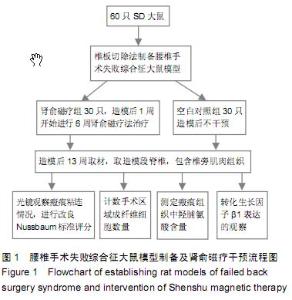
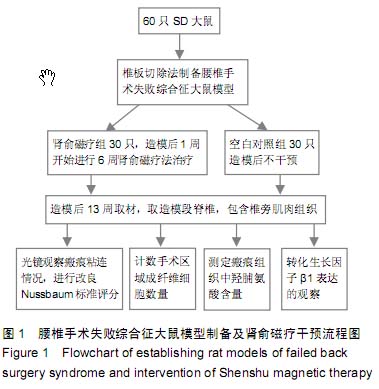
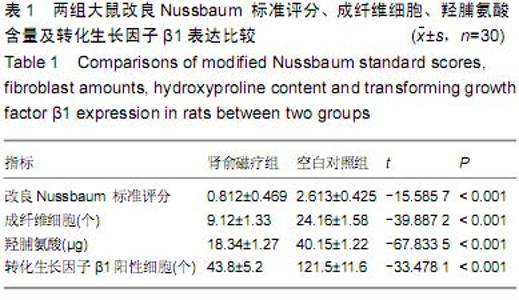
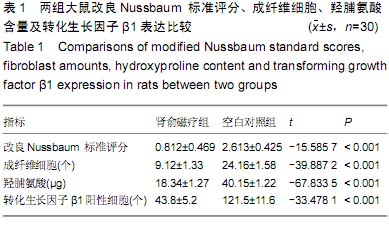
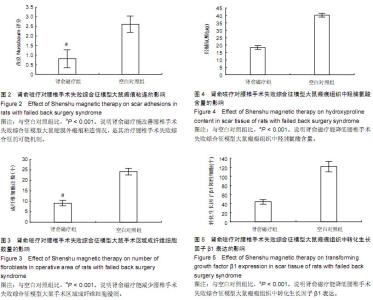
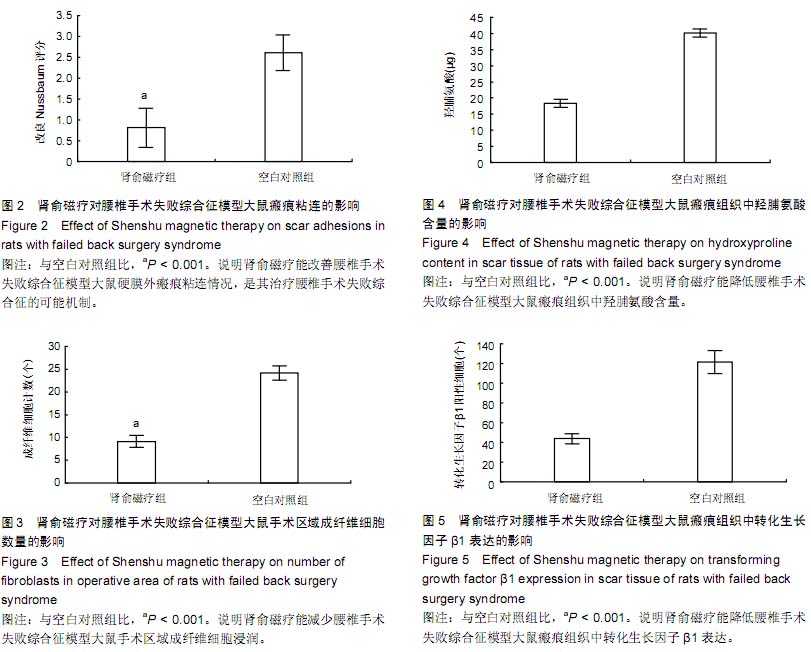
| [1] Han IH,Kim KS,Jin BH. Intradural lumbar disc hemiations associated with epidural adhesion: report of twocases.J Korean Neurosurg Soc.2009;46(2):168-171.
[2] Kelly GA, Blake C, Power CK, et al. The impact of spinal cord stimulation on physical function and sleep quality in individuals with failed back surgery syndrome: a systematic review. Eur J Pain.2012; 16(6): 793-802.
[3] Alkalay RN,Kim DH,Urry DW,et al.Prevention of postlaminectomy epidural fibrosis using bioelastie materials.Spine.2003;28(15):1659-1665.
[4] Akeson WH, Massie JB, Huang B, et al.Topical high-molecular- weight hyaluronan and a roofing barrier sheet equally inhibit postlaminectomy fibrosis.Spine J. 2005; 5(2):180-190.
[5] 刘军.丝裂霉素聚乳酸控释膜预防脊柱术后粘连的研究[D].上海.第二军医大学,2010.
[6] 张科峰.可吸收PLGA膜预防椎板切除术后硬膜外粘连的实验研究[D].济南,山东大学.2008.
[7] 朱亮.腰椎手术失败综合征的临床研究及预防硬膜外瘢痕粘连的实验研究[D].上海.第二军医大学,2012.
[8] 张伟,王立新,姜黄素对椎板切除术后大鼠硬膜外瘢痕组织中羟脯氨酸含量的影响[J].蚌埠医学院学报,2011,36(4):332-334.
[9] 周辉,范希玲,夏志敏,等.活血止痛汤对硬膜外瘢痕中TGF-β1和TGF-β2基因表达的影响[J].中国骨伤,2007,20(10):674-678.
[10] 王玉光,张超,沈文,等. 椎板切除模型大鼠局部应用绿原酸对硬膜外纤维化及硬脑膜粘连的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2015, 19(5):704-709.
[11] 孙旭.当归注射液对FBSS兔模型形态学观察及CTGF表达的影响[D].西安,陕西中医学院,2010.
[12] 酒涛.黄芪注射液对椎板切除术后硬膜外粘连干预作用的实验研究[D].西安,陕西中医学院,2009.
[13] 张兆杰.三七凝胶预防腰椎术后硬膜外粘连的实验研究[D].北京,中国中医研究院,2005.
[14] 张朝鑫,郭静科,王云强,等.穴位物理刺激对体内自由基代谢的影响[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2014,36(2):151-153.
[15] 王利森,金广江.穴位刺激消除男子中跑运动员一周大强度训练所致疲劳的效果研究[J].武汉体育学院学报.2006.40(6):75-77.
[16] 黄国付,张红星,张唐法,等.电针夹脊穴治疗腰椎间盘突出症的镇痛时效及对血浆相关因子的干预[J].中国临床康复, 2006,10(43):1-6.
[17] Einhuas SL,Robertsory JT,Dohan FC, et al.Reduction of peridural fibrosis after lumber laminectomy and discectomy in dog by a resorbablegel (ADCON-L).Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997;22(13):1140-1147.
[18] de Tribolet N, Porchet F, Lutz TW, et al.Clinical assessment of a novel antiadhesion barrier gel: prospective, randomized, multicenter, clinical trial of ADCON-L to inhibit postoperative peridural fibrosis and related symptoms after lumbar discectomy.Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 1998; 27(2): 111-120.
[19] LaRocca H, Macnab I.The laminectomy membrane. Studies in its evolution, characteristics, effects and prophylaxis in dogs.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1974;56B(3):545-550.
[20] Songer MN, Carson EW, Pandit SM. Analysis of peridural scar formation and its prevention after lumbar laminotomy and discectomy in dogs. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995;20(5): 571-580.
[21] Robertson JT.Role of peridural fibrosis in the failed back: a review.Eur Spine J. 1996;5 Suppl 1:S2-6.
[22] Dullerud R, Graver V, Haakonsen M,et al. Influence of fibrinolytic factors on scar formation after lumbar discectomy. A magnetic resonance imaging follow-up study with clinical correlation performed 7 years after surgery.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1998;23(13):1464-1469.
[23] Gruber J, Fong S, Chen CB, et al. Mitochondria-targeted antioxidants and metabolic modulators as pharmacological interventions to slow ageing. Biotechnol Adv. 2013;31(5): 563-592.
[24] 张玉琼,丁建英. 经颅磁刺激对脑性瘫痪患儿粗大运动功能的影响[J].中国康复理论与实践,2012,18(6):515-517.
[25] 金妍,冉平,陈树立.经颅磁刺激结合穴位注射早期治疗智力低下幼儿疗效观察[J].中国康复理论与实践,2011,17(12):1167-1169.
[26] 于洪丽,徐桂芝,杨硕,等. 磁刺激穴位镇痛诱发的脑电信号特征成分及源定位[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(9): 1639-1642. |