Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (29): 4395-4401.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.29.020
Previous Articles Next Articles
Lisfranc injury in an athletic population: diagnostic and therapeutic strategies
Ru Jiang-ying1, Niu Yun-fei2
- 1Yangzhou No. 1 People’s Hospital, the Second Clinical School of Yangzhou University, Yangzhou 225000, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Changhai Hospital Affiliated to the Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 200433, China
-
Received:2016-04-12Online:2016-07-08Published:2016-07-08 -
Contact:Niu Yun-fei, M.D., Associate chief physician, Changhai Hospital Affiliated to the Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 200433, China -
About author:Ru Jiang-ying, M.D., Associate chief physician, Yangzhou No. 1 People’s Hospital, the Second Clinical School of Yangzhou University, Yangzhou 225000, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Yangzhou Scientific and Technological Foundation for Young Talents, China, No. YZ2014051
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ru Jiang-ying, Niu Yun-fei. Lisfranc injury in an athletic population: diagnostic and therapeutic strategies[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(29): 4395-4401.
share this article
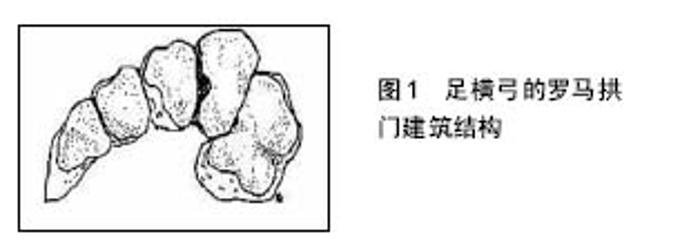
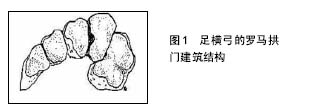
2.1 解剖学特点及损伤机制 2.1.1 解剖学特点 Lisfranc关节或跖跗关节复合体,由第1,2,3跖骨基底部与内、中、外楔骨之间和第4,5跖骨基底部与骰骨之间构成,呈S形,分为3柱。外侧柱由骰骨和第4,5跖骨之间的关节构成,中间柱由第2,3跖骨和中间、外侧楔骨的之间关节组成,内侧柱由内侧楔骨和第1跖骨构成[6]。跖骨、楔骨与骰骨所具有的独特的骨、韧带解剖结构,形成稳定的足纵弓与横弓。 横弓横截面显示其构造类似于具有潜在稳定性的罗马半圆形拱门建筑结构(图1)。而在足稳定的横弓复合体中,由第2跖骨基底部与中楔骨之间形成的关节扮演着中央基石的角色,楔形内、外侧楔骨则提供了强大的支撑作用[6-7]。Lisfranc韧带是跖跗关节复合体中强度最大的韧带(其测量高度和厚度分别为1.0 cm和0.5 cm),第2跖骨通过坚韧的Lisfranc韧带锚固于跖跗关节复合体中的内侧柱[7]。在骨与韧带结构的限制下,跖跗关节的活动弧较小,第1跖跗关节的背屈和跖屈分别约为4°和1°,而第2和3跖跗关节的活动弧较其更小[6]。中足的外侧柱(包括4和5跖跗关节)活动弧最大(约10°的背屈和跖屈范围),因此,它可代偿运动员中足损伤中存在的隐匿性不稳定。相比跖侧Lisfranc韧带而言,足背的Lisfranc韧带强度较薄弱。尸体生物力学结果显示,跖侧的Lisfranc韧带的强度是背侧Lisfranc韧带的3倍,因此增加了跖跗关节背侧脱位损伤的倾向性[6-7]。由于跖跗关节面接近垂直于地面,故站立期跖跗关节骨结构内在稳定性不足,而周围韧带组织对维持恰当力线与关节面接触显得至关重要[7]。"
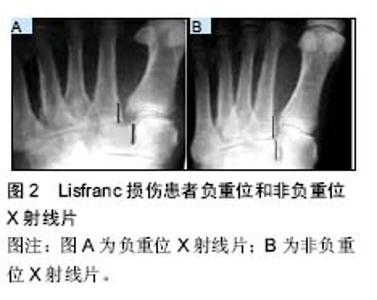
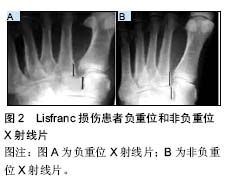
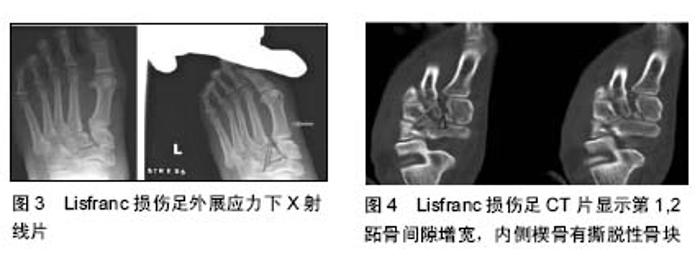
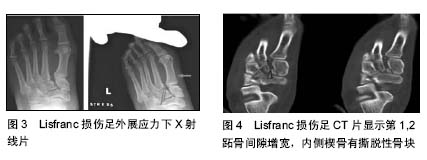
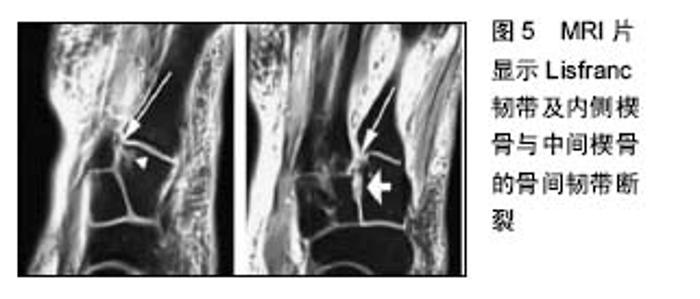
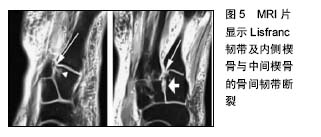
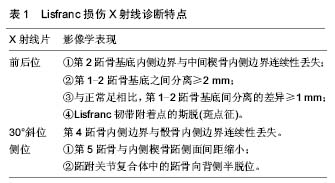
2.1.2 损伤机制 运动员Lisfranc损伤大致可分为2类,即跖屈位损伤和外展位损伤[8-9]。在跖趾关节背屈位下,轴向负荷作用于跖屈的足踝部,导致跖跗关节的背侧韧带损伤,在身体的旋转外力作用下发生中足跖跗关节半脱位或脱位的跖屈性损伤。此类损伤常见于足球远动员中的线锋球员,是截锋球员在阻截过程中摔倒在线锋球员的后跟上所致[8]。外展性损伤是前足相对于固定的后足骤然外展所致,此类损伤常见于后跟相对固定的运动比赛,如马术、冲浪等。实际上,运动员的Lisfranc损伤是由多种应力的联合作用导致,许多损伤类型并不能由这2种机制简单予以归类[9]。 2.2 临床表现与影像学诊断 2.2.1 临床表现 运动员Lisfranc损伤多为隐匿性或低能量损伤,如出现中足跖跗部位不同程度的肿胀、背侧触痛、跖侧淤斑、负重位及下楼梯时出现疼痛症状和“琴键征”,都是有价值的高度怀疑Lisfranc损伤的诊断线索[10]。Shapiro等[4]推荐了2种诊断运动员Lisfranc损伤的激发性试验方法,一种是中足加压试验,另一种是将第1跖骨头相对于第2跖骨头的跖屈和背屈活动试验。Myerson等[5]提醒通过第1跖骨在矢状面上的触痛试验来诊断Lisfranc损伤可能出现假阴性结果。他建议另一种临床试验方法,即通过对第1,2跖骨在冠状面上的纵向加压作用于内侧和中间柱的基底部,如出现疼痛或触及弹跳感可提示发生Lisfranc损伤。在临床检查中应注意整个足踝部的检查,以发现相关联的骨折或韧带损伤后作出相应的治疗。 2.2.2 影像学诊断 当怀疑有Lisfranc复合体损伤时,最有价值的检查便是首先考虑拍摄负重下前后位(图2)、30°斜位X射线和侧位X射线(表1)。 拍摄足外展应力下X射线片(图3)对于鉴别动力性不稳定具有重要作用。传统的方法是在使足保持旋前、外展位下辅助内柱和中柱间的挤压试验,则可鉴别中足是否存在不稳定性。由于检查者的施力差异和缺乏统一的阳性结果标准,应力下的X射线片检查受到质疑[11-12]。还有学者提出,针对部分患者在门诊检查时顺从性差,可考虑在镇静或麻醉作用下施于应力下的X射线片检查,但增加了评估风险及花费[13-14]。另外,应力下的X射线片检查在术中评估Lisfranc关节复位或固定是否充分时也发挥一定的指导作用。"
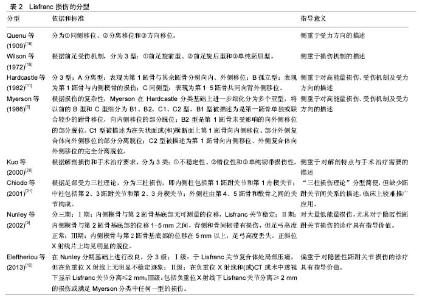
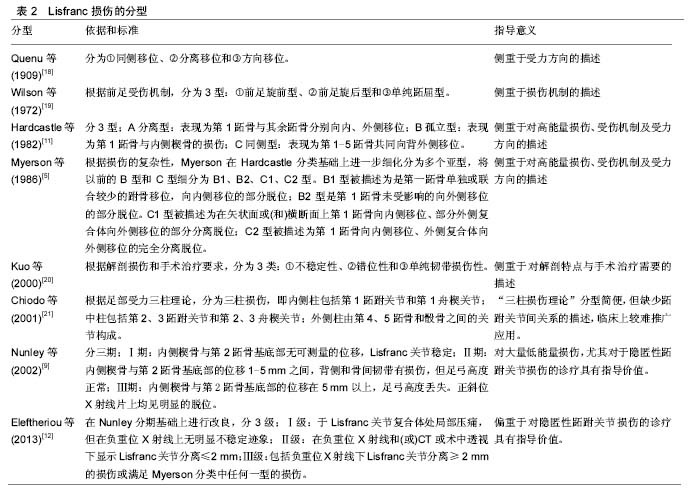
| [1] Garrick JG,Requa RK.The epidemiology of foot and ankle injuries in sports. Clin Sports Med.1988;7(1): 29-36. [2] Meyer SA,Callaghan JJ, Albright JP, et al.Midfoot sprains in collegiate football players. Am J Sports Med.1994;22(3):392-401. [3] Myerson MS,Cerrato RA.Current management of tarsometatarsal injuries in the athlete. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2008;90(11):2522-2533. [4] Shapiro MS,Wascher DC,Finerman GA.Rupture of Lisfranc’s ligament in athletes.Am J Sports Med. 1994;22(5):687-691. [5] Myerson MS,Fisher RT,Burgess AR,et al.Fracture dislocations of the tarsometatarsal joints: end results correlated with pathology and treatment. Foot Ankle. 1986;6(5):225-242. [6] Curtis MJ,Myerson M,Szura B.Tarsometatarsal joint injuries in the athlete. Am J Sports Med.1993;21(4): 497-502. [7] Solan MC,Moorman CT 3rd,Miyamoto RG,et al. Ligamentous restraints of the second tarsometatarsal joint: a biomechanical evaluation.Foot Ankle Int 2001; 22(8):637-641. [8] Mantas JP,Burks RT.Lisfranc injuries in the athlete.Clin Sports Med 1994;13(4):719-730. [9] Nunley JA, Vertullo CJ.Classification, investigation, and management of midfoot sprains: Lisfranc injuries in the athlete.Am J Sports Med. 2002;30(6):871-878. [10] DeOrio M,Erickson M,Usuelli FG,et al.Lisfranc injuries in sport.Foot Ankle Clin 2009;14(2):169-186. [11] Hardcastle PH,Reschauer R,Kutscha-Lissberg E,et al.Injuries to the tarsometatarsal joint. Incidence, classification and treatment.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1982;64(3):349-356. [12] Eleftheriou KI,Rosenfeld PF.Lisfranc injury in the athlete: evidence supporting management from sprain to fracture dislocation. Foot Ankle Clin 2013;18(2): 219-236. [13] Coss HS, Manos RE, Buoncristiani A, et al.Abduction stress and AP weight bearing radiography of purely ligamentous injury in the tarsometatarsal joint.Foot Ankle Int.1998;19(8):537-541. [14] Raikin SM, Elias I, Dheer S, et al.Prediction of midfoot instability in the subtle Lisfranc injury. Comparison of magnetic resonance imaging with intraoperative findings.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2009;91(4):892-899. [15] Lattermann C, Goldstein JL, Wukich DK, et al.Practical management of Lisfranc injuries in athletes. Clin J Sport Med.2007;17(4):311-315. [16] Ceroni D, De Rosa V, De Coulon G, et al.The importance of proper shoe gear and safety stirrups in the prevention of equestrian foot injuries. J Foot Ankle Surg.2007;46(1):32-39. [17] Hsu JC, Chang JH, Wang SJ, et al.The nutcracker fracture of the cuboid in children:a case report. Foot Ankle Int.2004;25(6):423-425. [18] Quenu E,Kuss G.Etude sur les luxations du metatarse (luxations metatarso-tarsiennes)du diastasis entre le 1er et le 2e metatarsien.Rev Chir 1909;39:281-336, 720-791,1093-1134. [19] Wilson DW.Injuries of the tarso-metatarsal joints.Etiology,classification and results of treatment.J Bone and Joint Surg(Br).1972;54(4):677-686. [20] Kuo RS,Tejwani NC,Digiovanni CW,et al.Outcome after open reduction and internal fixation of Lisfranc joint injuries.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82-A(11): 1609-1618. [21] Chiodo CP,Myerson MS.Developments and advances in the diagnosis and treatment of injuries to the tarsometatarsal joint. Orthop Clin North Am.2001; 32(1):11-20. [22] Teng AL,Pinzur MS,Lomasney L,et al.Functional outcome following anatomic restoration of tarsal-metatarsal fracture dislocation. Foot Ankle Int 2002;23(10):922-926. [23] Lee CA,Birkedal JP,Dickerson EA,et al.Stabilization of Lisfranc joint injuries: abiomechanical study. Foot Ankle Int.2004;25(5):365-370. [24] [Mulier T, Reynders P, Sioen W, et al.The treatment of Lisfranc injuries. Acta Orthop Belg.1997;63(2):82-90. [25] Richter M,Wippermann B,Krettek C,et al.Fractures and fracture dislocations of the midfoot: occurrence, causes and long-term results.Foot Ankle Int.2001; 22(5):392-398. [26] Purushothaman B,Robinson E,Lakshmanan P,et al. Extra-articular fixation for treatment of Lisfranc injury. Surg Technol Int.2010;19:199-202. [27] Coetzee JC.Making sense of Lisfranc injuries. Foot Ankle Clin 2008;13(4):695-704. [28] Stern RE,Assal M.Dorsal multiple plating without routine transarticular screws for fixation of Lisfranc injury. Orthopedics.2014;37(12):815-819. [29] Alberta FG,Aronow MS,Barrero M,et al.Ligamentous Lisfranc joint injuries: abiomechanical comparison of dorsal plate and transarticular screw fixation.Foot Ankle Int.2005;26(6):462-473. [30] Hu SJ, Chang SM, Li XH, et al. Outcome comparison of Lisfranc injuries treated through dorsal plate fixation versus screw fixation. Acta Ortop Bras 2014;22(6): 315-320. [31] Stavlas P,Roberts CS,Xypnitos FN,et al.The role of reduction and internal fixation of Lisfranc fracture-dislocations: a systematic review of the literature. Int Orthop.2010;34(8):1083-1091. [32] Brin YS,Nyska M,Kish B.Lisfranc injury repair with the TightRope device: a short-term case series.Foot Ankle Int.2010;31(7):624-627. [33] Panchbhavi VK,Vallurupalli S,Yang J,et al.Screw fixation compared with suturebutton fixation of isolated Lisfranc ligament injuries. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2009; 91(5):1143-1148. [34] Pelt CE,Bachus KN,Vance RE,et al.A biomechanical analysis of a tensioned suture device in the fixation of the ligamentous Lisfranc injury.Foot Ankle Int 2011; 32(4):422-431. [35] Thordarson DB,Hurvitz G.PLA screw fixation of Lisfranc injuries.Foot Ankle Int.2002;23(11): 1003-1007. [36] Ly TV,Coetzee JC.Treatment of primarily ligamentous Lisfranc joint injuries: primary arthrodesis compared with open reduction and internal fixation. A prospective, randomized study.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2006;88(3): 514-520. [37] Henning JA,Jones CB,Sietsema DL,et al.Open reduction internal fixation versus primary arthrodesis for Lisfranc injuries: a prospective randomized study. Foot Ankle Int.2009;30(10):913-922. [38] Filippi J, Myerson MS, Scioli MW, et al. Midfoot arthrodesis following multi-jointstabilization with a novel hybrid plating system.Foot Ankle Int. 2012; 33(3):220-225. [39] Reinhardt KR,Oh LS,Schottel P,et al.Treatment of Lisfranc fracture-dislocations with primary partial arthrodesis. Foot Ankle Int.2012;33(1):50-56. [40] Wagner E,Ortiz C,Villalon IE,et al.Early weight-bearing after percutaneous reduction and screw fixation for low-energy Lisfranc injury.Foot Ankle Int 2013;34(7): 978-983. [41] Schepers T,Oprel PP,Van Lieshout EM.Influence of approach and implant onreduction accuracy and stability in Lisfranc fracture-dislocation at the tarsometatarsal joint. Foot Ankle Int 2013;34(5): 705-710. [42] Vertullo CJ,Nunley JA.Participation in sports after arthrodesis of the foot or ankle.Foot Ankle Int.2002; 23(7):625-628. [43] Philbin T,Rosenberg G,Sferra JJ.Complications of missed or untreated Lisfranc injuries. Foot Ankle Clin.2003;8(1):61-71. |
| [1] | Dong Qizheng. Effect of kinesio taping on delayed onset muscle soreness in athletes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(3): 367-371. |
| [2] | Liang Maohua, Mao Keya, Xia Bo, Liu Qiang,Tang Peifu, Wang Jifang. Osteogenic property of beta-tricalcium phosphate/alpha-calcium sulphate hemihydrate combined bone graft in multi-segment posterolateral arthrodesis of rabbit thoracic vertebrae [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(22): 3500-3505. |
| [3] | Liang Maohua, Mao Keya, Xia Bo, Liu Qiang, Tang Peifu, Wang Jifang. Application of beta-tricalcium phosphate/alpha-calcium sulfate hemihydrate combined bone grafts in multi-segment arthrodesis of spine: micro-CT evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(18): 2800-2805. |
| [4] | Xu Jun, Xie Lin. Artificial ankle arthroplasty versus ankle joint fusion for traumatic ankle arthritis: efficacy and safety [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(3): 368-373. |
| [5] | Chen Zhen-yong. Correlation of bone mineral density with sports ability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(28): 4452-4456. |
| [6] | Chen Wei1, Li Jiang-hua2, Gu Jian-ren1, Chen Feng1, Xia Hua1, Zhang Bin1, Jiao Qi-bin1, Zheng Feng3. Nicotinamide N-methyl transferase gene polymorphism and its correlation with the athletic ability of handball players [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(28): 4544-4549. |
| [7] | Mi Si-qi1, Qian Li2. Muscle strength parameters of single joint or joint chain under different motion modes and angular velocities by isokinetic muscle test [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(24): 3798-3800. |
| [8] |
Fu Tao, Wu Peng, Zhao Lin-liang, Cheng Ji.
Graft healing and functional recovery after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a case study of rehabilitation training
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(2): 281-287.
|
| [9] | Yang Xue-qing, Cheng Liang. Isokinetic strength of the trunk and lower limbs in basketball players [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(12): 1835-1840. |
| [10] | Ju Xiu-kui. Isokinetic muscle strength characteristics of the main joints in juvenile male gymnasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(46): 6922-6929. |
| [11] | Chen Pei-jin, Mayinuer Maimaitiming, Hou Xia, Zhang Ai-hong, Liu Chun-hong. High frequency ultrasonic imaging of the dorsal Lisfranc ligament in the adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(24): 3609-3614. |
| [12] | Song Ai-jing, Deng Jing-jie, Lv Xiao-hong, Zhang Yuan. Isokinetic muscle strength characteristics of the knee, ankle and trunk [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(46): 7425-7429. |
| [13] | Xiao Bing, Ye Zhan-hong, Pang Jie. Biomechanical characteristics of waist flexor and extensor muscles in outstanding juvenile male basketball athletes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(24): 3889-3893. |
| [14] | Yang Ruo-yu, Wang Yu-bin, Shen Xun-zhang, Cai Guang . Association of elite athlete performance and gene polymorphisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(7): 1121-1128. |
| [15] | Lou Yan-tao. Distribution of joint isokinetic muscle strength in shot putters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(29): 4647-4652. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||