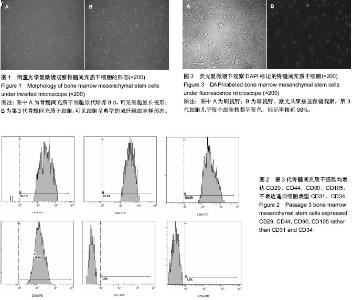
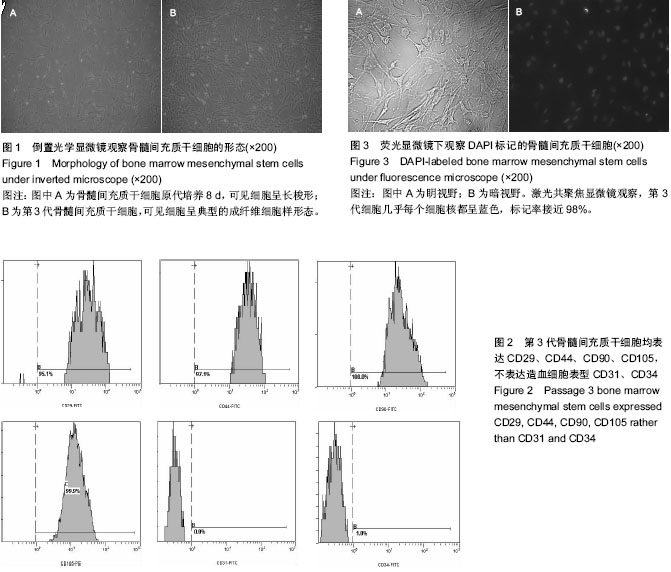
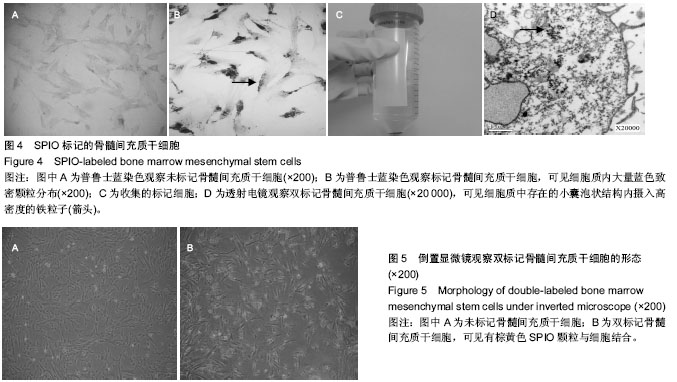
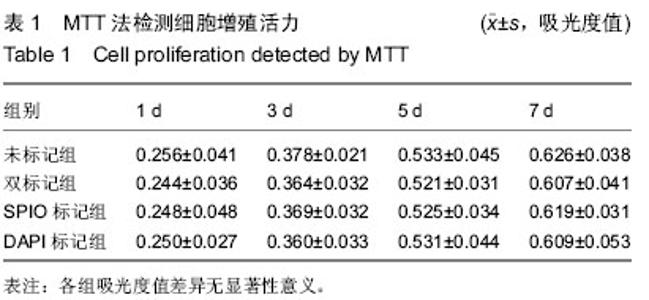
| [1] Pourrajab F, Forouzannia SK, Tabatabaee SA. Molecular characteristics of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, source of regenerative medicine. Int J Cardiol. 2013;163(2): 125-131.
[2] Urbán VS, Kiss J, Kovács J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells cooperate with bone marrow cells in therapy of diabetes. Stem Cells. 2008;26(1):244-253.
[3] Sordi V, Melzi R, Mercalli A, et al. Mesenchymal cells appearing in pancreatic tissue culture are bone marrow-derived stem cells with the capacity to improve transplanted islet function. Stem Cells. 2010;28(1):140-151.
[4] Castanheira P, Torquetti LT, Magalhãs DR, et al. DAPI diffusion after intravitreal injection of mesenchymal stem cells in the injured retina of rats. Cell Transplant. 2009;18(4): 423-431.
[5] Jiang Y, Zhang Y, Zhang L, et al. Therapeutic effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on laser-induced retinal injury in mice. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(6):9372-9385.
[6] Ji F, Duan HG, Zheng CQ, et al. Comparison of chloromethyl- dialkylcarbocyanine and green fluorescent protein for labeling human umbilical mesenchymal stem cells. Biotechnol Lett. 2015;37(2):437-447.
[7] Nagyova M, Slovinska L, Blasko J, et al. A comparative study of PKH67, DiI, and BrdU labeling techniques for tracing rat mesenchymal stem cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2014; 50(7):656-663.
[8] 林国领,叶青海,李涛,等. 应用染色体8p微卫星杂合性缺失标记观察同一肝细胞癌结节内部不同肿瘤细胞群克隆差异[J].中华实验外科杂志,2007, 24(7) :778-780.
[9] Leiker M, Suzuki G, Iyer VS, et al. Assessment of a nuclear affinity labeling method for tracking implanted mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Transplant. 2008;17(8):911-922.
[10] Bos C, Delmas Y, Desmoulière A, et al. In vivo MR imaging of intravascularly injected magnetically labeled mesenchymal stem cells in rat kidney and liver. Radiology. 2004;233(3): 781-789.
[11] Barczewska M, Wojtkiewicz J, Habich A, et al. MR monitoring of minimally invasive delivery of mesenchymal stem cells into the porcine intervertebral disc. PLoS One. 2013;8(9):e74658.
[12] Wang J, Xie J, Zhou X, et al. Ferritin enhances SPIO tracking of C6 rat glioma cells by MRI. Mol Imaging Biol. 2011;13(1): 87-93.
[13] Xie H, Zhu Y, Jiang W, et al. Lactoferrin-conjugated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as a specific MRI contrast agent for detection of brain glioma in vivo. Biomaterials. 2011;32(2):495-502.
[14] 李鹏翠,卫小春. 骨髓间充质干细胞的分离培养及体外分化[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2005,2(4):34-36.
[15] 张利,查振刚.骨髓间充质干细胞及其诱导成骨的研究进展[J].临床骨科杂志,2006,9(5)477-480.
[16] Kraitchman DL, Kedziorek DA, Bulte JW. MR imaging of transplanted stem cells in myocardial infarction. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;680:141-152.
[17] Trounson A, Thakar RG, Lomax G, et al. Clinical trials for stem cell therapies. BMC Med. 2011;9:52.
[18] Sordi V, Melzi R, Mercalli A, et al. Mesenchymal cells appearing in pancreatic tissue culture are bone marrow-derived stem cells with the capacity to improve transplanted islet function. Stem Cells. 2010;28(1):140-151.
[19] Huang ZY, Ge JB, Yang S, et al. In vivo cardiac magnetic resonance imaging of superparamagnetic iron oxides-labeled mesenchymal stem cells in swines. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2007;35(4):344-349.
[20] Zhou R, Idiyatullin D, Moeller S, et al. SWIFT detection of SPIO-labeled stem cells grafted in the myocardium. Magn Reson Med. 2010;63(5):1154-1161.
[21] Cromer Berman SM, Kshitiz, Wang CJ, et al. Cell motility of neural stem cells is reduced after SPIO-labeling, which is mitigated after exocytosis. Magn Reson Med. 2013;69(1): 255-262.
[22] Ocarino NM, Bozzi A, Pereira RD, et al. Behavior of mesenchymal stem cells stained with 4', 6-diamidino-2- phenylindole dihydrochloride (DAPI) in osteogenic and non osteogenic cultures. Biocell. 2008;32(2):175-183. |