Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (23): 3764-3772.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2686
Meta-analysis of muscle strength of exercisers undergoing electrical muscle stimulation training
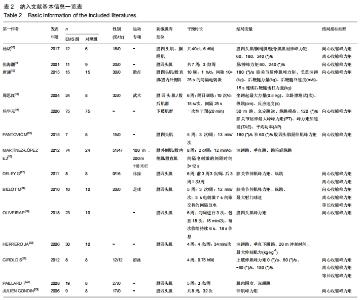
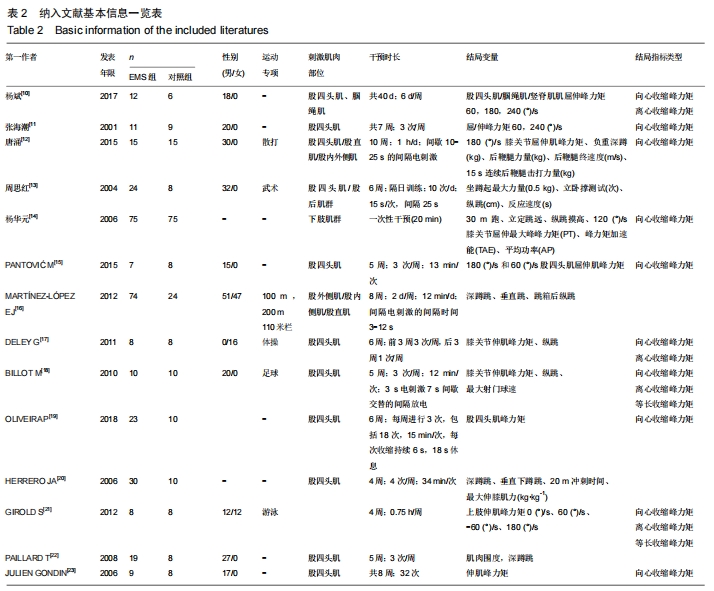
Hou Xiao1, Lü Yifan2, Liu Jingmin3
- 1Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China; 2Chinese People’s Public Security University, Beijing 100038, China; 3Division of Sports Science and Physical Education, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
-
Received:2019-09-03Revised:2019-09-05Accepted:2019-10-15Online:2020-08-18Published:2020-07-30 -
Contact:Liu Jingmin, PhD, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Division of Sports Science and Physical Education, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China -
About author:Hou Xiao, PhD candidate, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Hou Xiao, Lü Yifan, Liu Jingmin. Meta-analysis of muscle strength of exercisers undergoing electrical muscle stimulation training[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(23): 3764-3772.
share this article
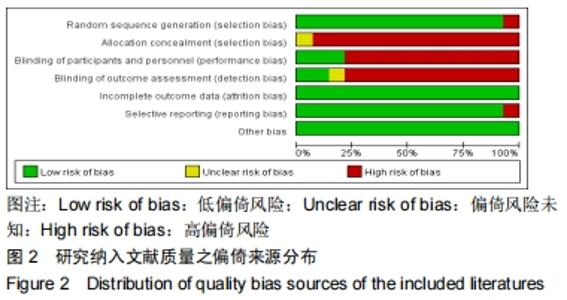
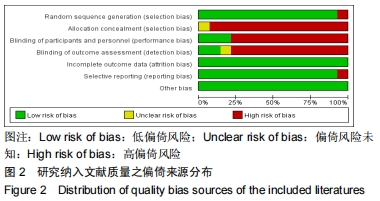
2.2 纳入文献质量评价 利用Cochrane文献质量评价条目对纳入的14篇文献进行文章质量偏倚风险评估[25],Cochrane的评价条目共有6项,分别为序列产生(sequence generation)、分配隐藏(allocation concealment)、盲法(blinding)、不完全结局数据(incomplete outcome data)、选择性结局报告(no selective outcome reporting)和其他偏倚来源(other sources of bias)。 在利用review manager 5.3软件对文献质量进行评分分析时,将Cochrane条目中的盲法细化为实验参与者盲法(blinding of participants and personnel)和实验分析盲法 (blinding of outcome assessment),因此最终文献质量评价条目共为7项。其中low risk of bias记为1分;high risk of bias和 unclear risk of bias记为0分,将文献质量评分≤2分的文献进行剔除。剔除文献篇数为0。 研究纳入文献的整体偏倚来源分布见图2;各篇文献的偏倚详情见图3。 "
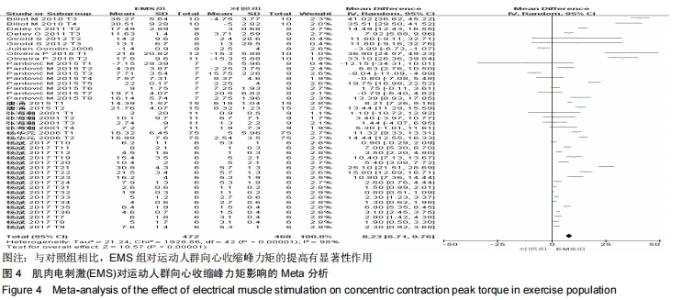
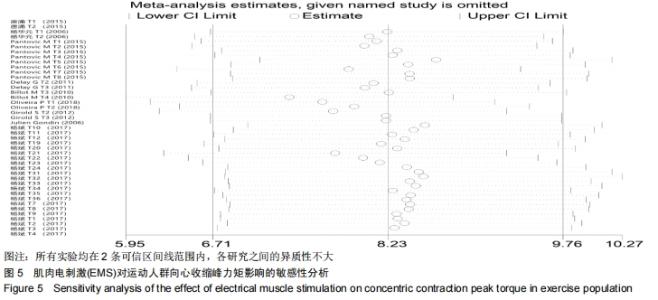
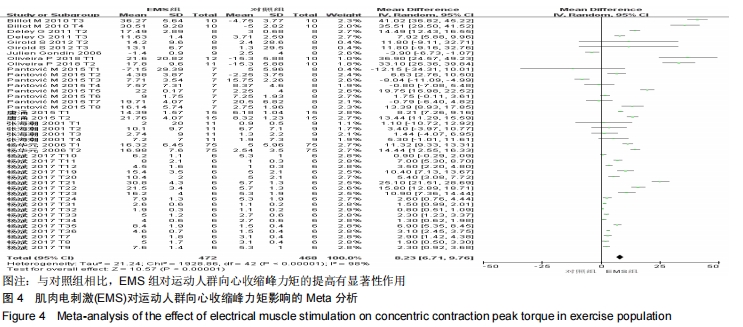
2.3 Meta分析结果 对纳入文献的肌肉向心收缩峰力矩(N·m)、肌肉离心收缩峰力矩(N·m)、肌肉等动收缩峰力矩(N·m)3项指标进行Meta分析。其中,涉及向心收缩峰力矩的文献实验数目为43个(因为部分文献测试了不同肌肉的峰力矩或对电刺激的干预安排有不同设计,所以同一篇文献的不同实验用T1,T2…Tn来表示);涉及离心收缩峰力矩的文献实验数目为21个;涉及等长收缩峰力矩的文献实验数目仅为2个。 2.3.1 电刺激对运动人群向心收缩肌峰力矩的影响 森林图是以统计学的合并效应值的分析方法为基础,通过统计学运算所绘制的图形,图中垂直的线为无效线,位于森林图的中心;平行于横坐标轴多条横线为各个研究的效应值和可信区间(Confidence Interval,CI)的范围;其中的黑色菱形为纳入研究文献的合并效应量,若菱形与无效线相交,则表示合并效应量无统计学意义,即EMS组与对照组相比,对因变量的影响无显著性差异[26]。 从图4可以看出,有关结局指标为向心收缩峰力矩的纳入实验为42个,EMS组合并样本量为472,对照组合并样本量为468。所有实验的合并效应量WMD=8.23,合并效应量的95%CI:(6.71,9.76),P < 0.0001,表示EMS组与对照组相比,对运动人群向心收缩峰力矩的提高有显著性作用。但是该合并研究的I2=98%,说明文献之间具有很大的异质性,因此还需对文献实验的异质性来源进行探究,分别运用敏感性分析、Meta回归和亚组分析进行研究。 "
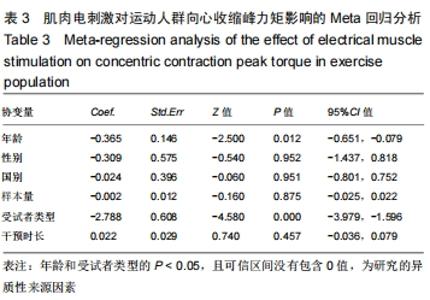
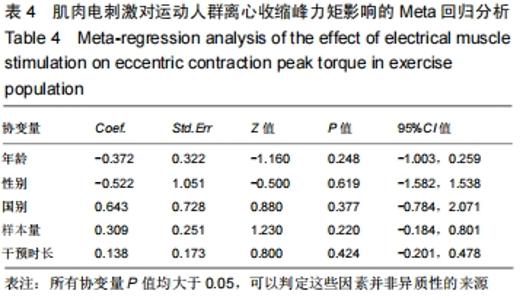
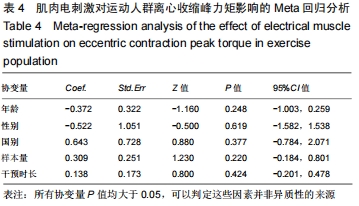
根据实验的基本特征将年龄、性别、国别、样本量、受试者类型以及干预时长6个可能对实验具有影响的因素定义为协变量。其中年龄(岁)、样本量(人)和干预时长(d)为数值型变量,直接导入。而对性别、国别和受试者类型这类变量进行赋值,其中,性别为1(仅男生)、2(仅女生)、3(男女混合);国别为1(中国)、2(南斯拉夫)、3(法国)、4(巴西);受试者类型为1(专业运动员)、2(体育院校运动人群)。运用stata 15.1软件进行Meta回归后汇总数据得到表3,根据表3可以看出:年龄(P=0.012)和受试者类型(P=0.000)的P < 0.05,且可信区间没有包含0值,因此这2个因素为该研究的异质性来源因素。需要根据年龄和受试者类型进行相应的亚组分析。 "
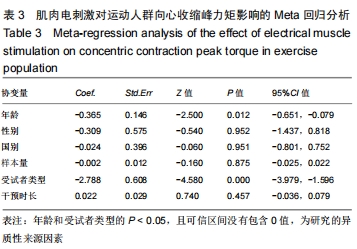
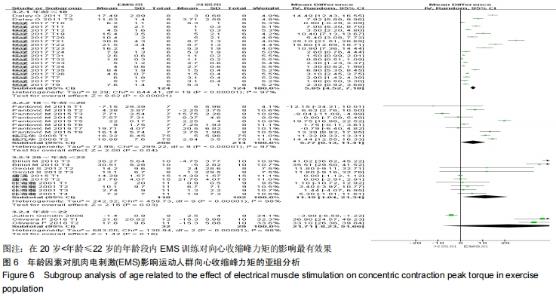
图6,7分别为按照年龄和受试者类型作为协变量因素对该结局指标研究进行的亚组分析森林图。由图6可知当年龄≤18岁时,合并效应值WMD=5.85(P < 0.000 01),说明该年龄段的受试者在进行EMS训练时,与对照组相比,对向心收缩的峰力矩有非常显著的促进作用。当年龄在18-20岁和20-22岁这两个区间范围内,合并效应值WMD分别为5.77(P=0.04< 0.05)和11.19(P=0.03< 0.05),EMS训练与无EMS训练相比,也可显著促进受试者的向心收缩峰力矩。当受试者的年龄超过22岁时,合并效应值WMD= 21.71(P=0.16> 0.05),说明EMS组与对照组相比,对向心收缩峰力矩无显著影响。因此在今后采用EMS电刺激进行运动人群的力量训练时,应考虑年龄因素,P < 0.05的3个年龄段(年龄≤18岁、18岁<年龄≤20岁、20岁<年龄≤22岁)中,在20岁<年龄≤22岁的年龄段内,合并效应值WMD=11.19,可知此年龄阶段EMS训练对向心收缩峰力矩的影响最有效果。 "

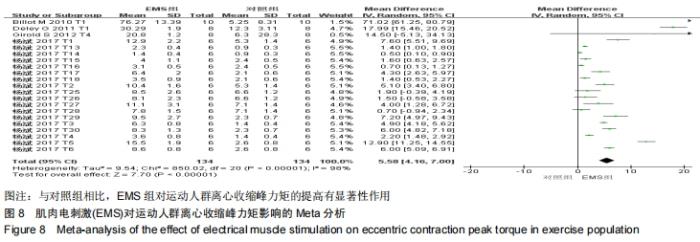
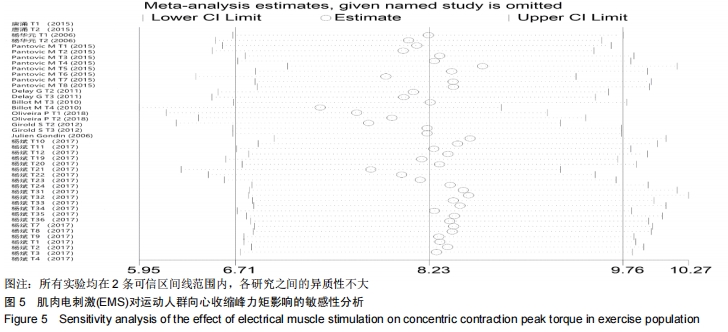
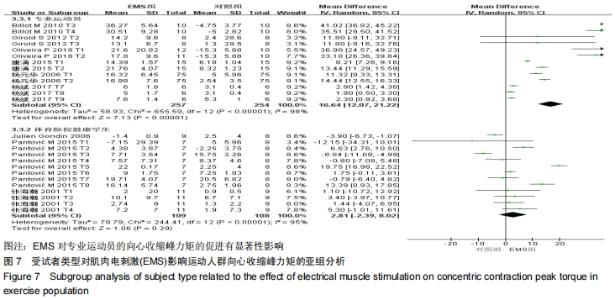
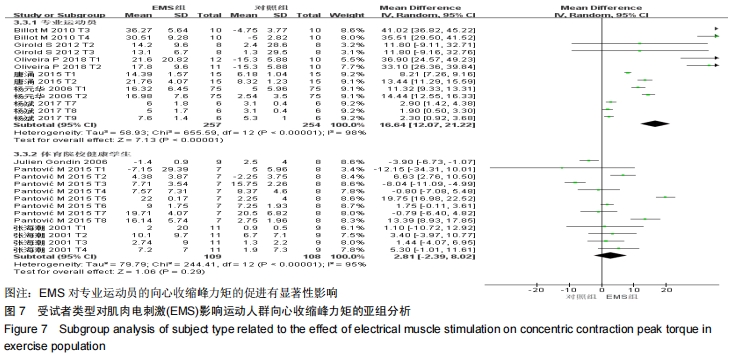
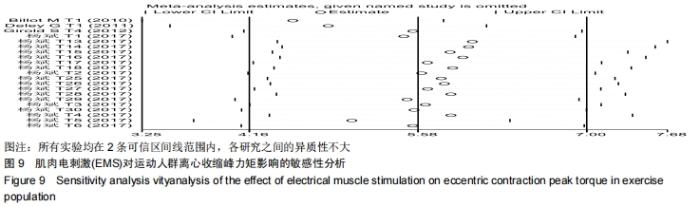
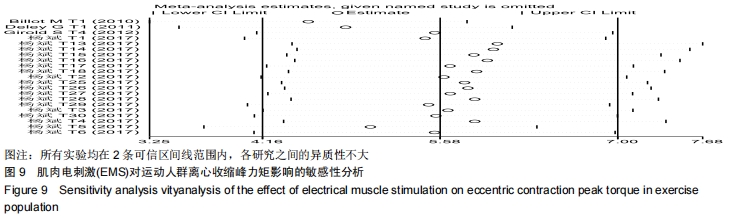
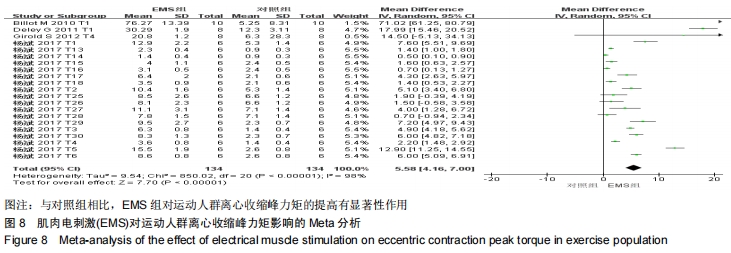
由于在纳入文献时,将体育院校的健康人群也作为运动人群纳入研究中,且在进行Meta回归时,判定该因素为实验总体异质性来源的因素之一,因此进行了如图7的亚组分析。当受试者为专业运动员时,向心收缩峰力矩的合并效应值WMD=16.64(P < 0.000 01);当受试者为体育院校有运动经验的健康人群时,合并效应值WMD=2.81(P= 0.29 < 0.05)。这说明EMS电刺激对专业运动员的向心收缩峰力矩的促进有显著性影响,而对于非专业运动员的运动人群,虽有一定的促进作用,但与专业运动员相比,促进效果较低。这提醒训练者,在选择EMS作为力量训练手段时,应考虑受试者的运动水平和专业性。 2.3.2 电刺激对运动人群离心收缩峰力矩的影响 从图8可以看出,有关结局指标为离心收缩峰力矩的纳入实验为21个,实验组合并样本量为134,对照组合并样本量为134。所有文献实验合并效应值WMD=5.58,95%CI:(4.16,7.00),P < 0.000 01,表示EMS组与对照组相比,对运动人群离心收缩峰力矩的提高有显著性作用。但是该合并研究的I2=98%,说明文献之间具有很大的异质性,采用随机效应模型,同时需对文献实验的异质性来源进行探究,分别运用敏感性分析、Meta回归进行研究。对纳入的42个实验进行敏感性分析,如图9所示,所有实验均在两条可信区间线范围内,各研究之间的异质性不大,剔除某一篇文章对结局指标的影响不大,因此该研究的异质性来源并非来自于单个实验[27]。 "
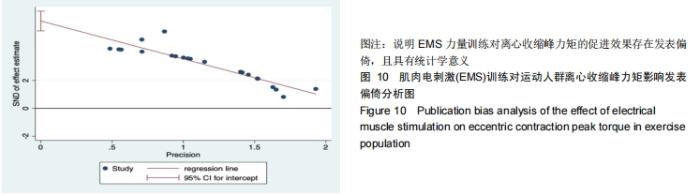
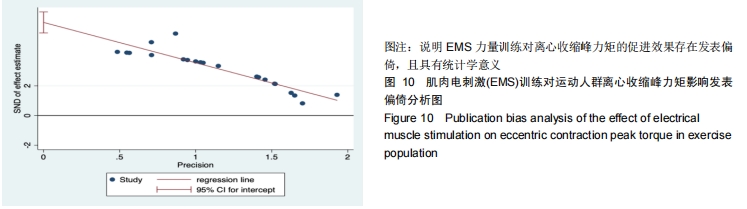
由于Meta分析中,异质性是天然存在的,在对合并效应值进行分析时(见图8),I2值很大,因此作者选择随机效应模型更加可靠,Meta分析是基于以往的一些研究,在这些原始研究中,可能没有提供与异质性有关的一些数据,例如可能只发表了阳性结果的研究而导致发表偏倚,因而可能无从分析异质性来源。因此进行该部分发表偏倚的检验,连续型变量选择Egger’s test检验,如图10所示。截距线段横跨0点线,则为发表偏倚较低;截距线段不予0点线相交时,则为有明显的发表偏倚[29]。EMS力量训练对离心收缩峰力矩促进效果的发表偏倚检验结果:t=-9.87,P=0.000< 0.01,95%CI:(-3.301,-2.146),置信区间不包含0,说明EMS力量训练对离心收缩峰力矩的促进效果存在发表偏倚,且具有统计学意义。可能是出现异质性的原因。 "
| [1]吕一帆.同步电刺激与交替电刺激训练对力量的影响[D].北京:北京体育大学,2019. [2]MILLER C, THÉPAUT-MATHIEU C. Strength training by electrostimulation conditions for efficacy. Int J Sports Med. 1993;14(1):20-28. [3]VITENZON AS, BUROVOĬ AM. Method and construction of programmed electric muscle stimulation in gait disorders.Med Tekh. 2002;(1):14-19. [4]王保成,杨汉雄.竞技体育力量训练指导[M].人民体育出版社, 2001:1-300. [5]宋德海,巢晓春.力量训练方式发展研究[J].山东体育科技,2011, 33(4):8-12. [6]周欣星. SEMG和NMES仪的设计及对肌肉的强化效果研究[D].长沙:中南大学,2014. [7]FUKASAWA Y, OHNO N, SAITOH Y, et al. Immunohistochemical and morphofunctional studies of skeletal muscle tissues with electric nerve stimulation by in vivo cryotechnique.Acta Histochem Cytochem. 2015;48(2): 27-36. [8]黄志刚,周里,王煜,等.电刺激训练前后肌肉力量交叉迁移效果的实验观察[J].中国运动医学杂志,2002,21(2):203-205. [9]王丽,梁潇.电刺激影响力量增长与退化的轨迹[J].武汉体育学院学报,2013,47(10):59-62. [10]杨斌.不同强度电刺激对足球运动员专项力量的影响[J].唐山师范学院学报,2017,39(5): 89-92. [11]张海潮,潘浩.电刺激对肌肉力量作用的研究分析[J].北京体育大学学报,2001,24(2):189-190+196. [12]唐涌,曹云.电刺激训练对散打运动员下肢力量及鞭腿影响的实验研究[J].武汉体育学院学报,2015,49(2):90-94. [13]周思红,张海潮.电刺激方法对武术运动员反应速度和肌肉力量的实验研究[J].北京体育大学学报,2004,27(12):1647-1648+ 1683. [14]杨华元,刘堂义,蒯乐,等.穴位电刺激增强运动员快速力量的作用观察[J].中国针灸,2006,26(5):313-315. [15]PANTOVIĆ M, POPOVIĆ B, MADIĆ D, et al. Effects of neuromuscular electrical stimulation and resistance training on knee extensor/flexor muscles.Coll Antropol. 2015;39 Suppl 1:153-157. [16]MARTÍNEZ-LÓPEZ EJ, BENITO-MARTÍNEZ E, HITA-CONTRERAS F, et al. Effects of electrostimulation and plyometric training program combination on jump height in teenage athletes.J Sports Sci Med. 2012;11(4):727-735. [17]DELEY G, COMETTI C, FATNASSI A, et al. Effects of combined electromyostimulation and gymnastics training in prepubertal girls.J Strength Cond Res. 2011;25(2):520-526. [18]BILLOT M, MARTIN A, PAIZIS C, et al. Effects of an electrostimulation training program on strength, jumping, and kicking capacities in soccer players.J Strength Cond Res. 2010;24(5):1407-1413. [19]OLIVEIRA P, MODESTO KAG, BOTTARO M, et al. Training Effects of Alternated and Pulsed Currents on the Quadriceps Muscles of Athletes.Int J Sports Med. 2018;39(7):535-540. [20]HERRERO JA, IZQUIERDO M, MAFFIULETTI NA, et al. Electromyostimulation and plyometric training effects on jumping and sprint time.Int J Sports Med. 2006;27(7): 533-539. [21]GIROLD S, JALAB C, BERNARD O, et al. Dry-land strength training vs. electrical stimulation in sprint swimming performance. J Strength Cond Res. 2012;26(2):497-505. [22]PAILLARD T, NOE F, BERNARD N, et al. Effects of two types of neuromuscular electrical stimulation training on vertical jump performance. J Strength Cond Res. 2008;22(4): 1273-1278. [23]GONDIN J, GUETTE M, BALLAY Y, et al. Neural and muscular changes to detraining after electrostimulation training.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2006;97(2):165-173. [24]李雪迎.Meta分析研究设计中的PICOS原则[J].中国介入心脏病学杂志,2016,24(11):611. [25]HIGGINS JPT,GREEN S.Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions 5.2.0. http://www.cochrane.org/resources/handbook/hbook.htm (accessed June 2017). [26]刘关键,吴泰相.Meta-分析的森林图及临床意义[J].中国循证医学杂志,2004(03):198-201. [27]SILVA AB, SOUSA N, AZEVEDO LF, et al. Physical activity and exercise for erectile dysfunction: systematic review and meta-analysis.Br J Sports Med.2017;51(19): 1419-1424. [28]THOMPSON SG, SHARP SJ. Explaining heterogeneity in meta-analysis: a comparison of methods.Stat Med. 1999; 18(20):2693-2708. [29]王丹,牟振云,翟俊霞,等.Stata软件在Meta-分析发表性偏倚识别中的探讨[J].现代预防医学,2008,35(15):2819-2822. [30]杜承润,史衍.肌肉电刺激训练研究综述[J].运动,2018(1): 26-27+46. [31]鲁建清,常永玲,黎冬.电刺激增强肌肉力量的机制及应用[J].湘南学院学报,2011,32(2):116-119. [32]OVERDUIN SA, D’AVELLA A, CARMENA JM, et al. Microstimulation activates a handful of muscle synergies. Neuron.2012;76(6):1071-1077. [33]HEIDLAND A, FAZELI G, KLASSEN A, et al.Neuromuscular electrostimulation techniques: historical aspects and current possibilities in treatment of pain and muscle waisting. Clin Nephrol.2013; 79(Suppl 1): S12-S23. [34]OGASAWARA R, KOBAYASHI K, TSUTAKI A, et al. mTOR signaling response to resistance exercise is altered by chronic resistance training and detraining in skeletal muscle.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2013;114(7):934-940. [35]FUKAZAWA T, MATSUMOTO M, IMURA T, et al. Electrical stimulation accelerates neuromuscular junction formation through ADAM19/neuregulin/ErbB signaling in vitro.Neurosci lett.2013;545: 29-34. [36]曾宪涛,李胜,马钻,等.Meta分析系列之八:Meta分析的报告规范[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志,2012,4(6):500-503. |
| [1] | Jing Jinpeng, Zhang Yue, Liu Xiaomin, Liu Yi. Traditional Chinese medicine injection for promoting blood circulation in prevention of deep vein thrombosis after orthopedic surgery: network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1467-1476. |
| [2] | Zhao Jing, Liu Xiaobo, Zhang Yue, Zhang Jiaming, Zhong Dongling, Li Juan, Jin Rongjiang. Visualization analysis of neuromuscular electrical stimulation therapy based on CiteSpace: therapeutic effects, hot spots, and developmental trends [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1234-1241. |
| [3] | Liu Gang, Ma Chao, Wang Le, Zeng Jie, Jiao Yong, Zhao Yi, Ren Jingpei, Hu Chuanyu, Xu Lin, Mu Xiaohong. Ankle-foot orthoses improve motor function of children with cerebral palsy: a Meta-analysis based on 12 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1299-1304. |
| [4] | Liu Yiyi, Qiu Junqiang, Yi Longyan, Zhou Cailiang. Effect of resistance training on interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein in middle-age and elderly people: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 804-812. |
| [5] | Wang Nan, Qian Yuzhang, Xie Lin. Network Meta-analysis of different acupuncture methods for the treatment of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 813-820. |
| [6] | Wei Zhoudan, Li Wenjin, Zhu Li, Wang Yu, Zhao Jiaoyang, Chen Yanan, Guo Dong, Hao Min. Platelet-rich fibrin as a material for alveolar ridge preservation significantly reduces the resorption of alveolar bone height and width after tooth extraction: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 643-648. |
| [7] | Ou Liang, Kong Dezhong, Xu Daoqing, Ni Jing, Fu Xingqian, Huang Weichen. Comparative clinical efficacy of polymethyl methacrylate and self-solidifying calcium phosphate cement in vertebroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 649-656. |
| [8] | Yang Ruijia, Jiang Lingkai, Dong Zhengquan, Wang Yunfei, Ma Zhou, Cong Linlin, Guo Yanjing, Gao Yangyang, Li Pengcui. Open reduction and internal fixation versus circular external fixation for tibial plateau fractures: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 480-486. |
| [9] | Zhong Yuanming, He Bingkun, Wu Zhuotan, Wu Sixian, Wan Tong, Zhong Xifeng. Meta-analysis of efficacy and safety of Jack kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 487-492. |
| [10] | Zhao Shuying, Guo Guangling, Liu Chenchen, Zhang Chao, Dong Sirui, Gong Qinqin, Ji Luwei. Stem cell transplantation in the treatment of premature ovarian failure: a meta-analysis based on 13 animal studies [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(25): 4084-4092. |
| [11] | Shi Yao, Han Shufeng, Yuan Yitong, Du Ruochen, Jing Zhijie, Zhao Bichun, Zhang Ruxin, Zhang Yujuan, Wang Chunfang. Efficacy and safety of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of spinal cord injury: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(25): 4093-4100. |
| [12] | Liang Meifu, Guo Wenxia, Zhao Ningning, Pan Lei. Determination and characteristics of skeletal muscle output power in different strength training methods under optimal power load [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(23): 3638-3643. |
| [13] | Hao Zhixin, Wu Yixin, Wang Xin, Xia Zhongliang. Effect of anodal transcranial direct current stimulation on muscle strength and endurance: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(20): 3273-3280. |
| [14] | Diao Yulei, Zong Xiaorui, Deng Zhibo, Shu Han. Analgesic effect of adductor canal block versus femoral nerve block after autogenous bone-tendon-bone reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament: an updated Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 315-320. |
| [15] | Zhou Junli, Wang Xiaojun, Wang Haijiao, Li Chun. A network meta-analysis of the efficacy of new medical dressings for diabetic foot ulcers [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(16): 2562-2569. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||