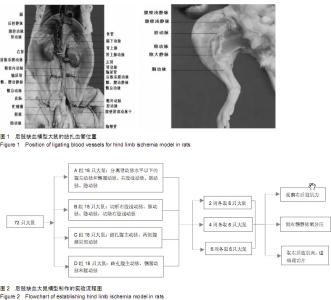
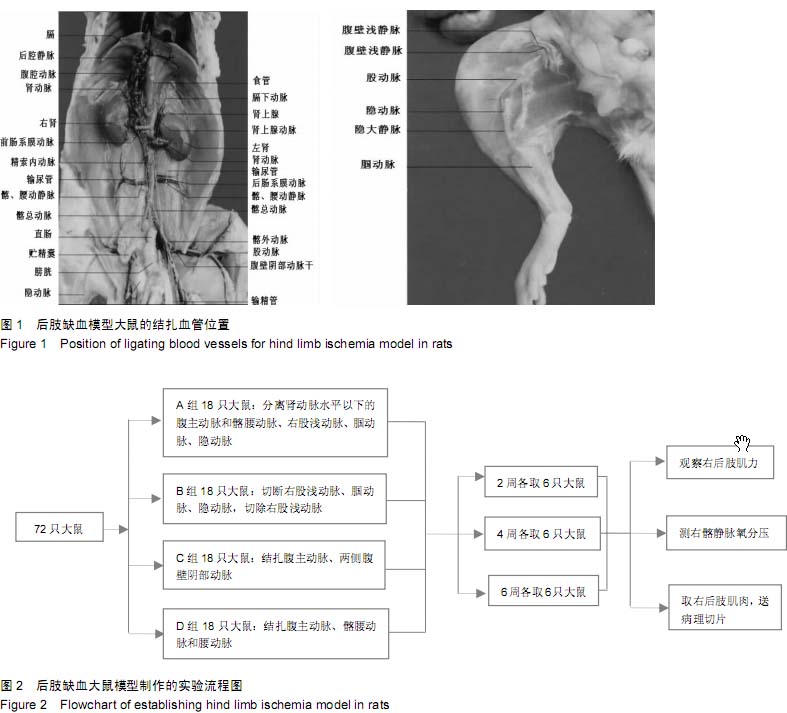
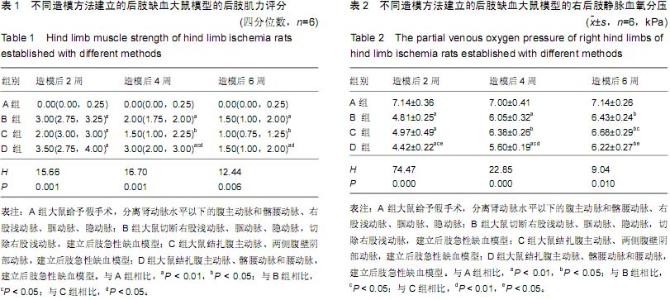
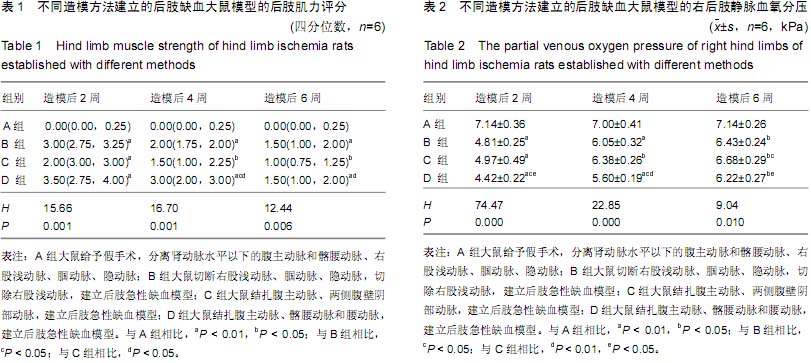
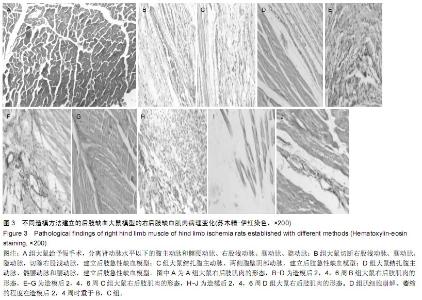
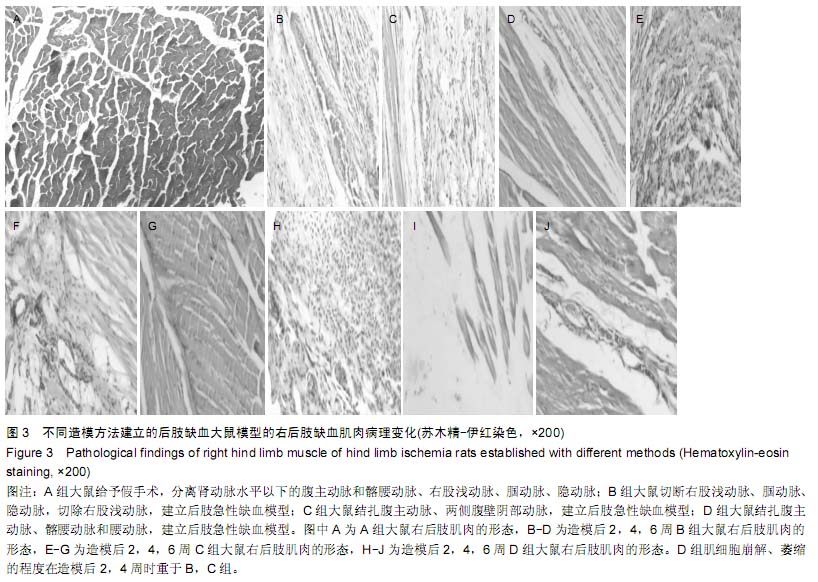
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (40): 6492-6497.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.40.018
Previous Articles Next Articles
Construction and evaluation of acute hind limb ischemia model in rats
Bai Chao, Yang Kun, Wang Yang, Li Xin-xi, Tian Ye, Luo Jun
- Department of Vascular and Thyroid Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China)
-
Online:2015-09-30Published:2015-09-30 -
Contact:Luo Jun, M.D., Chief physician, Department of Vascular and Thyroid Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Bai Chao, Master, Attending physician, Department of Vascular and Thyroid Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region of China, No. 2010211A48
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Bai Chao, Yang Kun, Wang Yang, Li Xin-xi, Tian Ye, Luo Jun. Construction and evaluation of acute hind limb ischemia model in rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(40): 6492-6497.
share this article
| [1] 张兴.下肢慢性缺血的治疗进展[J].心血管病学进展,2013,34(3): 324-329. [2] Egorova NN, Guillerme S, Gelijns A, et al. An analysis of the outcomes of a decade of experience with lower extremity revascularization including limb salvage, lengths of stay, and safety. J Vasc Surg. 2010;51(4):878-885, 885.e1. [3] de Franciscis S, Gallelli L, Battaglia L, et al. Cilostazol prevents foot ulcers in diabetic patients with peripheral vascular disease. Int Wound J. 2013. in press. [4] Souza Júnior SS, Moreira Neto AA, Schmidt Júnior AF, et al. Biochemical study of the effects of cilostazol in rats subjected to acute ischemia and reperfusion of hind limbs. Acta Cir Bras. 2013;28(5):361-366. [5] Vandvik PO, Lincoff AM, Gore JM, et al. Primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest. 2012;141(2 Suppl): e637S-668S. [6] Hori K, Tsujii M, Iino T, et al. Protective effect of edaravone for tourniquet-induced ischemia-reperfusion injury on skeletal muscle in murine hindlimb. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2013; 14:113. [7] Liang H, Yu F, Tong Z, et al. Effect of ischemia post- conditioning on skeletal muscle oxidative injury, mTOR, Bax, Bcl-2 proteins expression, and HIF-1α/β-actin mRNA, IL-6/ β-actin mRNA and caveolin-3/β-actin mRNA expression in ischemia-reperfusion rabbits. Mol Biol Rep. 2013;40(1):507-514. [8] Li BY, Li XL, Gao HQ, et al. Grape seed procyanidin B2 inhibits advanced glycation end product-induced endothelial cell apoptosis through regulating GSK3β phosphorylation. Cell Biol Int. 2011;35(7):663-669. [9] 王雁彬,李廷荃,化金凤,等.鹿茸对大鼠下肢缺血模型CD34+、FLK-1+阳性细胞比例影响[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2015,17(1): 24-26. [10] Schwarzwalder U, Zeller T. Below-the-knee revascularization. Advanced techniques. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 2009; 50(5):627-634. [11] Giles TD, Sander GE, Nossaman BD, et al. Impaired vasodilation in the pathogenesis of hypertension: focus on nitric oxide, endothelial-derived hyperpolarizing factors, and prostaglandins. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2012;14(4):198-205. [12] Rand T, Uberoi R. Current status of interventional radiology treatment of infrapopliteal arterial disease. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2013;36(3):588-598. [13] 王晓威,于振海.人工血管搭桥术后或介入治疗术后血管通畅率的研究[J].中国现代普通外科进展,2012,15(2):123-145. [14] Yongquan G, Lianrui G, Lixing Q, et al. Plaque excision in the management of lower-limb ischemia of atherosclerosis and in-stent restenosis with the SilverHawk atherectomy catheter. Int Angiol. 2013;32(4):362-367. [15] Brazeau NF, Pinto EG, Harvey HB, et al. Critical limb ischemia: an update for interventional radiologists. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2013;19(2):173-180. [16] Dhinsa BS, Adesida AB. Current clinical therapies for cartilage repair, their limitation and the role of stem cells. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2012;7(2):143-148. [17] 陈明卫,李燕萍,唐益忠,等.不同来源和移植途径的自体干细胞治疗糖尿病缺血性下肢血管病变的随机对照研究[J].中华临床医师杂志:电子版,2013,7(14):6418-6423. [18] Gu Y, Zhang J, Guo L, et al. A phase I clinical study of naked DNA expressing two isoforms of hepatocyte growth factor to treat patients with critical limb ischemia. J Gene Med. 2011; 13(11):602-610. [19] Li M, Zhou H, Jin X, et al. Autologous bone marrow mononuclear cells transplant in patients with critical leg ischemia: preliminary clinical results. Exp Clin Transplant. 2013;11(5):435-439. [20] Subrammaniyan R, Amalorpavanathan J, Shankar R, et al. Application of autologous bone marrow mononuclear cells in six patients with advanced chronic critical limb ischemia as a result of diabetes: our experience. Cytotherapy. 2011; 13(8): 993-999. [21] Murphy MP, Lawson JH, Rapp BM, et al. Autologous bone marrow mononuclear cell therapy is safe and promotes amputation-free survival in patients with critical limb ischemia. J Vasc Surg. 2011;53(6):1565-1574.e1. [22] Qin SL, Li TS, Kubo M, et al. Transient increase of cytokines in the acute ischemic tissue is beneficial to cell-based therapeutic angiogenesis. Circ J. 2008;72(12):2075-2080. [23] Wragg A, Mellad JA, Beltran LE, et al. VEGFR1/CXCR4- positive progenitor cells modulate local inflammation and augment tissue perfusion by a SDF-1-dependent mechanism. J Mol Med (Berl). 2008;86(11):1221-1232. [24] Iohara K, Zheng L, Wake H, et al. A novel stem cell source for vasculogenesis in ischemia: subfraction of side population cells from dental pulp. Stem Cells. 2008;26(9):2408-2418. [25] Tajima H, Iwai-Takano M, Yaoita H, et al. Mast cells contribute to flow restoration by bone marrow cell transplantation in rats with ischemic limbs. Int Heart J. 2009;50(2):247-257. [26] 汪忠镐,李震.我国血管外科的现状和发展[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志,2006,13(6):625-628. [27] 张弛,肖日军,张娜,等.脐血干细胞移植治疗糖尿病大鼠下肢缺血的实验研究[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版),2012,7(1):12-16. [28] Hamada Y, Gonda K, Takeda M, et al. In vivo imaging of the molecular distribution of the VEGF receptor during angiogenesis in a mouse model of ischemia. Blood. 2011; 118(13):e93-e100. [29] 梁翠宏.Wistar大鼠后肢缺血模型的实验研究[D].济南:山东大学, 2005. [30] Ubbink DT, Vermeulen H. Spinal cord stimulation for non-reconstructable chronic critical leg ischaemia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005;(3):CD004001. [31] 钟咏红.干细胞移植治疗糖尿病下肢血管病变:细胞因子与血管新生[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(32):5225-5229. [32] 赵金武,王晓玲,刘红宇,等.下肢动脉硬化闭塞症206例外科手术治疗经验[J].中国老年学杂志,2013,33(23):6022-6023. [33] 丁敏勇,周子花,叶永根.急性下肢动脉缺血的个体化诊治[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2014,16(8):867-868. [34] 何明坤,黄萍,傅明捷.注射用丹参多酚酸盐治疗下肢慢性缺血性疾病的临床研究[J].广州医药,2013,44(3):24-27. [35] 谷涌泉.下肢动脉硬化闭塞症的外科治疗[J].中国血管外科杂志(电子版),2014,6(2):65-67. [36] 尹德馨,李叶舟,孙大军,等.杂交手术治疗多平面动脉硬化闭塞症36例[J].中国老年医学杂志,2013,33(9):2151-2153. [37] 王佩双,胡何节,方征东,等. 股腘动脉闭塞腔内成形术与旁路转流术的临床疗效对比分析[J].中国血管外科杂志,2014,6(1): 41-44. [38] 赵巨伟,仇晓华,陈为国.动静脉转流术治疗下肢动脉闭塞性缺血[J].健康必读(中旬刊),2013,12(8):227. [39] 黄新天,刘晓兵.下肢重症缺血:腔内治疗时代的来临[J].中国血管外科杂志(电子版),2013,5(2):65-68. [40] 李孝成,潘光栋,肖运平,等.导管溶栓治疗急性下肢缺血30例[J].介入放射学杂志,2014,23(3):250-252. [41] 冯海,陈学明,李晨宇,等.股总动脉内膜切除联合股浅动脉支架植入治疗慢性下肢缺血[J].中华普通外科杂志,2014,29(8):292- 295. [42] Sumi M, Sata M, Toya N, et al. Transplantation of adipose stromal cells, but not mature adipocytes, augments ischemia-induced angiogenesis. Life Sci. 2007;80(6):559- 565. [43] Padilla L, Krötzsch E, Schalch P, et al. Administration of bone marrow cells into surgically induced fibrocollagenous tunnels induces angiogenesis in ischemic rat hindlimb model. Microsurgery. 2003;23(6):568-574. [44] 刘文亮,尹邦良,喻风雷,等.骨髓单个核细胞缺血组织局部移植对血运重建的影响[J].中南大学学报(医学版),2004,29(5): 572-576. [45] Hiasa K, Ishibashi M, Ohtani K, et al. Gene transfer of stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha enhances ischemic vasculogenesis and angiogenesis via vascular endothelial growth factor/endothelial nitric oxide synthase-related pathway: next-generation chemokine therapy for therapeutic neovascularization. Circulation. 2004;109(20):2454-2461. [46] Sato Y, Matsui K, Ajiki T, et al. Can a bone marrow cell contribute to organ regeneration? In vivo analysis using transgenic rats with reporter genes. Transplant Proc. 2005; 37(1):273-275. [47] Otsuka H, Akashi H, Murohara T, et al. The prostacyclin analog beraprost sodium augments the efficacy of therapeutic angiogenesis induced by autologous bone marrow cells. Ann Vasc Surg. 2006;20(5):646-652. [48] de Nigris F, Balestrieri ML, Williams-Ignarro S, et al. Therapeutic effects of autologous bone marrow cells and metabolic intervention in the ischemic hindlimb of spontaneously hypertensive rats involve reduced cell senescence and CXCR4/Akt/eNOS pathways. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2007;50(4):424-433. [49] 汪忠镐,李震.我国血管外科的现状和发展[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志,2006,13(6):625-628. [50] 彭新桂,柏盈盈,居胜红.小鼠下肢急性缺血模型的制作及影像评价[J].东南大学学报(医学版),2014,33(3):254-259. [51] 董素明,常文凯,罗俊茜,等.下肢缺血再灌注损伤模型大鼠接受依达拉奉干预后的超微结构变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 18(18):2867-2871. [52] Ziegler MA, Distasi MR, Bills RG, et al. Marvels, mysteries, and misconceptions of vascular compensation to peripheral artery occlusion. Microcirculation. 2010;17(1):3-20. |
| [1] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [2] | Fan Junchao, Chen Yong, Song Junjie. Sevoflurance combined with xenon pretreatment protects against spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury in a rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3660-3665. |
| [3] | Zhu Rui, Zeng Qing, Huang Guozhi. Ferroptosis and stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3734-3739. |
| [4] | Dong Liping, Luo Huaiqing, Yuan Heng, Long Juan, Xu Shaohui. Effect of aging on collateral vessel growth in rats with ischemic hind limbs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3156-3161. |
| [5] | Zhi Yibo, Zhang Jie, Liu Jian, Li Weiyan. Chemokine CCL21 in anterior cingulate cortex is involved in chronic neuropathic pain in a rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 242-246. |
| [6] | Liu Feng, Zhang Yu, Wang Yanli, Luo Wei, Han Chaoshan, Li Yangxin. Application of temperature-sensitive chitosan hydrogel encapsulated exosomes in ischemic diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2479-2487. |
| [7] | Fan Feiyan, Zhang Yunke. Effect and mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine for replenishing qi and promoting blood combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in promoting angiogenesis in ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 2060-2069. |
| [8] | Lin Yi, Feng Jierong, Luo Xingwen. Mobilization with movement facilitates early functional recovery after fixed-bearing posterior stabilized total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(12): 1842-1846. |
| [9] | Wang Feng, Ju Xiaocong, Wang Bing, Sun Haining. Lateral unicompartmental knee arthroplasty and total knee arthroplasty for treating lateral single compartment knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(12): 1836-1841. |
| [10] | Zhang Xujian, Zhao Zhenqun, Liu Wanlin. The role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in the pathogenesis of steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1759-1765. |
| [11] | Zhang Shiyong, Wang Chengwei, Wang Xue, Yan Xiangli, Wang Jie. Application of digital subtraction angiography in dog hindlimb arteriography [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 704-708. |
| [12] | Zou Haibo, Sun Xiaofeng. Variation of Fas/Fasl pathway in limb ischemia-reperfusion lung injury rats after etomidate post-treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(32): 5162-5167. |
| [13] | Yang Feng, Chang Lipu, Huang Changshan, Gong Xiaoguang, Chang Shunwu. Macrolide antibiotics protects against ischemia-reperfusion injury after liver transplantation in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(26): 4176-4182. |
| [14] |
Shang Zhizhong, Jiang Yanbiao, Yao Lan, Wang Anan, Wang Hongxia, Tian Yuanxin, Liu Dengrui, Ma Bin .
Feasibility of stem cell therapy for renal ischemia/reperfusion injury: a systematic review based on animal experiments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(25): 4094-4100. |
| [15] | Hou Xiao, Lü Yifan, Liu Jingmin. Meta-analysis of muscle strength of exercisers undergoing electrical muscle stimulation training [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(23): 3764-3772. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||