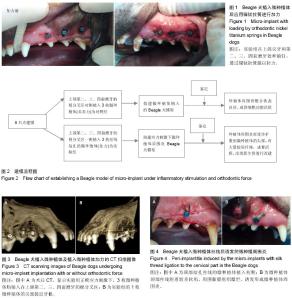
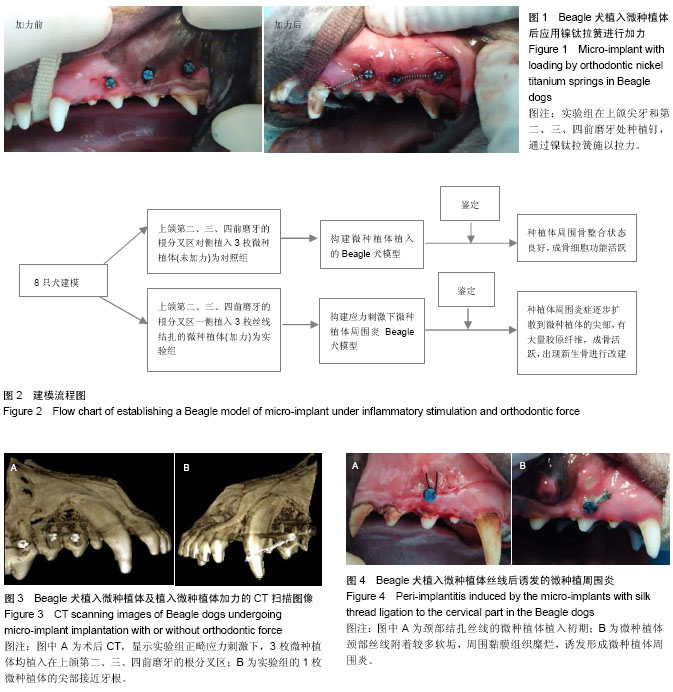
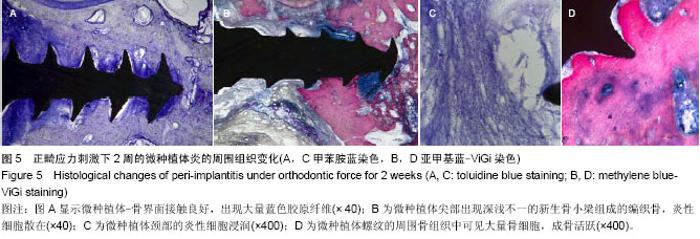
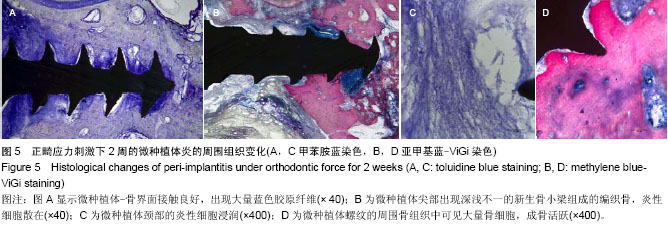
| [1] Moon CH, Lee DG, Lee HS, et al. Factors associated with the success rate of orthodontic miniscrews placed in the upper and lower posterior buccal region. Angle Orthod. 2008;78(1): 101-106.
[2] Chopra SS, Chakranarayan A. Clinical evaluation of immediate loading of titanium orthodontic implants. Med J Armed Forces India. 2015;71(2):165-170.
[3] Singh S, Mogra S, Shetty VS, et al. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of strength, stability, and stress distribution in orthodontic anchorage: a conical, self-drilling miniscrew implant system. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2012;141(3): 327-336.
[4] Chen Y, Kyung HM, Zhao WT, et al. Critical factors for the success of orthodontic mini-implants: a systematic review. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2009;135(3):284-291.
[5] Papageorgiou SN, Zogakis IP, Papadopoulos MA. Failure rates and associated risk factors of orthodontic miniscrew implants: a meta-analysis. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2012;142(5): 577-595.e7.
[6] Chang HP, Tseng YC. Miniscrew implant applications in contemporary orthodontics. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2014;30(3): 111-115.
[7] Lee J, Kim JY, Choi YJ, et al. Effects of placement angle and direction of orthopedic force application on the stability of orthodontic miniscrews. Angle Orthod. 2013;83(4): 667-673.
[8] Park, HS, Jeong SH, Kwon OW. Factors affecting the clinical success of screw implants used as orthodontic anchorage. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2006;130(1):18-25.
[9] Miyawaka S, Koyama I, Inoue M, et al. Factors associated with the stability of titanium screws placed in the posterior region for orthodontic anchorage. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2003; 124(4):373-378.
[10] 刘博,宋宁,步捷,等.种植体周围炎时的白细胞介素17:是骨保护还是骨破坏?[J].中国组织工程研究,2000,18(25):4062-4067.
[11] Esposito M, Grusovin MG, Worthington HV. Interventions for replacing missing teeth: treatment of peri-implantitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;1:CD004970.
[12] Park HS, Lee SK, Kwon OW. Group distal movement of teeth using microscrew implant anchorage. Angle Orthod. 2005; 75(4): 602-609.
[13] Nienkemper M, Wilmes B, Pauls A, et al. Multipurpose use of orthodontic mini-implants to achieve different treatment goals. J Orofac Orthop. 2012;73(6):467-476.
[14] Türköz C, Ataç MS, Tuncer C, et al. The effect of drill-free and drilling methods on the stability of mini-implants under early orthodontic loading in adolescent patients. Eur J Orthod. 2011; 33(5):533-536.
[15] 唐甜.不同愈合时间下微种植体稳定性的研究[D].成都:四川大学, 2007.
[16] Chen Y, Kang ST, Bae SM, et al. Clinical and histologic analysis of the stability of microimplants with immediate orthodontic loading in dogs. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2009;136(2):260-267.
[17] 刘雯,胡赟.邓锋,等.比格犬下颌骨微种植体的置入部位和方法[J].中国组织工程研究,2011,15(41):7635-7638.
[18] Asscherickx K, Vannet BV, Wehrbein H, et al. Root repair after injury from mini-screw. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2005;16(5): 575-578.
[19] Kuroda S, Yamada K, Deguchi T, et al. Root proximity is a major factor for screw failure in orthodontic anchorage. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2007;131(4 Suppl):S68-S73.
[20] Kadioglu O, Büyükyilmaz T, Zachrisson BU, et al. Contact damage to root surfaces of premolars touching miniscrews during orthodontic treatment. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2008;134(3):353-560.
[21] Watanabe H, Deguchi T, Hasegawa M, et al. Orthodontic miniscrew failure rate and root proximity, insertion angle, bone contact length, and bone density. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2013;16(1):44-55.
[22] Laursen MG, Melsen B, Cattaneo PM. An evaluation of insertion sites for mini-implants: a micro-CT study of human autopsy material. Angle Orthod. 2013;83(2):222-229.
[23] Estelita S, Janson G, Chiqueto K, et al. Predictable drill-free screw positioning with a graduated 3-dimensional radiographic-surgical guide: a preliminary report. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2009;136(5):722-735.
[24] Kalra S, Tripathi T, Rai P, et al. Evaluation of orthodontic mini-implant placement: a CBCT study. Prog Orthod. 2014; 15:61.
[25] Wilmes B, Su YY, Drescher D. Insertion angle impact on primary stability of orthodontic mini-implants. Angle Orthod. 2008;78(6):1065-1070.
[26] Reynders R, Ronchi L, Bipat S. Mini-implants in orthodontics: a systematic review of the literature. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2009;135(5):564.e1-e19.
[27] Gritsch K, Laroche N, Morgon L, et al. A systematic review of methods for tissue analysis in animal studies on orthodontic mini-implants. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2012;15(3):135-147.
[28] Cho UH, Yu W, Kyung HM. Root contact during drilling for microimplant placement. Affect of surgery site and operator expertise. Angle Orthod. 2010;80(1):130-136.
[29] Migliorati M, Benedicenti S, Signori A, et al. Thread shape factor: evaluation of three different orthodontic miniscrews stability. Eur J Orthod. 2013;35(3):401-405.
[30] Renvert S, Polyzois I, Persson GR. Treatment modalities for peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis. Am J Dent. 2013; 26(6):313-318.
[31] Li F, Li J, Kou H, et al. Compressive mechanical compatibility of anisotropic porous Ti6Al4V alloys in the range of physiological strain rate for cortical bone implant applications. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2015;26(9):233.
[32] Garitaonaindia U, Alcaraz JL. Influence of a micro-thread at cervical position and a cylindrical intermediate zone on the mechanical behaviour of dental implants: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2015;229(9): 670-80.
[33] Rezende CE, Chase-Diaz M, Costa MD, et al. Stress distribution in single dental implant system: three-dimensional finite element analysis based on an in vitro experimental model. J Craniofac Surg. 2015.
[34] Chevalier Y. Numerical methodology to evaluate the effects of bone density and cement augmentation on fixation stiffness of bone-anchoring devices. J Biomech Eng. 2015;137(9).
[35] Moon W, Wu KW, MacGinnis M, et al. The efficacy of maxillary protraction protocols with the micro-implant-assisted rapid palatal expander (MARPE) and the novel N2 mini-implant-a finite element study. Prog Orthod. 2015;16:16.
[36] Ruso JM, Sartuqui J, Messina PV. Multiscale Inorganic Hierarchically Materials: Towards an Improved Orthopaedic Regenerative Medicine. Curr Top Med Chem. 2015;15(22): 2290-2305.
[37] Wee H, Armstrong AD, Flint WW, et al. Peri-implant stress correlates with bone and cement morphology: Micro-FE modeling of implanted cadaveric glenoids. J Orthop Res. 2015.
[38] Mazza E, Ehret AE. Mechanical biocompatibility of highly deformable biomedical materials. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2015;48:100-124.
[39] Li F, Li J, Xu G, Liu G, et al. Fabrication, pore structure and compressive behavior of anisotropic porous titanium for human trabecular bone implant applications. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2015;46:104-114.
[40] Mattheos N, Li X, Zampelis A, et al. Investigating the micromorphological differences of the implant-abutment junction and their clinical implications: a pilot study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2015.
[41] Cha JY, Pereira MD, Smith AA, et al. Multiscale analyses of the bone-implant interface.J Dent Res. 2015;94(3):482-490.
[42] Ichim PI, Hu X, Bazen JJ, et al. Design optimization of a radial functionally graded dental implant. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2015.
[43] Penarrocha-Oltra D, Rossetti PH, Covani U, et al. Microbial leakage at the implant/abutment connection due to implant insertion maneuvers: cross-sectional study 5 years post loading in healthy patients. J Oral Implantol. 2014.
[44] Jaber SA, Taddei P, Tozzi S, et al. In vitro effects on mobile polyethylene insert under highly demanding daily activities: stair climbing. Int Orthop. 2015;39(7):1433-1440. |