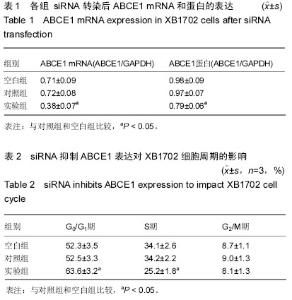
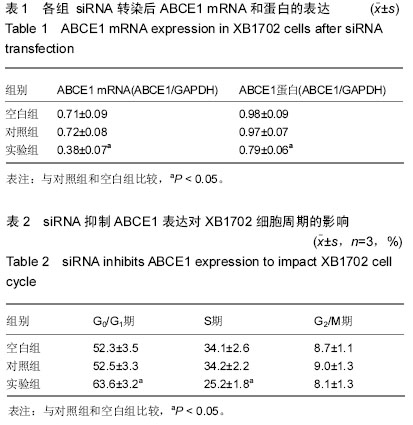
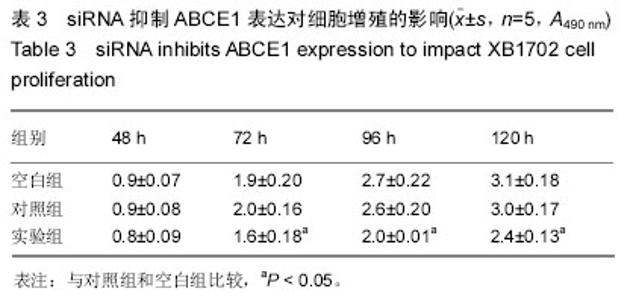
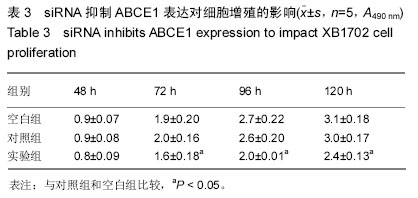
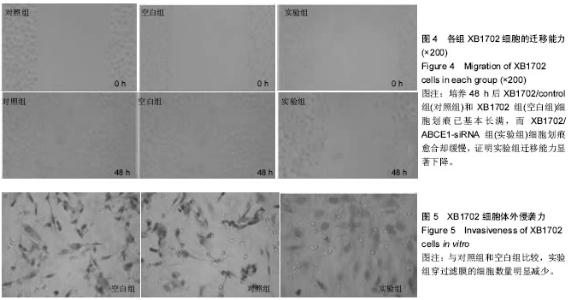
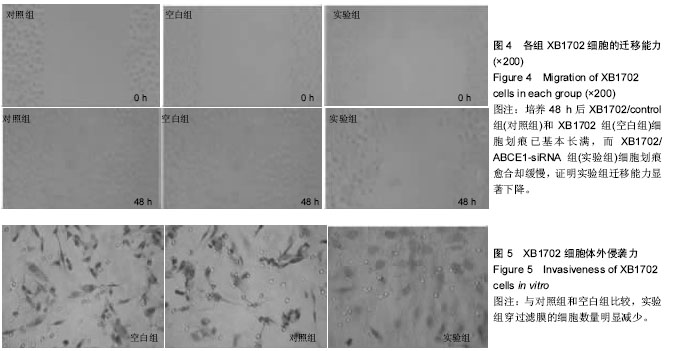
| [1] Zaman ZK, Ung NM, Malik RA, et al. Comparison of planned and measured rectal dose in-vivo during high dose rate Cobalt-60 brachytherapy of cervical cancer. Phys Med. 2014; 30(8):980-984.
[2] 朱介宾,肖亦明,孔宪和,等. 肝动脉栓塞术联合艾迪注射液与替比夫定治疗晚期原发性肝癌50例[J].医药导报,2012,31(1):25-27.
[3] Yap ML, Cuartero J, Yan J, et al. The role of elective para-aortic lymph node irradiation in patients with locally advanced cervical cancer. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2014; 26(12):797-803.
[4] Wang HC, Chow WC, Tzeng CC. Analysis of promoter methylation of four cancer-related genes in samples of cervical tissue with high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions, squamous cell carcinoma in situ, and early squamous cell carcinoma. Tzu Chi Me J. 2014;26(4):161-165.
[5] Tian Y, Han X, Tian DL.The biological regulation of ABCE1. IUBMB Life. 2012;64(10):795-800.
[6] Terova G, Rimoldi S, Bernardini G, et al. Inhibition of myostatin gene expression in skeletal muscle of fish by in vivo electrically mediated dsRNA and shRNAi delivery. Mol Biotechnol. 2013;54(2):673-684.
[7] Pisareva VP, Skabkin MA, Hellen CU, et al. Dissociation by Pelota, Hbs1 and ABCE1 of mammalian vacant 80S ribosomes and stalled elongation complexes. EMBO J. 2011;30(9):1804-1817.
[8] Ren Y, Li Y, Tian D. Role of the ABCE1 gene in human lung adenocarcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2012;27(4):965-970.
[9] 吴宁,朱博慧,薛英姿,等.干细胞生长因子反义寡核苷酸对肝癌细胞中原癌基因蛋白质c-kit及碱性成纤维细胞生长因子表达的影响[J].中华临床医师杂志:电子版,2011,5(12):3449-3454.
[10] Sims LM, Igarashi RY. Regulation of the ATPase activity of ABCE1 from Pyrococcus abyssi by Fe-S cluster status and Mg²?: implication for ribosomal function. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2012;524(2):114-122.
[11] Preis A, Heuer A, Barrio-Garcia C, et al. Cryoelectron microscopic structures of eukaryotic translation termination complexes containing eRF1-eRF3 or eRF1-ABCE1. Cell Rep. 2014;8(1):59-65.
[12] Pisarev AV, Skabkin MA, Pisareva VP, et al. The role of ABCE1 in eukaryotic posttermination ribosomal recycling. Mol Cell. 2010;37(2):196-210.
[13] 陈燕,林莺莺,陈岩松,等. 原发性肝癌早期诊断中甲胎蛋白异质体检测的意义[J].福建医药杂志,2012,34(1):3-6.
[14] Menon G, Huang F, Sloboda R, et al. Practically achievable maximum high-risk clinical target volume doses in MRI-guided intracavitary brachytherapy for cervical cancer: a planning study. Brachytherapy. 2014;13(6):572-578.
[15] 温秋婷,孙玉荣,李春红,等.成纤维细胞激活蛋白对卵巢癌细胞增殖、迁徙和侵袭的影响[J].中国癌症杂志,2011, 21(6):441-445.
[16] Campagne S, Saurel O, Gervais V, et al. Structural determinants of specific DNA-recognition by the THAP zinc finger. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38(10):3466-3476.
[17] Sabogal A, Lyubimov AY, Corn JE, et al. THAP proteins target specific DNA sites through bipartite recognition of adjacent major and minor grooves. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010;17(1): 117-123.
[18] 范宇飞,朱严冰,孟继昌,等.Survivin、p53蛋白与细胞周期蛋白D1在乳腺癌中的表达及相关性[J].临床误诊误治,2010,23(2): 101-103.
[19] 张红霞,郭佑民. 成纤维细胞活化蛋白(FAP)的研究进展[J].现代肿瘤医学,2010,18(9): 1866-1869.
[20] 邵洪江,靳占峰. FAP在胃癌间质中的表达及其与微血管密度的关系[J].国际遗传学杂志, 2010,33(3): 134-137.
[21] LeBeau AM, Brennen WN, Aggarwal S, et al. Targeting the cancer stroma with a fibroblast activation protein-activated promelittin protoxin. Mol Cancer Ther. 2009;8(5):1378-1386.
[22] Ospelt C, Mertens JC, Jüngel A, et al. Inhibition of fibroblast activation protein and dipeptidylpeptidase 4 increases cartilage invasion by rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(5):1224-1235.
[23] Xu J, Chen S, Chen H, et al. STAT5 mediates antiapoptotic effects of methylprednisolone on oligodendrocytes. J Neurosci. 2009;29(7):2022-2026.
[24] 赵志娟,米小轶,刘树立,等.FAP在乳腺癌间质中的表达及其与微血管密度的关系[J]. 中国组织化学与细胞化学杂志,2007, 16(5): 559-563.
[25] 宋敬,李越.成纤维细胞激活蛋白P和转化生长因子在子宫内膜癌组织中的表达及其意义[J].中国临床保健杂志,2010,13(5): 485-487.
[26] 曾广平.子宫颈恶性肿瘤介入治疗及护理进展[J]. 齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2011, 32(9):1454-1456.
[27] 李海侠.影响子宫颈癌根治术后并发症的因素分析[J].中国中医药咨讯,2011,3(13):353.
[28] 朱素文.子宫颈病变筛查的研究进展[J].医学理论与实践, 2011, 24(7): 774-775.
[29] 王伟,殷红梅.宫颈癌组织中Fhit、survivin和Bcl-2的表达变化及意义[J].山东医药, 2011,51(30):42-43.
[30] 胡慧敏,张广美. FHIT、WWOX蛋白在子宫内膜癌中的表达及临床意义[J].齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2010,31(17):2693-2694.
[31] Wu SR, Cheng TS, Chen WC, et al. Matriptase is involved in ErbB-2-induced prostate cancer cell invasion. Am J Pathol. 2010;177(6):3145-3158.
[32] Willmott LJ, Monk BJ. Cervical cancer therapy: current, future and anti-angiogensis targeted treatment. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2009;9(7):895-903.
[33] Monneret C. Histone deacetylase inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem. 2005;40(1):1-13.
[34] Chang TH, Szabo E. Enhanced growth inhibition by combination differentiation therapy with ligands of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma and inhibitors of histone deacetylase in adenocarcinoma of the lung. Clin Cancer Res. 2002;8(4):1206-1212. |