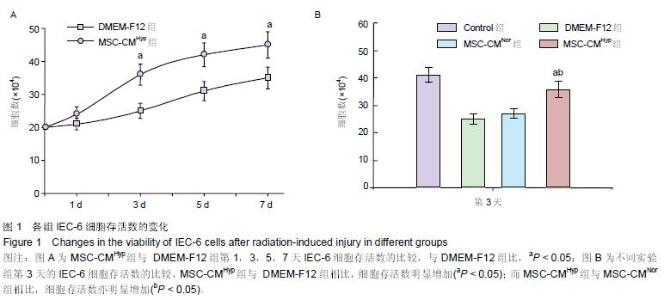
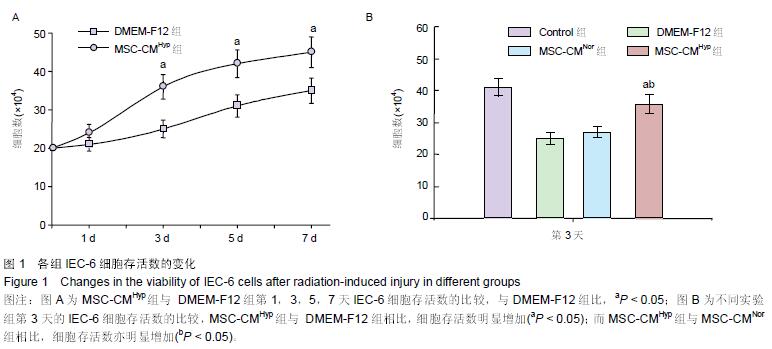
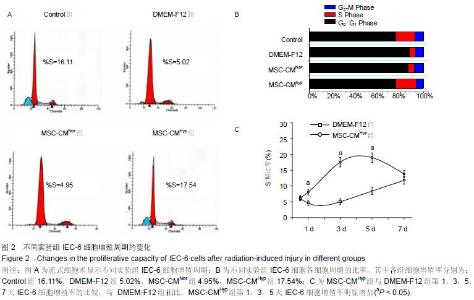
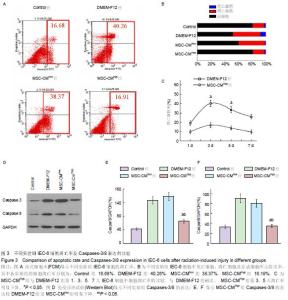
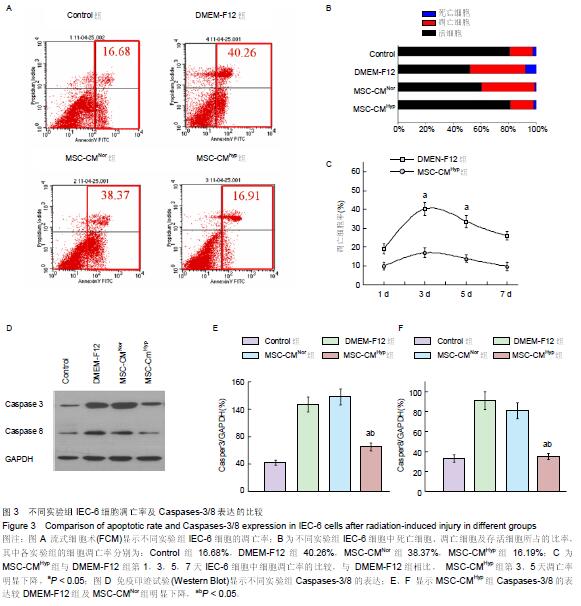
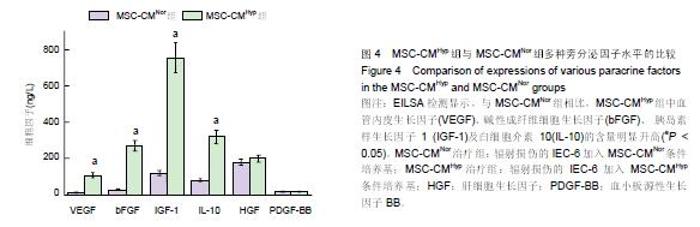
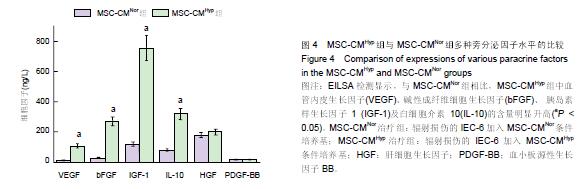
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (45): 7230-7236.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.45.003
Previous Articles Next Articles
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium with hypoxic activation enhances its effects on radiation-induced intestinal epithelial cell injury in vitro
Zheng Yuei, Chen Hao, Sha Wei-hong, Wang Qi-yi, Liu Wan-wei
- Department of Gastroenterology, Guangdong General Hospital and Guangdong Academy of Medical Science, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2015-09-23Online:2015-11-05Published:2015-11-05 -
Contact:Liu Wan-wei, Associate chief physician, Department of Gastroenterology, Guangdong General Hospital and Guangdong Academy of Medical Science, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Zheng Yue, Attending physician, Department of Gastroenterology, Guangdong General Hospital and Guangdong Academy of Medical Science, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China Chen Hao, M.D., Department of Gastroenterology, Guangdong General Hospital and Guangdong Academy of Medical Science, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China Zheng Yue and Chen Hao contributed equally to this work. -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81300279; China Postdoctoral Science Foundation, No. 2012M521579; the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, No. S2013040013549; the Medical Science Research Foundation of Guangdong Province, No. A2014020; the Scientific Plan Project of Guangdong Province, No. 2015A020212029
Cite this article
Zheng Yuei, Chen Hao, Sha Wei-hong, Wang Qi-yi, Liu Wan-wei. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium with hypoxic activation enhances its effects on radiation-induced intestinal epithelial cell injury in vitro[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(45): 7230-7236.
share this article
|
[1] Zhang J, Gong JF, Zhang W, et al. Effects of transplanted bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on their radiated intestine of mice. J Biomed Sci. 2008;15:585-594.
[2] Kudo K, Liu Y, Takhashi K, et al. Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells to prevent radiation-induced intestinal injury in mice. J Radiat Res. 2010;51:73-79.
[3] Lange C, Brunswig-Spickenheier B, Cappallo-Obermann H, et al. Radiation rescue: mesenchymal stromal cells protect from lethal irradiation. PLoS One. 2011;6:e14486.
[4] Weil BR, Markel TA, Herrmann JL, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells enhance the viability and proliferation of human fetal intestinal epithelial cells following hypoxic injury via paracrine mechanisms. Surgery. 2009;146(2):190-197.
[5] Bossolasco P, Cova L, Calzarossa C, et al. Neuro-glial differentiation of human bone marrow stem cells in vitro. Exp Neurol. 2005;193:312-325.
[6] Kinnaird T,Stabile E,Burnett MS, et al. Local delivery of marrow- derived stromal cells augments collateral perfusion through paracrine mechanisms. Circulation. 2004;109:1543-1549.
[7] Gnecchi M, He H, Liang OD, et al. Paracrine action accounts for marked protection of ischemic heart by Akt-modified mesenchymal stem cells. Nat Med. 2005;11:367-368.
[8] Zhou X, Gu J, Gu Y, et al. Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve learning and memory function in hypoxic-ischemic brain-damaged rats via an IL-8-mediated secretion mechanism rather than differentiation pattern induction. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;35(6): 2383-2401.
[9] Wairiuko GM, Crisostomo PR, Wang M, et al. Stem cells improve right ventricular functional recovery after acute pressure overload and ischemia reperfusion injury. J Surg Res. 2007;141(2):241-246.
[10] Boyette LB, Creasey OA, Guzik L, et al. Human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells display enhanced clonogenicity but impaired differentiation with hypoxic preconditioning. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2014;3(2):241-254.
[11] Rosova I, Dao M, Capoccia B, et al. Hypoxic preconditioning results in increased motility and improved therapeutic potential of human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells. 2008; 26(8):2173-2182.
[12] 刘婉薇,陈韵,郑跃,等.炎症预激活骨髓间充质干细胞条件培养基修复小肠黏膜急性辐射损伤[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(10): 1544-1550.
[13] Zhang B, Wang M, Yang Y, et al. ERp29 is a radiation-responsive gene in IEC-6 cell. J Radiat Res. 2008;49:587-596
[14] Wróblewski R, Jalnäs M, Van Decker G, et al. Effects of irradiation on intestinal cells in vivo and in vitro. Histol Histopathol, 2002;17:165-177.
[15] Miyahara Y, Nagaya N, Kataoka M, et al. Monolayered mesenchymal stem cells repair scarred myocardium after myocardial infarction. Nat Med. 2006;12(4):459-465.
[16] Xu J, Qu J, Cao L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-based angiopoietin-1 gene therapy for acute lung injury induced by lipopolysaccharide in mice. J Pathol. 2008;214:472-481.
[17] Rowart P, Erpicum P, Detry O, et al. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Therapy in Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. J Immunol Res. 2015;2015:602597.
[18] Jeong JO, Han JW, Kim JM, et al. Malignant tumor formation after transplantation of short-term cultured bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in experimental myocardial infarction and diabetic neuropathy. Circ Res. 2011;108(11):1340-1347.
[19] Hernanda PY, Pedroza-Gonzalez A, van der Laan LJ, et al. Tumor promotion through the mesenchymal stem cell compartment in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 2013;34(10):2330-2340.
[20] Gupta N, Su X, Popov B, et al. Intrapulmonary delivery of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improves survival and attenuates endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in mice. J Immunol. 2007;179(3):1855-1863.
[21] Samper E, Diez-Juan A, Montero JA, et al. Cardiac cell therapy: boosting mesenchymal stem cells effects. Stem Cell Rev. 2013;9(3):266-280.
[22] Gnecchi M, He H, Noiseux N, et al. Evidence supporting paracrine hypothesis for Akt-modified mesenchymal stem cell-mediated cardiac protection and functional improvement. FASEB J. 2006;20(6):661-669.
[23] van Poll D, Parekkadan B, Cho CH, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell–derived molecules directly modulate hepatocellular death and regeneration in vitro and in vivo. Hepatology. 2008;47(5): 1634-1643.
[24] Duijvestein M, Wildenberg ME, Welling MM, et al. Pretreatment with interferon-γ enhances the therapeutic activity of mesenchymal stromal cells in animal models of colitis. Stem Cells. 2011;29(10):1549-1558.
[25] Ren G, Zhang L, Zhao X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-mediated immunosuppression occurs via concerted action of chemokines and nitric oxide. Cell Stem Cell. 2008; 2(2): 141-150.
[26] Gunn WG, Conley A, Deininger L, et al. A crosstalk between myeloma cells and marrow stromal cells stimulates production of DKK1 and interleukin-6: a potential role in the development of lytic bone disease and tumor progression in multiple myeloma. Stem Cells. 2006;24(4):986-991.
[27] Chang P, Qu Y, Liu Y, et al. Multi-therapeutic effects of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells on radiation- induced intestinal injury. Cell Death Dis. 2013;4:e685.
[28] Ozen S, Akisu M, Baka M, et al. Insulin-like growth factor attenuates apoptosis and mueosal damage in hypoxia/ reoxygenation-induced intestinal injury. Biol Neonate. 2005; 87(2):91-96.
[29] Baregamian N, Song J, Chung DH. Effects of oxidative stress on intestinal type I insulin-like growth factor receptor expression. Eur J Pediatr Surg. 2012;22(1):97-104.
[30] Xu B, Luo Y, Liu YL, et al. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB enhances MSC-mediated cardioprotection via suppression of miR-320 expression. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015; 308(9):H980-H989.
|
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [5] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [6] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [7] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [8] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [9] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [10] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [11] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [12] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [13] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [14] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [15] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||