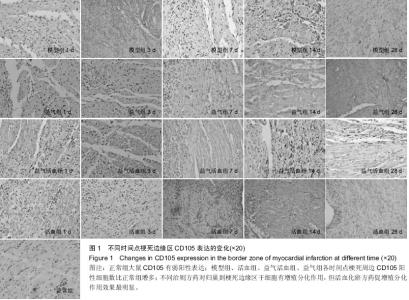
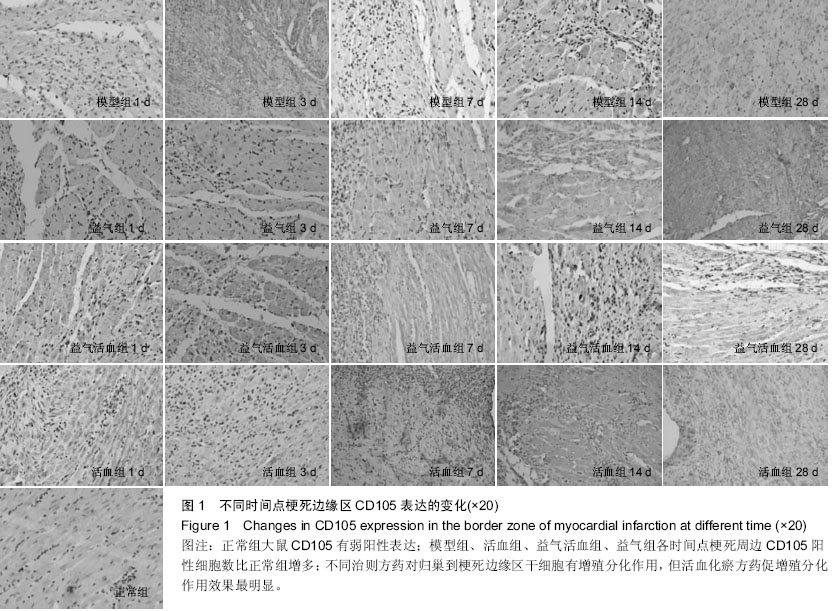
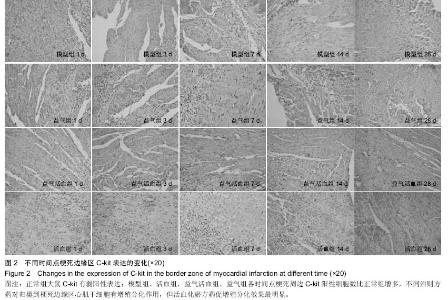
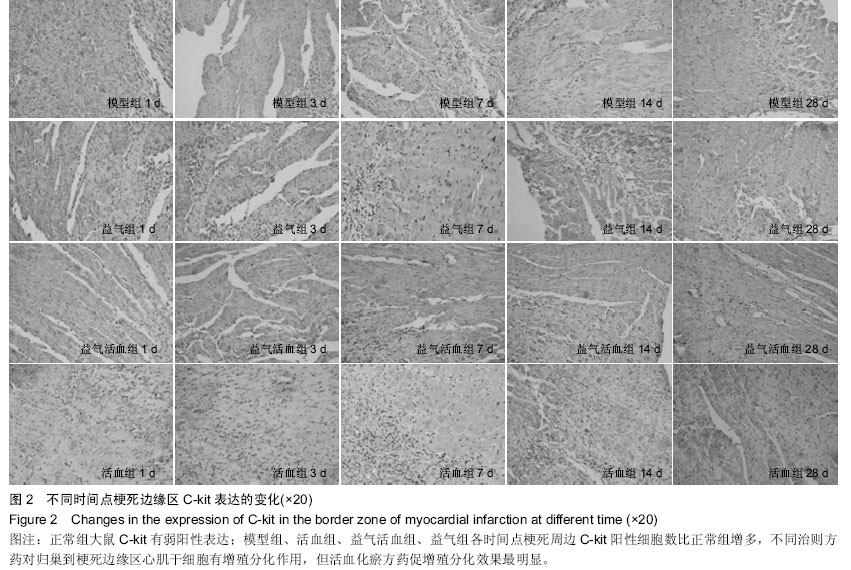
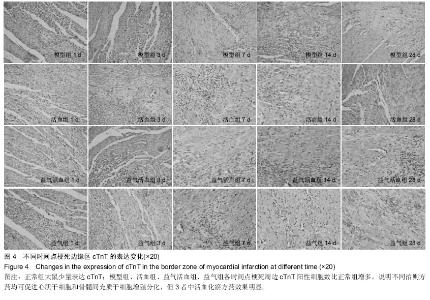
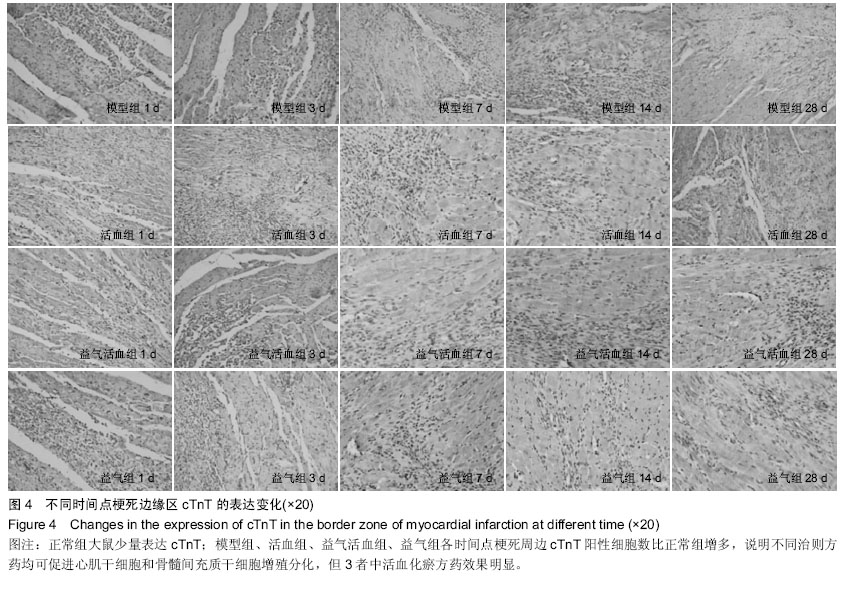
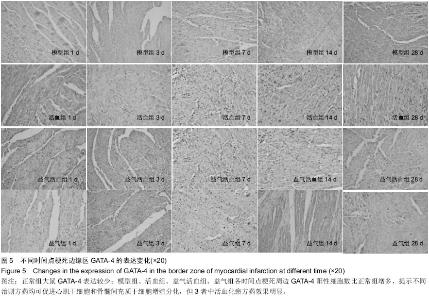
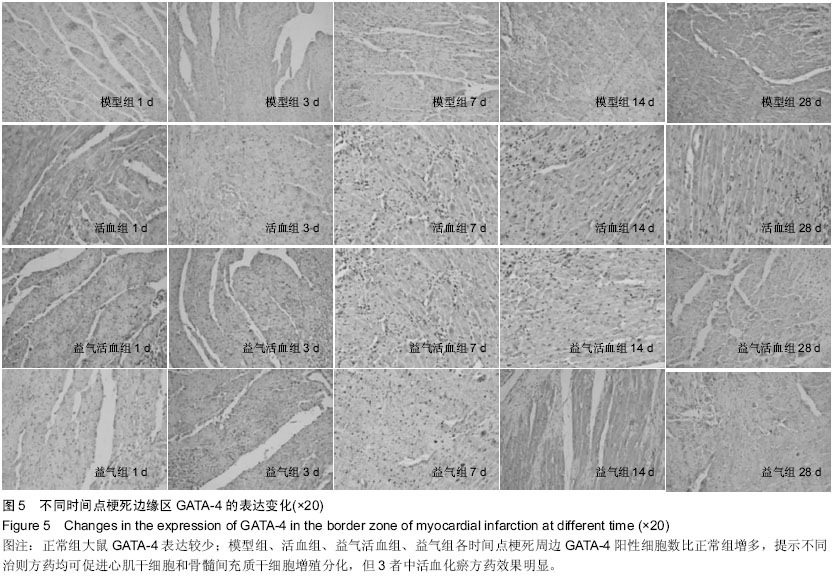
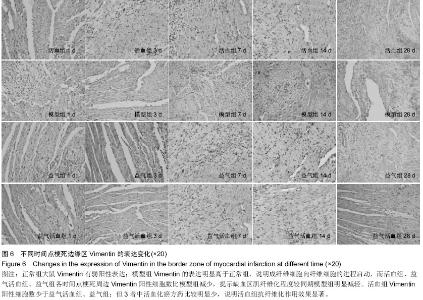
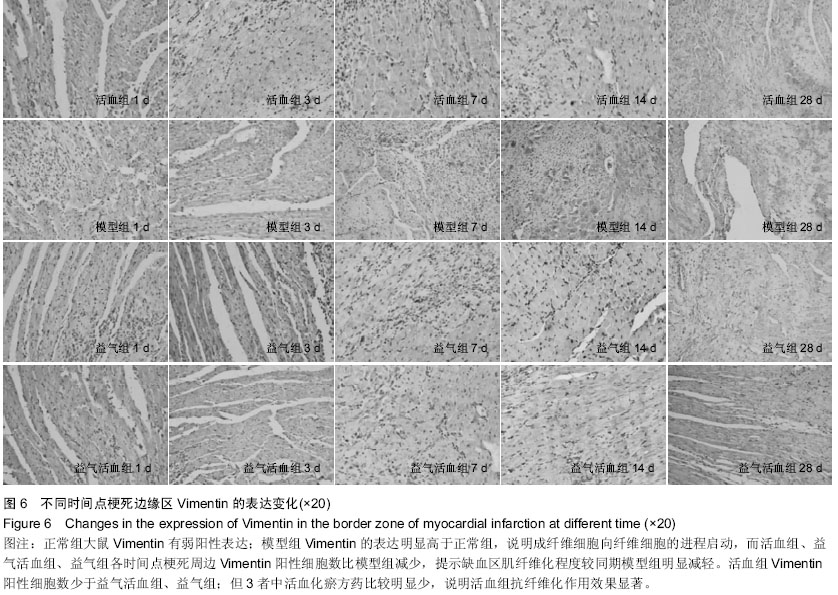
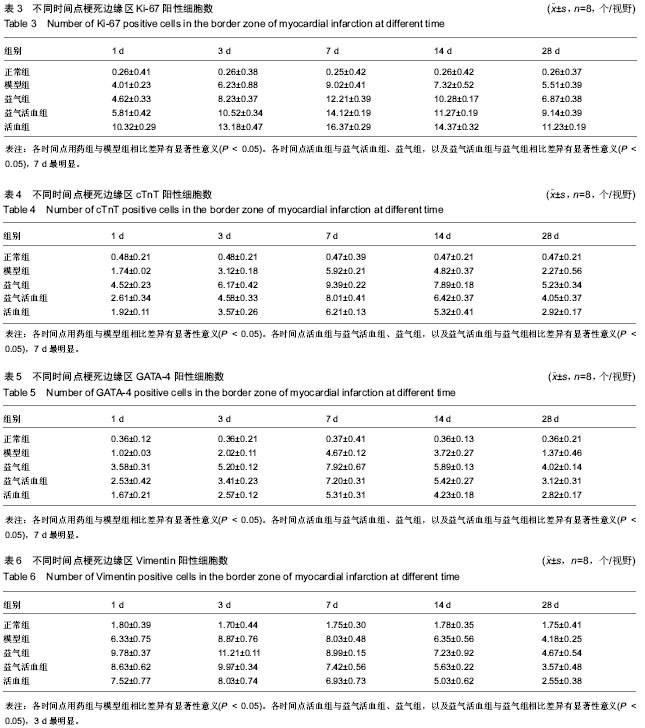
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (36): 5774-5781.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.36.007
Previous Articles Next Articles
Interventional effects of different Chinese medicine therapies on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells homing to the border zone of myocardial infarction
Zhang Jin-sheng1, Zhang Bao-xia2, Zhang Yang-yang1, Zhu Hui-fang1
- 1Third Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China; 2First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450008, Henan Province, China