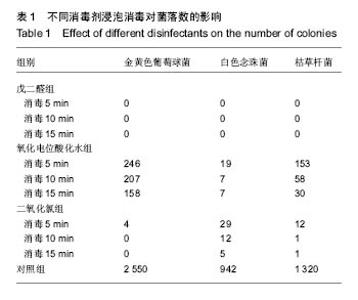
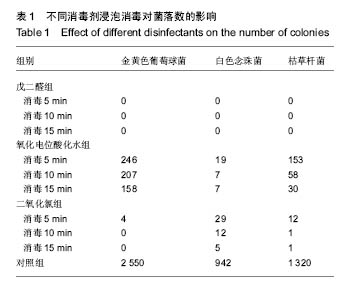
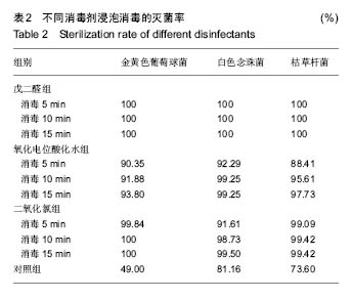
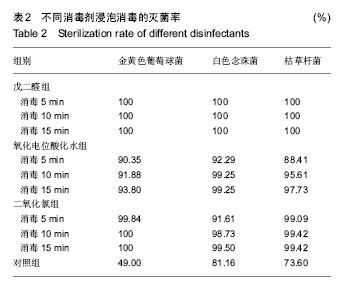
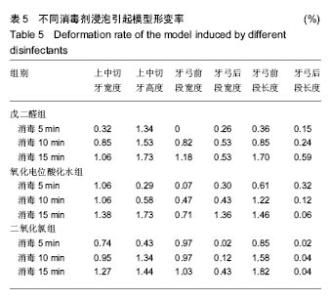
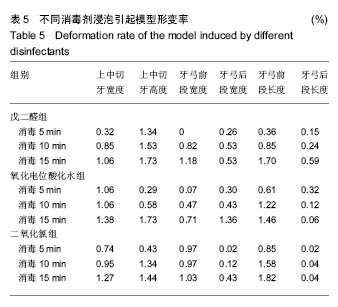
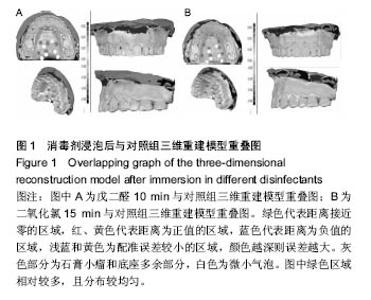
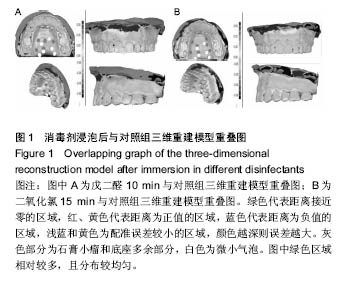
| [1]赵信义.口腔材料学[M].5版.北京:人民卫生出版,2012:126-130.[2]刘琴,董海东,顾钰.口腔印模消毒效果的研究现状[J].中国消毒学杂志,2013,30(10):959- 962.[3]Maller SV, Karthik KS, Maller US, et al. Drug and dental impression materials. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2012;4(Suppl 2): S316-318. [4]高传飞,张怀勤.口腔印模消毒的研究进展[J].口腔医学, 2013, 33(4):271-272.[5]Pal PK, Kamble SS, Chaurasia RR, et al. Evaluation of Different Disinfactants on Dimensional Accuracy and Surface Quality of Type IV Gypsum Casts Retrieved from Elastomeric Impression Materials. J Int Oral Health. 2014;6(3):77-81.[6]Johnson GH, Chellis KD, Gordon GE, etal. Dimensional stability and detail reproduction of irreversible hydrocolloid and elastomeric impressions disinfected by immersion. J Prosthet Dent. 1998;79(4):446-453.[7]Amin WM, Al-Ali MH, Al Tarawneh SK, et al. The effects of disinfectants on dimensional accuracy and surface quality of impression materials and gypsum casts. J Clin Med Res. 2009;1(2):81-89. [8]Taylor RL, Wright PS, Maryan C. Disinfection procedures: their effect on the dimensional accuracy and surface quality of irreversible hydrocolloid impression materials and gypsum casts. Dent Mater. 2002;18(2):103-110.[9]Kronström MH, Johnson GH, Hompesch RW. Accuracy of a new ring-opening metathesis elastomeric dental impression material with spray and immersion disinfection. J Prosthet Dent. 2010;103(1):23-30.[10]Suprono MS, Kattadiyil MT, Goodacre CJ, et al. Effect of disinfection on irreversible hydrocolloid and alternative impression materials and the resultant gypsum casts. J Prosthet Dent. 2012;108(4):250-258. [11]Ahmad S, Tredwin CJ, Nesbit M, et al. Effect of immersion disinfection with Perform-ID on alginate, an alginate alternative, an addition-cured silicone and resultant type III gypsum casts. Br Dent J. 2007;202(1):E1; discussion 36-37.[12]Samra RK, Bhide SV. Efficacy of different disinfectant systems on alginate and addition silicone impression materials of Indian and international origin: a comparative evaluation. J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2010;10(3):182-189. [13]Shambhu HS, Gujjari AK. A study on the effect on surface detail reproduction of alginate impressions disinfected with sodium hypochlorite and ultraviolet light - An In Vitro study. J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2010;10(1):41-47. [14]Amalan A, Ginjupalli K, Upadhya N. Evaluation of properties of irreversible hydrocolloid impression materials mixed with disinfectant liquids. Dent Res J (Isfahan). 2013;10(1):65-73.[15]Al-Jabrah O, Al-Shumailan Y, Al-Rashdan M. Antimicrobial effect of 4 disinfectants on alginate, polyether, and polyvinyl siloxane impression materials. Int J Prosthodont. 2007; 20(3): 299-307.[16]Giammanco GM, Melilli D, Rallo A, et al. Resistance to disinfection of a polymicrobial association contaminating the surface of elastomeric dental impressions. New Microbiol. 2009;32(2):167-172.[17]Parnia F, Hafezeqoran A, Moslehifard E, et al. Effect of Different Disinfectants on Staphylococcus aureus and Candida albicans Transferred to Alginate and Polyvinylsiloxane Impression Materials. J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects. 2009;3(4):122-125. [18]Hutchings ML, Vandewalle KS, Schwartz RS, et al. Immersion disinfection of irreversible hydrocolloid impressions in pH-adjusted sodium hypochlorite. Part 2: Effect on gypsum casts. Int J Prosthodont. 1996;9(3):223-229.[19]Jeyapalan V, Krishnan CS, Ramasubramanian H, et al. Comparative Evaluation of the Antimicrobial Efficacy of Three Immersion Chemical Disinfectants on Clinically Derived Poly(Vinyl Siloxane) Impressions. J Prosthodont. 2016. in press.[20]Kotsiomiti E, Tzialla A, Hatjivasiliou K. Accuracy and stability of impression materials subjected to chemical disinfection - a literature review. J Oral Rehabil. 2008;35(4):291-299.[21]Lad PP, Gurjar M, Gunda S, et al. The Effect of Disinfectants and a Surface Wetting Agent on the Wettability of Elastomeric Impression Materials: An In Vitro Study. J Int Oral Health. 2015; 7(6):80-83.[22]林红.口腔弹性印模材料及临床使用注意事项[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2009,7(2):391-394.[23]于洪丹,崔广,张爱军,等.两种不同藻酸盐印模消毒效果对比研究[J].中国美容医学,2013,22(1):190-191.[24]薛广波.传染病消毒技术规范[M].北京:中国质检出版, 2013: 29-40.[25]韩秀欣,张振庭,杨圣辉,等. 2%酸性戊二醛对藻酸盐印模浸泡消毒的效果评价[J].北京口腔医学,2009,17(4):199-202.[26]王利民,曾贤铭,曹谅,等.酸性氧化电位水流动浸泡法对藻酸盐印模的消毒效果[J].苏州大学学报,2010,30(3):510-512.[27]宋玉琦,毕良佳,石连仲,等.氧化电位水对口腔器械消毒效果的探讨[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2007,17(1):55-58.[28]王珍珍,逯宜,宋君,等.光栅投影技术及逆向工程在重建和测量牙颌数字化模型中的应用[J].华西口腔医学杂志, 2015,33(1): 71-74.[29]赵一姣,原福松,谢晓艳,等.牙颌模型激光扫描数据与锥形束CT数据配准方法的精度比较[J].中华口腔医学杂志, 2013,48(3): 173-176.[30]郝鹏,林红,孙志辉,等.消毒液浸泡消毒对藻酸盐印模尺寸稳定性影响的评价研究[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2009,23(1):45-48. |