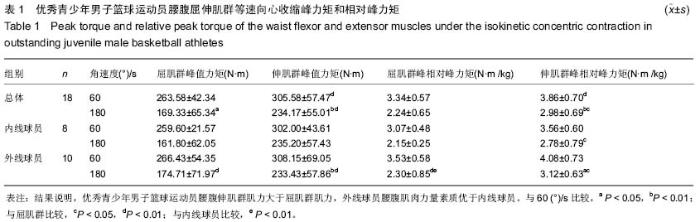
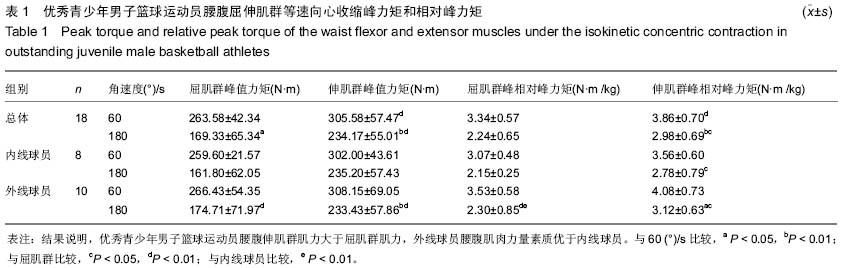
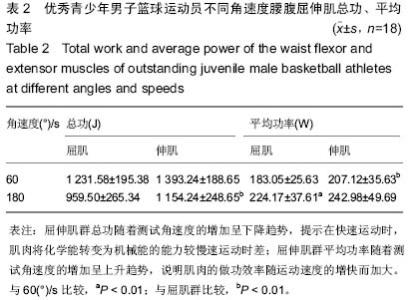
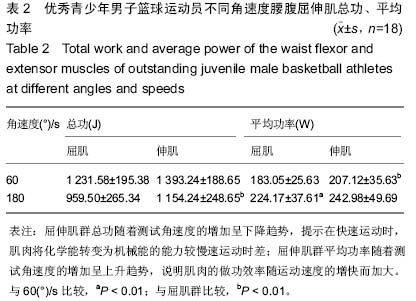
| [1] Vern Gambetta.Athletic development:The Art﹠Science of Functional Sports Conditioning.Human Kinetics.2006; 12: 280-285.
[2] 王建玲.我国优秀男子篮球运动员运动损伤调查研究[J].成都体育学院学报,2012,38(9):52-54.
[3] 温爱玲,游永豪,周多伟.篮球运动员运动损伤与预防的调查研究[J].淮南师范学院学报,2014,16(3):79-82.
[4] 吴毅,占飞.等速肌力测试和训练技术在运动医学中的运用[J].中国运动医学杂志,2002,21(1):81-84.
[5] 纪之光,庄洁,黄亮.不同速度下膝关节等速肌力和自然步速下步态的时空参数比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(7): 1027-1032.
[6] 娄彦涛.铅球运动员主要关节等速肌力配布特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(29):4647-4652.
[7] 董仁卫,郭琪,刘诗琦,等.等速肌力测试和训练技术在脑卒中偏瘫患者临床康复中的应用[J].中国康复医学杂志,2015,30(2): 207-210.
[8] 刘辉,刘波,伍萨,等.踝关节不稳患者踝关节等速肌力和动态平衡能力的临床研究[J]. 中医正骨,2015,27(2):7-11.
[9] 岳建军.不同级别竞技健美操运动员髋、膝和踝关节等速肌力特征研究[J].中国体育科技,2014,50(6):59-66.
[10] 夏晴,高东,黄婷婷,等.等速肌力检测在辨别伪肢体瘫中的应用[J].法医学杂志,2014,30(6):427-430.
[11] 张丽艳,李光欣.我国优秀男子自由式摔跤运动员膝、踝关节肌力矩峰值的特征[J].体育学刊,2013,20(4):129-133.
[12] 卢澎涛.优秀男子游泳运动员肩关节等速肌力特征分析[J].成都体育学院学报,2014,30(12):58-62.
[13] 汪洋,王雁,衣龙燕,等.我国优秀男子花剑运动员下肢等速肌力测试分析[J].中国体育科技,2013,49(6):66-69.
[14] 陈玉霞.优秀男子手枪运动员上肢关节屈伸肌群等速肌力测试研究[J].福建体育科技,2012,31(1):30-32.
[15] 殷翔.我国优秀男子自由跤运动员腰背部等速肌力测试分析[J].山东体育科技,2014,36(6):76-80.
[16] 刘夏,王惠娟,吴红瑛,等.腰背核心肌群在等速旋转运动中力矩和表面肌电的特征[J]. 中国康复医学杂志,2013,28(4):315-318.
[17] 熊维志.优秀男子举重运动员腰背、膝关节等速肌力与专项成绩的相关性研究[J].成都体育学院学报,2013,39(4):57-62.
[18] 成鹏,黄杰,仇瑶琴,等.躯干等速肌力测试重测信度研究[J].中国康复医学杂志,2006,21(1):50-52.
[19] Karatas,GK,GOGUS F,Meray J.Reliability of isokinetic trunk muscle strength measurement.Am J Phys Med Rehabil.2002; 81(2):79-85.
[20] Rochcongar P.Ioskinetic thigh muscle sterngth in soprts.Ann Readapt Med Phys.2004;47(6):274.
[21] Suedder GN. Torgue curves produed at the knee during isometric and isokinetic exereise.Areh Phys Med Rehabil . 1980; 61(2): 68-73.
[22] 路泽全.我国优秀青年男子篮球运动员力量素质研究[D].苏州大学,2008.
[23] 何强.我国优秀女子摔跤运动员腰背肌力特征研究[J].西安体育学院学报,2013,30(6):731-736.
[24] Abernethy PJ,Howard A,Quigley BM.Isokinetic torque and instantaneous power date do not necessarily mirror one another.Journal of Strengh and Conditioning Research.1996; 10:220-223.
[25] 张德辉,黄昌林,刘鼎成,等.青年下背痛患者躯干肌及腰椎曲度的临床研究[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2003,29(4):289-291.
[26] Haake M,Muller HH,Schade-Brittinger C,et al. The German multicenter, randomized,partially blinded, prospective trial of acupuncture for chronic low back pain: a preliminary report on the rationale and design of the trial. J Altern Complement Med, 2003;9(5):763-770.
[27] 吴伟峰,糜迅.等速肌力测试和训练技术在我国康复医学领域应用现状[J].中国伤残医学,2014,22(9):45-46.
[28] Ripamonti M,Colin D,Rahmani A.Torque-velocity and power-velocity relationships during isokinetic trunk flexion and extension.Clin Biomech.2008;23(5):520-526.
[29] Davies GJ.A compendium of isokinetics in clinical usage and rehabilitation techniques.4th Ed Wisconsin USA S&S Publishers.1992:35-47.
[30] Dvir Z,Keating J.Reproducibility and validity of a new test protocol for measuring isokinetic trunk extension strength,Clin Biomech Bristol,AvoⅡ1.2001;16(7):627-630.
[31] Comb s R,Garbutt G.Developments in the use of the ham-string/quadriceps ratio for the assessment of muscle balance.J Sports Science Med.2002:1(1):56.
[32] Lee JH,Hoshino Y, Nakamura K,et al.Trunk muscle weakness as a risk factor for low back pain.A 5-year prospective study. Spine.1999;24(1):54-57.
[33] 田麦久,刘大庆.运动训练学[M].北京:人民体育出版社, 2012: 280-286. |