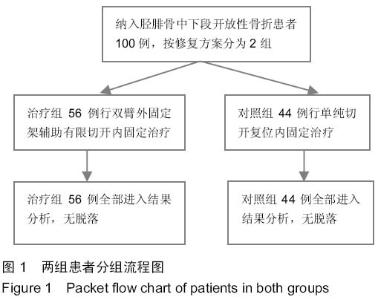
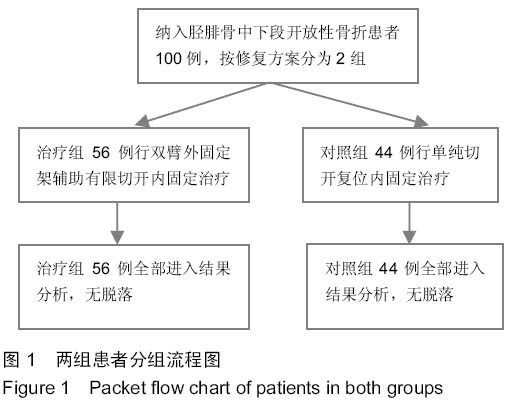
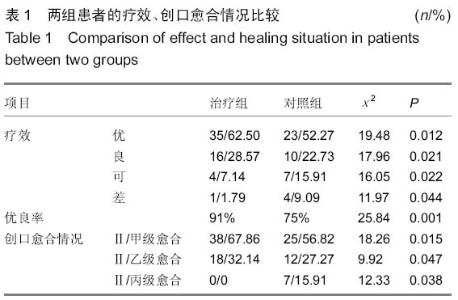
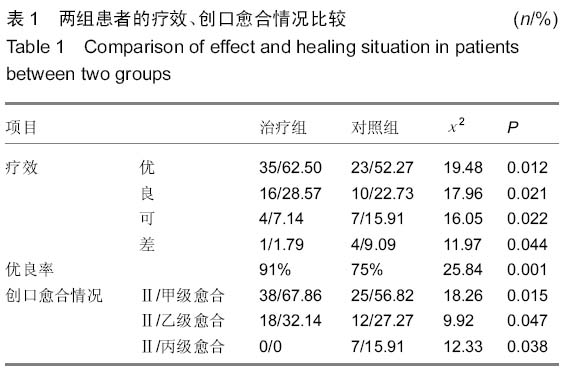
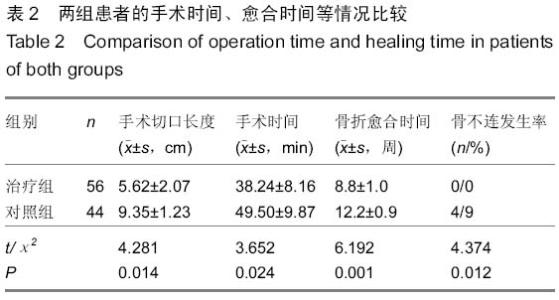
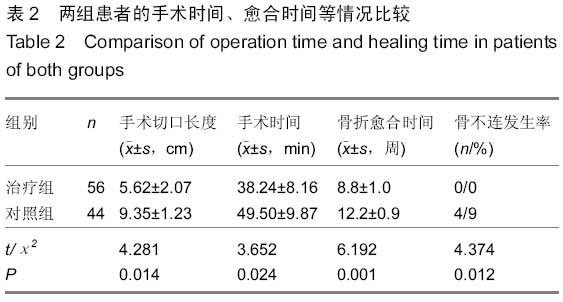
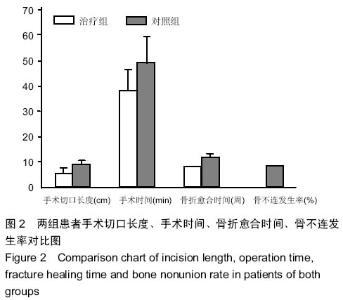
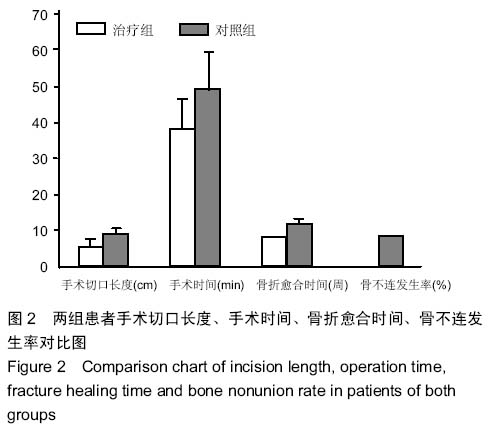
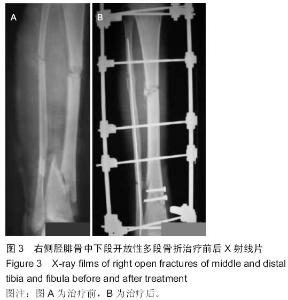
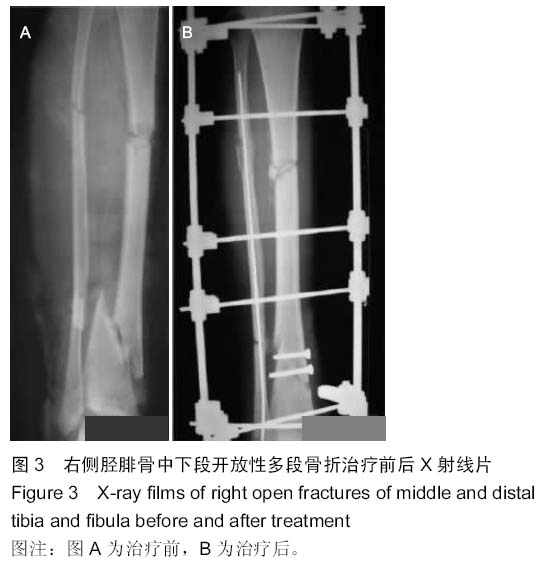
| [1] 梁红锁,黄克,李林,等.双臂外固定架结合有限切开内固定治疗胫腓骨多段开放性骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2010,13(3):352.
[2] 李金生.外固定支架结合有限内固定治疗胫腓骨多段粉碎性开放性骨折[J].吉林医学,2011,32(1):110-111.
[3] Ramlee MH, Kadir MR, Murali MR, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of two commonly used external fixators in the treatment of open subtalar dislocation-a finite element analysis.Med Eng Phys. 2014;36(10):1358-1366.
[4] 梁红锁,黄克,李林,等.双臂外固定支架结合有限内固定治疗胫骨平台开放性SchatzkerⅤ、Ⅵ型骨折[J].医学与哲学,2012,33(20): 43-44.
[5] Vives JM, Doussoux PC, Garín DM. Open fractures. Rev Traumatol. 2010;54(6):399-410.
[6] 陈文,边竟,关韶勇,等.跟骨外固定器的研制与临床应用[J].中华骨科杂志,2012,32(3):240-244.
[7] 贾文鹏,张双民,黄友祥,等.外固定支架结合有限内固定治疗开放性胫腓骨骨折56例[J]. 陕西医学杂志,2010,39(4):509.
[8] 李玉茂,谢晓勇,蔡奋忠,等.胫膝骨开放粉碎性骨折三种固定方法的疗效比较田.中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2010,25(10):942-843.
[9] 林永绥,王春,凌广烽,等.MIPPO技术治疗胫骨远端骨折的疗效观察[J].中国现代医生,2012,50(8):157-160.
[10] Penera K, Manji K, Wedel M, et al. Ankle syndesmotic fixation using two screws: risk of injury to the perforating branch of the peroneal artery. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2014;53(5):534-538.
[11] 梁红锁,黄克,李林,等.双臂外固定架结合有限切开内固定治疗胫腓骨中下段开放性粉碎性骨折[J].创伤外科杂志,2013,15(1): 75-76.
[12] Ramlee MH, Kadir MR, Murali MR, et al. Finite element analysis of three commonly used external fixation devices for treating Type III pilon fractures. Med Eng Phys. 2014;36(10): 1322-1330.
[13] 张延琴,牛志霞,郭妍,等.单侧双臂多功能外固定架加自体髂骨植骨治疗肱骨干大段骨缺损的护理[J].中华现代护理杂志,2013, 19(21):2550-2552.
[14] 李盛华.胫骨远端骨折治疗的思考[J].中国骨伤,2012,25(3): 179-183.
[15] Zhao X, Wang PF, Zhang YT, et al. [Advanced bone graft combined with locking compression plate for the treatment of middle anddistal tibia nonunion]. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2014; 27(12):1008-1011.
[16] Erdil M, Ozkunt O, Polat G, et al. Is the addition of a foot ring to the circular external fixator necessary in the treatment of extra-articular distal tibia fractures? J Orthop Trauma. 2014; 28(9):e216-220.
[17] Oh CW, Apivatthakakul T, Oh JK, et al. Bone transport with an external fixator and a locking plate for segmental tibial defects. Bone Joint J. 2013;95-B(12):1667-1672.
[18] Jha AK, Bhattacharyya A, Kumar S,et al. Evaluation of results of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) of distal tibial fractures in adults. J Indian Med Assoc. 2012;110(11): 823-824.
[19] Horn DM, Fragomen AT, Rozbruch SR. Supramalleolar osteotomy using circular external fixation with six-axis deformity correction of thedistal tibia.Foot Ankle Int. 2011; 32(10):986-993. |