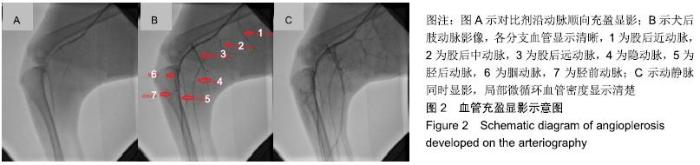
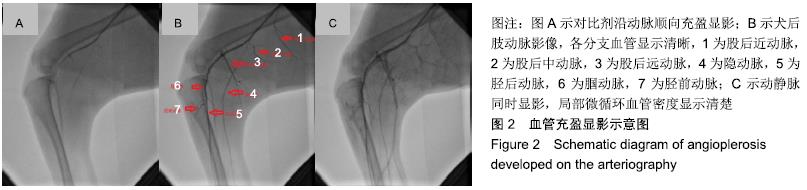
[1] 肖婷,王爱红,许樟荣,等. 436例糖尿病足截肢相关因素分析[J].中华内分泌代谢杂志,2009,25(6):591-594.
[2] ERDEM M, BOSTAN B, GÜNEŞ T, et al. Protective effects of melatonin on ischemia-reperfusion injury of skeletal muscle. Eklem Hastalik Cerrahisi. 2010;21(3):166-171.
[3] PHELPS EA, LANDÁZURI N, THULÉ PM, et al. Bioartificial matrices for therapeutic vascularization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(8):3323-3328.
[4] 王华,王伯胤. 糖尿病足下肢动脉病变影像学诊断研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学,2010,13(23):2543-2546.
[5] 米晓云,石保新,张壮志,等. 细粒棘球绦虫幼虫——原头蚴感染比格犬(Beagle)试验[J].中国兽医学报,2010,30(9):1223-1224.
[6] 宋洁,曹燕,黄茜,等.国内比格犬的生物学指标研究及相关应用进展[J].医学动物防制,2012,27(6):650-652.
[7] 侯明明,于维良,孙振林.新型犬脊柱侧弯动物模型的建立[J].临床骨科杂志,2006,9(2):170-172.
[8] 李鸿帅,张长青,白跃宏,等.固定一侧前肢后对犬后肢负重的影响[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2008,22(1):66-69.
[9] KIM BJ, PIAO Y, WUFUER M. Biocompatibility and efficiency of biodegradable magnesium-based plates and screws in the facial fracture model of beagles. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018; 76(5):1055-1064.
[10] NAKAMURA T, HARA Y, TAGAWA M, et al. Recombinant human basic fibroblast growth factor accelerates fracture healing by enhancing callus remodeling in experimental dog tibial fracture. J Bone Miner Res.1998;13(6):942-949.
[11] OMOTO O, YASUNAGA Y, ADACHI N, et al. Histological and biomechanical study of impacted cancellous allografts with cement in the femur: a canine model. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2008;128(12):1357-1364.
[12] FENG S, ZUOQIN Y, CHANGAN G, et al. Prediction of traumatic avascular necrosis of the femoral head by single photon emission computerized tomography and computerized tomography: an experimental study in dogs. Chin J Traumatol. 2011;14(4):227-232.
[13] 黄文华,蒋国民,张贤舜,等. DSA步进技术在下肢动脉疾病诊断中的应用[J].实用医学杂志, 2012, 28(4):622-623.
[14] POMPOSELLI F. Arterial imaging in patients with lower extremity ischemia and diabetes mellitus. J Vasc Surg. 2010; 100(5):412-423.
[15] 裴小燕,杜彦李,李双. CTA、MRA与DSA在脑血管狭窄疾病诊断中的应用[J].临床合理用药杂志,2016,9(15):174-175.
[16] TOEPKER M, MAHABADI AA, HEINZLE G, et al. Accuracy of MDCT in the determination of supraaortic artery stenosis using DSA as the reference standard. Eur J Radiol.2011; 80(3):351-355.
[17] YOSHINORI T, AKIHIKO K, YUTAKA K, et al. Clinical Experience of Dual-phase Cone Beam Computed Tomography during Hepatic Arteriography to Apply 3D-DSA. Japan J Radiol Technol. 2016;72(11):1091-1097.
[18] BLAGOJEVIC J, PIEMONTE G, BENELLI L, et al. Assessment, definition, and classification of lower limb ulcers in systemic sclerosis: a challenge for the rheumatologist. J Rheumatol.2016;43(3):592-598.
[19] 沈海刚,何俊玲,李鸣. DSA造影确定下肢动脉硬化闭塞性肢体坏疽截肢平面的评估[J].介入放射学杂志,2005,14(1):71-72.
[20] ABD-ELGAWAD EA, IBRAHEEM MA, SAMY LA, et al. Assessment of the distal runoff in patients with long standing diabetes mellitus and lower limb ischemia: MDCTA versus DSA. Egypt J Radiol Nucl Med. 2013;44(2):231-236.
[21] MCCOLLOUGH CH, MILLER WP, LYSEL MS, et al. Densitometric assessment of regional left ventricular systolic function during graded ischemia in the dog by use of dual-energy digital subtraction ventriculography. Am Heart J. 1993;125(6):1667-1675.
[22] 秦治刚,于伟东,杨小玉,等. DSA引导下山羊缺血性脊髓损伤模型的建立及形态学实验研究[J].中国实验诊断学,2011,15(2): 319-321.
[23] LIU B, JIANG Q, LIU W, et al. A vessel segmentation method for serialized cerebralvascular DSA images based on spatial feature point set of rotating coordinate system. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2018;161:55-72.
[24] 焦河,王凤英. DSA技术在兔髂总动脉造影中的应用[J].西部医学, 2009,21(4):550-552.
[25] 袁占奎,齐长明.舒泰和速眠新Ⅱ对犬呼吸和心血管系统影响的比较[J].中国兽医杂志,2009,45(1):62-64.
[26] 张世龙,翟仁友,戴定可,等. 高浓度造影剂和高速摄影在动物实验中获取高质量影像的应用[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2007, 13(8):54-57.
[27] 李清军,魏勤,赵红朴,等.DSA检查中对比剂的流速及其选择[J]. 医学影像学杂志,2002,12(5):3-5.
|