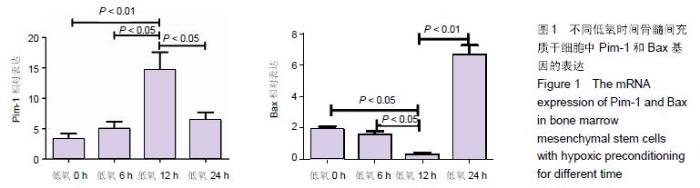
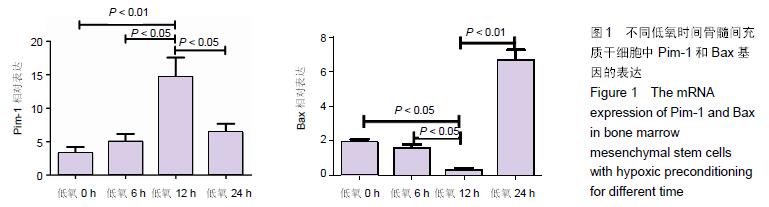
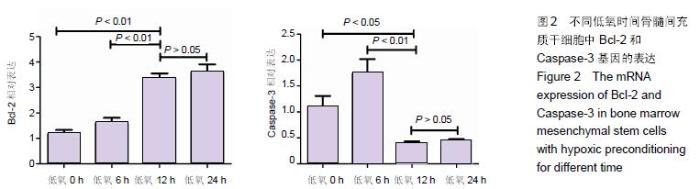
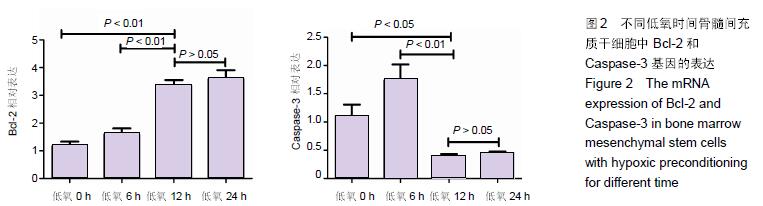
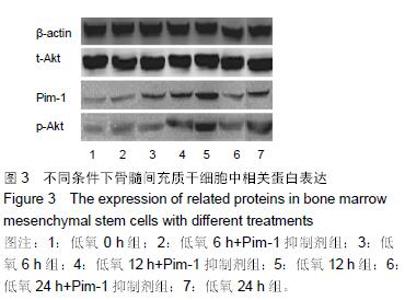
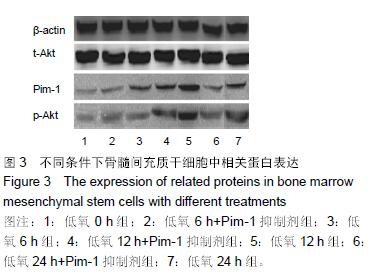
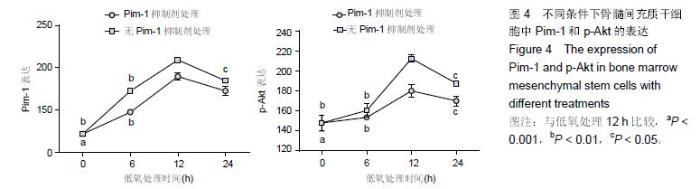
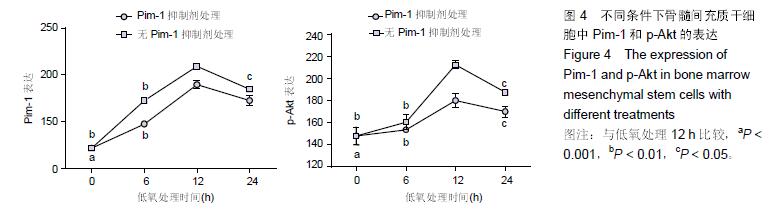
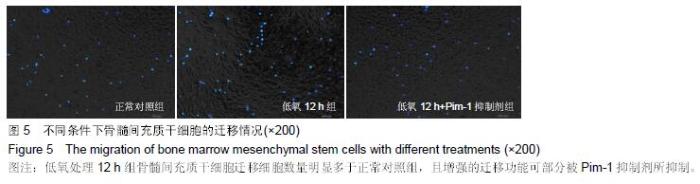
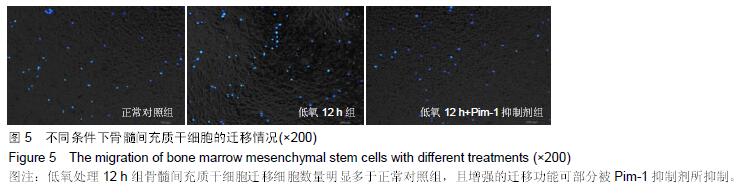
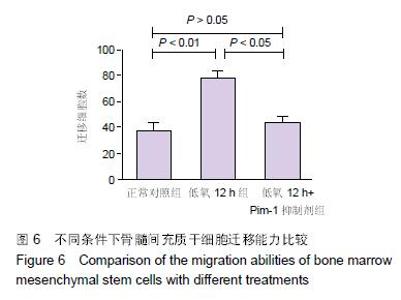
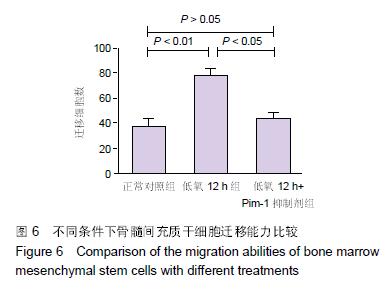
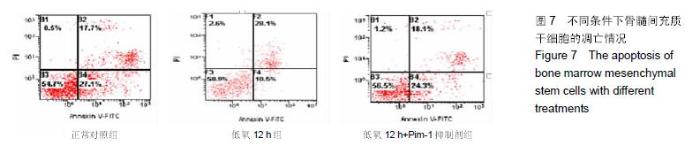
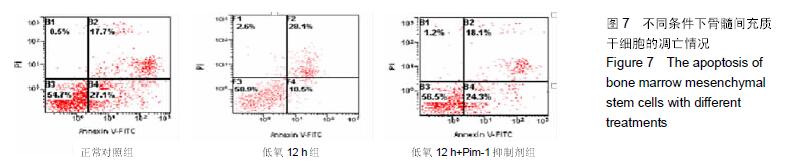
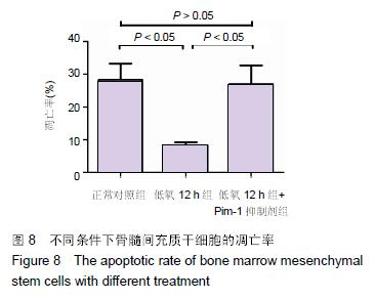
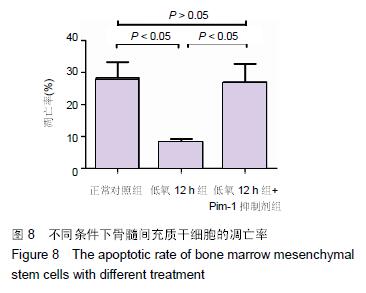
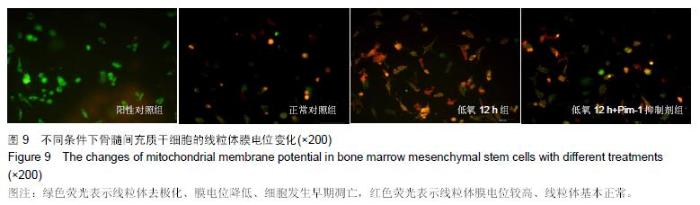
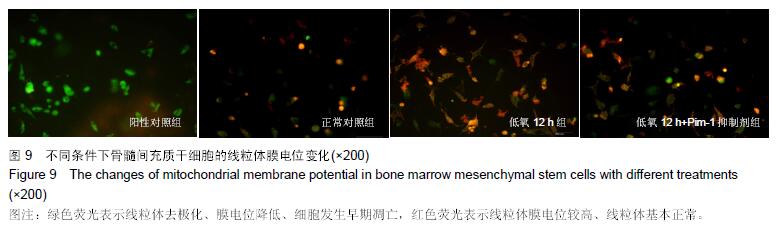
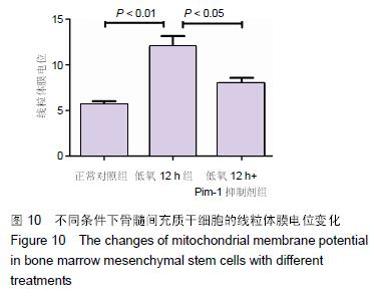
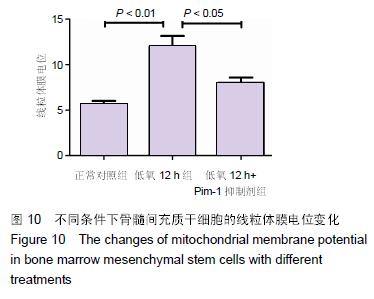
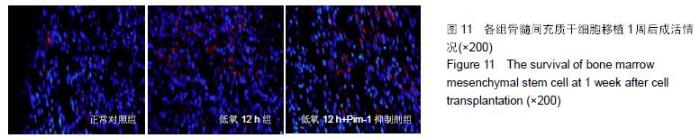
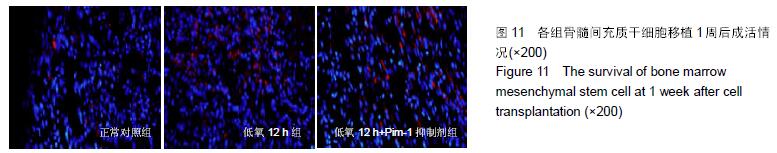
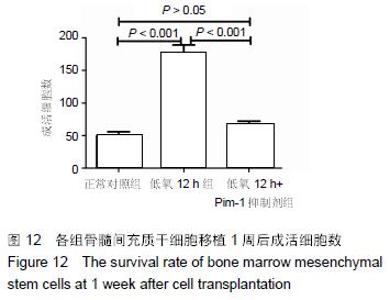
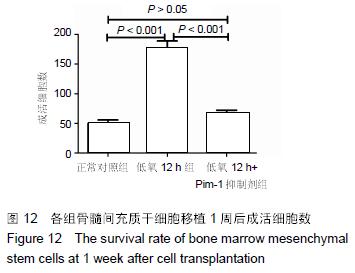
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (14): 1989-1998.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.14.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
Hypoxic preconditioning inhibits apoptosis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells through overexpressing Pim-1
Zhang You1, Yan Wei-ya2, Shen Zheng-ya2, Yang Jun-jie3, Hui Jie1
- 1Department of Cardiology, 2Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215000, Jiangsu Province, China; 3Institute of Cardiovascular Disease, Soochow University, Suzhou 215000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2016-02-08Online:2016-04-01Published:2016-04-01 -
Contact:惠杰,教授,博士生导师,苏州大学附属第一医院心内科,江苏省苏州市 215000 并列通讯作者:杨君杰,博士,副教授,苏州大学心血管病研究所,江苏省苏州市 215000 -
About author:Zhang You, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Cardiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215000, Jiangsu Province, China Yan Wei-ya, Master, Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215000, Jiangsu Province, China Zhaog You and Yan Wei-ya contributed to equally this work.
Cite this article
Zhang You, Yan Wei-ya, Shen Zheng-ya, Yang Jun-jie, Hui Jie. Hypoxic preconditioning inhibits apoptosis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells through overexpressing Pim-1[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(14): 1989-1998.
share this article
| [1] Available at: http:// www.who.int/healthinfo/global_ burden_disease/estimates/en/index1.html (accessed 16 Feb 2015). World Health Organization. Global Health Estimates. 2014 Summary tables: Deaths by cause, age and sex, by WHO region, 2000–2012, 2014. Available at: http:// www.who.int/healthinfo/global_ burden_disease/estimates/en/index1.html (accessed 16 Feb 2015). [2] Lloyd-Jones D, Adams RJ, Brown TM, et al. Executive summary: heart disease and stroke statistics--2010 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2010;121(7):948-954. [3] Task Force on the management of ST-segment elevation acute myocardial infarction of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC), Steg PG, James SK, et al. ESC Guidelines for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation.Eur Heart J. 2012;33(20):2569-2619. [4] O'Gara PT, Kushner FG, Ascheim DD, et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of ST-elevation myocardial infarction: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2013;127(4):e362-425. [5] Nair V, Madan H, Sofat S, et al. Efficacy of stem cell in improvement of left ventricular function in acute myocardial infarction--MI3 Trial. Indian J Med Res. 2015;142(2):165-174. [6] Schächinger V, Dimmeler S, Zeiher AM. Stem cells after myocardial infarction. Herz. 2006;31(2):127-136. [7] Lemarchand P. Cell therapy for acute myocardial infarction. Transfus Clin Biol. 2009;16(2):146-147. [8] Siu CW, Liao SY, Liu Y, et al. Stem cells for myocardial repair.Thromb Haemost. 2010;104(1):6-12. [9] Joggerst SJ, Hatzopoulos AK. Stem cell therapy for cardiac repair: benefits and barriers. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2009;11:e20. [10] Shiota M, Heike T, Haruyama M, et al. Isolation and characterization of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal progenitor cells with myogenic and neuronal properties. Exp Cell Res. 2007;313(5): 1008-1023. [11] Miyahara Y, Nagaya N, Kataoka M, et al. Monolayered mesenchymal stem cells repair scarred myocardium after myocardial infarction. Nat Med. 2006;12(4): 459-465. [12] Schächinger V, Erbs S, Elsässer A, et al. Intracoronary bone marrow-derived progenitor cells in acute myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(12): 1210-1221. [13] Bachmann M, Möröy T. The serine/threonine kinase Pim-1. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005;37(4):726-730. [14] Wang Z, Bhattacharya N, Weaver M, et al. Pim-1: a serine/threonine kinase with a role in cell survival, proliferation, differentiation and tumorigenesis. J Vet Sci. 2001;2(3):167-179. [15] Borillo GA, Mason M, Quijada P, et al. Pim-1 kinase protects mitochondrial integrity in cardiomyocytes. Circ Res. 2010;106(7):1265-1274. [16] Muraski JA, Rota M, Misao Y, et al. Pim-1 regulates cardiomyocyte survival downstream of Akt.Nat Med. 2007;13(12):1467-1475. [17] Gao Y, Li T, Wu C, et al. Pim-1 mediated signaling during the process of cardiac remodeling following myocardial infarction in ovine hearts. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2013;63:89-97. [18] Chen J, Kobayashi M, Darmanin S, et al. Hypoxia-mediated up-regulation of Pim-1 contributes to solid tumor formation. Am J Pathol. 2009;175(1): 400-411. [19] Hu S, Yan G, Xu H, et al. Hypoxic preconditioning increases survival of cardiac progenitor cells via the pim-1 kinase-mediated anti-apoptotic effect. Circ J. 2014;78(3):724-731. [20] Polisetti N, Chaitanya VG, Babu PP, et al. Isolation, characterization and differentiation potential of rat bone marrow stromal cells. Neurol India. 2010;58(2): 201-208. [21] Piao H, Youn TJ, Kwon JS, et al. Effects of bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells transplantation in acutely infarcting myocardium. Eur J Heart Fail. 2005;7(5):730-738. [22] Qu Z, Balkir L, van Deutekom JC, et al. Development of approaches to improve cell survival in myoblast transfer therapy. J Cell Biol. 1998;142(5):1257-1267. [23] Liu J, Hao H, Huang H, et al. Hypoxia regulates the therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells through enhanced autophagy. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2015;14(1):63-72. [24] Muraski JA, Fischer KM, Wu W, et al. Pim-1 kinase antagonizes aspects of myocardial hypertrophy and compensation to pathological pressure overload. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(37):13889- 13894. [25] Condorelli G, Drusco A, Stassi G, et al. Akt induces enhanced myocardial contractility and cell size in vivo in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002; 99(19):12333-12338. [26] Sussman M."AKT"ing lessons for stem cells: regulation of cardiac myocyte and progenitor cell proliferation. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2007;17(7):235-240. [27] Quijada P, Toko H, Fischer KM, et al. Preservation of myocardial structure is enhanced by pim-1 engineering of bone marrow cells. Circ Res. 2012;111(1):77-86. [28] Fischer KM, Cottage CT, Konstandin MH, et al. Pim-1 kinase inhibits pathological injury by promoting cardioprotective signaling. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2011; 51(4):554-558. [29] Zhao Y, Hu J, Buckingham B, et al. Pim-1 kinase cooperates with serum signals supporting mesenchymal stem cell propagation. Cells Tissues Organs. 2014;199(2-3):140-149. [30] Landes T, Martinou JC. Mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization during apoptosis: the role of mitochondrial fission. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011; 1813(4):540-545. [31] Sussman MA. Mitochondrial integrity: preservation through Akt/Pim-1 kinase signaling in the cardiomyocyte. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2009; 7(8):929-938. [32] Gustafsson AB, Gottlieb RA. Bcl-2 family members and apoptosis, taken to heart. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007;292(1):C45-51. [33] Hammerman PS, Fox CJ, Birnbaum MJ, et al. Pim and Akt oncogenes are independent regulators of hematopoietic cell growth and survival.Blood. 2005; 105(11):4477-4483. [34] Aho TL, Sandholm J, Peltola KJ, et al. Pim-1 kinase promotes inactivation of the pro-apoptotic Bad protein by phosphorylating it on the Ser112 gatekeeper site. FEBS Lett. 2004;571(1-3):43-49. [35] Macdonald A, Campbell DG, Toth R, et al. Pim kinases phosphorylate multiple sites on Bad and promote 14-3-3 binding and dissociation from Bcl-XL. BMC Cell Biol. 2006;7:1. [36] Datta SR, Katsov A, Hu L, et al. 14-3-3 proteins and survival kinases cooperate to inactivate BAD by BH3 domain phosphorylation. Mol Cell. 2000;6(1):41-51. [37] Murphy KM, Ranganathan V, Farnsworth ML, et al. Bcl-2 inhibits Bax translocation from cytosol to mitochondria during drug-induced apoptosis of human tumor cells. Cell Death Differ. 2000;7(1):102-111. [38] Ahmad N, Wang Y, Haider KH, et al. Cardiac protection by mitoKATP channels is dependent on Akt translocation from cytosol to mitochondria during late preconditioning. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006; 290(6):H2402-2408. [39] Javadov S, Karmazyn M. Mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening as an endpoint to initiate cell death and as a putative target for cardioprotection. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2007;20(1-4):1-22. [40] Fischer KM, Cottage CT, Wu W, et al. Enhancement of myocardial regeneration through genetic engineering of cardiac progenitor cells expressing Pim-1 kinase. Circulation. 2009;120(21):2077-2087. [41] Muraski JA, Fischer KM, Wu W, et al. Pim-1 kinase antagonizes aspects of myocardial hypertrophy and compensation to pathological pressure overload. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(37):13889-13894. [42] Nutt LK, Pataer A, Pahler J, et al. Bax and Bak promote apoptosis by modulating endoplasmic reticular and mitochondrial Ca2+ stores. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(11):9219-9225. [43] Wang M, Ruan Y, Chen Q, et al. Curcumin induced HepG2 cell apoptosis-associated mitochondrial membrane potential and intracellular free Ca(2+) concentration. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011;650(1):41-47. [44] Din S, Mason M, Völkers M, et al. Pim-1 preserves mitochondrial morphology by inhibiting dynamin- related protein 1 translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(15):5969-5974. [45] Hu X, Wei L, Taylor TM, et al. Hypoxic preconditioning enhances bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell migration via Kv2.1 channel and FAK activation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011;301(2):C362-372. [46] Vertelov G, Kharazi L, Muralidhar MG, et al. High targeted migration of human mesenchymal stem cells grown in hypoxia is associated with enhanced activation of RhoA. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013;4(1):5. [47] Raheja LF, Genetos DC, Wong A, et al. Hypoxic regulation of mesenchymal stem cell migration: the role of RhoA and HIF-1α. Cell Biol Int. 2011;35(10): 981-989. [48] Cerrada I, Ruiz-Saurí A, Carrero R, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha contributes to cardiac healing in mesenchymal stem cells-mediated cardiac repair. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(3):501-511. [49] Saller MM, Prall WC, Docheva D, et al. Increased stemness and migration of human mesenchymal stem cells in hypoxia is associated with altered integrin expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012; 423(2):379-385. [50] Liu X, Duan B, Cheng Z, et al. SDF-1/CXCR4 axis modulates bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell apoptosis, migration and cytokine secretion.Protein Cell. 2011;2(10):845-854.
|
| [1] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [2] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [5] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [6] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [7] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [8] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [9] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [10] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [11] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [12] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [13] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [14] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [15] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||