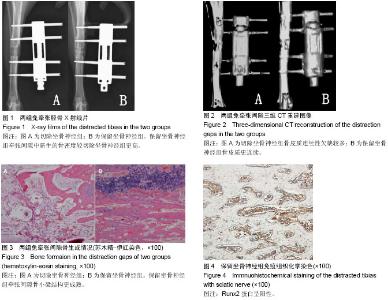
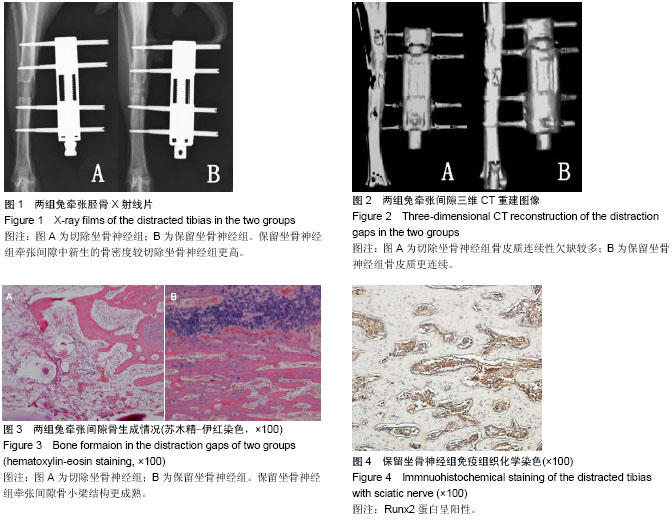
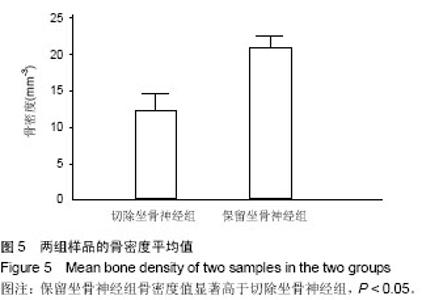
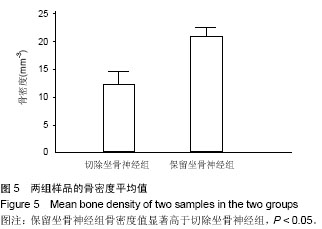
| [1] Recio JS, Álvarez-Dolado M, Díaz D, et al.Bone marrow contributes simultaneously to different neural types in the central nervous system through different mechanisms of plasticity. Cell Transplantation.2011;(20):1179-1192.
[2] Kwan P. Osteoporosis: From osteoscience to neuroscience and beyond. Mech Ageing Dev. 2015; (145):26-38.
[3] Ma WH, Liu YJ, Wang W, et al. Neuropeptide Y, substance P, and human bone morphogenetic protein 2 stimulate human osteoblast osteogenic activity by enhancing gap junction intercellular communication. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2015;48(4): 299-307.
[4] Cherruau M, Morvan FO, Schirar A, et al. Chemical sympathectomyinduced changes in TH-VIP-, and CGRP-immunoreactive fibers in the rat mandible periosteum: influence on bone resorption.Cell Physiol.2003; 194 (3): 341-348.
[5] Frymoyer J W, Pope MH. Facture healing in the sciatically denervated rat. Trauma. 1977; 17 (5): 355-361.
[6] Aro H, Eerola E, Aho A J,et al. Healing if experimental fracture in the denervated limb of the rat. Clin Orthop.1981; (155): 211-217.
[7] 顾新丰,蒋垚.RUNX2 研究进展[J].医学分子生物学杂志, 2006, 3(1):52-54.
[8] 马慧,赵红斌. Runx2蛋白与成骨细胞分化信号[J].医学综述,2007,13(24):1959-1962.
[9] Williams EH, Williams CG, Rosson GD, et al. Neurectomy for Treatment of Intercostal Neuralgia. Ann Thorac Surg. 2008; 85(5):1766-1770.
[10] 李彬,张柳.Runx2与骨代谢的调控[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2009, 15(1):63-67.
[11] 胡静,戚孟春,韩立赤,等. BMP-7基因促进大鼠下颌牵张成骨的研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2006,22(5):635-638.
[12] Ge C, Cawthorn WP, Li Y, et al. Reciprocal Control of Osteogenic and Adipogenic Differentiation by ERK/MAP Kinase Phosphorylation of Runx2 and PPARgamma Transcription Factors. J Cell Physiol. 2015 Jul 23.
[13] Sun JJ,Zheng XH,Wang LY,et al. New Bone Formation Enhanced by ADSCs Overexpressing hRunx2 During Mandibular Distraction Osteogenesis in Osteoporotic Rabbits.ORTHOP RES.2014; 32(5):709-720.
[14] Hurrell DJ. The nerve supply of bone.Anat.1937; 72(1): 54-61.
[15] Madsen JE, Hukkanen M, Aune AK,et al. Fracture healing and callus innervation after peripheral nerve resection in rats. Clin Orthop.1998; (351): 230-240.
[16] Honoré SM, Zelarayan LC, Genta SB, et al. Neuronal loss and abnormal BMP/Smad signaling in the myenteric plexus of diabetic rats. Auton Neurosci. 2011;164(1-2):51-61.
[17] Du ZJ,Wang L,Lei DL,et al. Sympathetic Denervation-Induced MSC Mobilization in Distraction Osteogenesis Associates with Inhibition of MSC Migration and Osteogenesis by Norepinephrine/adrb3. PLOS ONE.2014;9(8): e105976.
[18] Wang T,Cao J,Lei DL,et al.Effects of Sympathetic Innervation Loss on Mandibular Distraction Osteogenesis.CRANIOFAC SURG.2012; 23(5):1524-1528.
[19] 雷德林,王磊, 曹健,等.感觉神经缺失对兔下颌骨牵张成骨影的生物力学观察[J].创伤外科杂志,2009,11(3):260-263.
[20] Alzahrani MM, Anam EA, Makhdom AM,et al. The effect of altering the mechanical loading environment on the expression of bone regenerating molecules in cases of distraction osteogenesis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014;5:214.
[21] Tong H, Gao F, Yin J,et al. Transsutural Distraction Osteogenesis Applied to Maxillary Complex With New Internalized Distraction Device: Analysis of the Feasibility and Long-term Osteogenesis Outcome.J Craniofac Surg. 2015; 26(2):402-407.
[22] Satomura K, Tobiume S, Tokuyama R,et al. Melatonin at pharmacological doses enhances human osteoblastic differentiation in vitro and promotes mouse cortical bone formation in vivo. J Pineal Res.2007 ; 42(3):231-239.
[23] Persson E, Lerner UH. The neuropeptide VIP regulates the expression of osteoclastogenic factors in osteoblasts.J Cell Biochem. 2011 ;112(12):3732-3741.
[24] Zofková, Matucha P. New insights into the physiology of bone regulation: the role of neurohormones. Physiol Res.2014 ; 63(4):421-427.
[25] Long H, Ahmed M, Ackermann P,et al. Neuropeptide Y innervation during fracture healing and remodeling: A study of angulated tibial fracture in the rat. Acta Orthop.2010; 81(5): 639-646.
[26] Yu X, Lv L, Zhang J,et al.Expression of neuropeptides and bone remodeling-related factors during periodontal tissue regeneration in denervated rats. J Mol Histol. 2015;46(2): 195-203.
[27] Kingery WS, Offley SC, Guo TZ,et al. A substance P receptor (NK1) antagonist enhances the widespread osteoporotic effects of sciatic nerve section. Bone 2003; 33 (6): 927-936.
[28] Zhang YB, Wang L, Lei DL. Local injection of substance P increases bony formation during mandibular distraction osteogenesis in rats. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014; 52(8): 697-702.
[29] Hong HS, Um J, Lee ZH, et al. Long-term comparative study of Substance-P with methylprednisolone on the development of osteoporosis. The Journal of toxicological sciences. 2014; 39: 391-399.
[30] White J, Morton V, Whittington K, et al. The effects of demineralized bone matrix proteins, estrogen, and an antagonist to neuropeptide y on osteoblast and osteoclast viability and function related to osteoporosis. Biomedical sciences instrumentation. 2012;48:478-484.
[31] Lips KS, Kauschke V, Hartmann S, et al. Cholinergic nerve fibers in bone defects of a rat osteoporosis model and their regulation by implantation of bone substitution materials. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2014;14:173-188. |