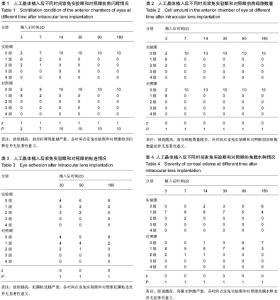
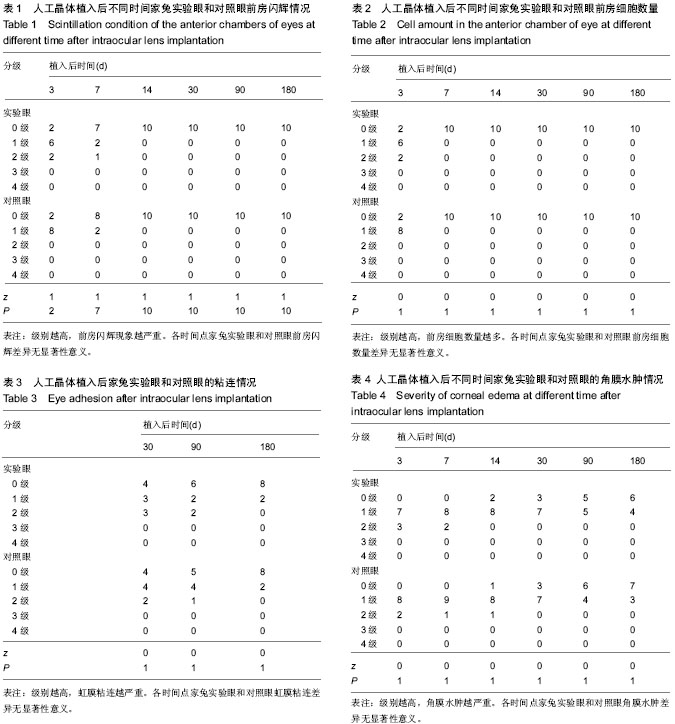
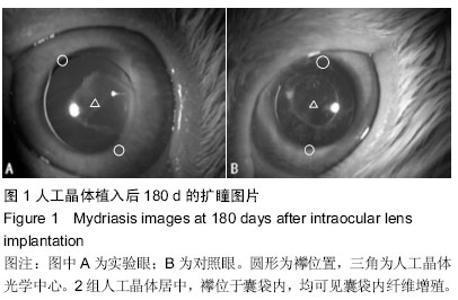
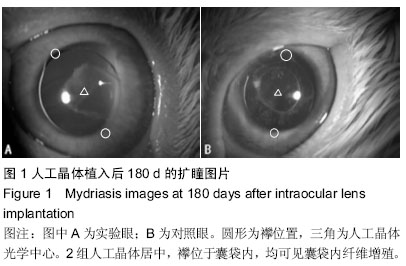
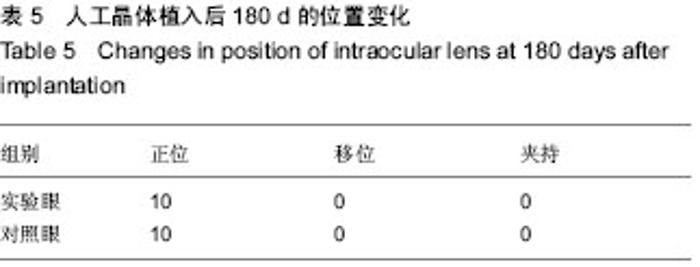
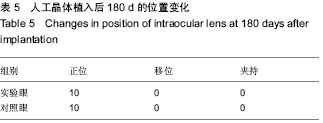
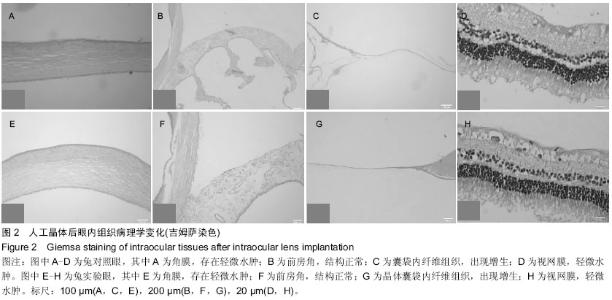
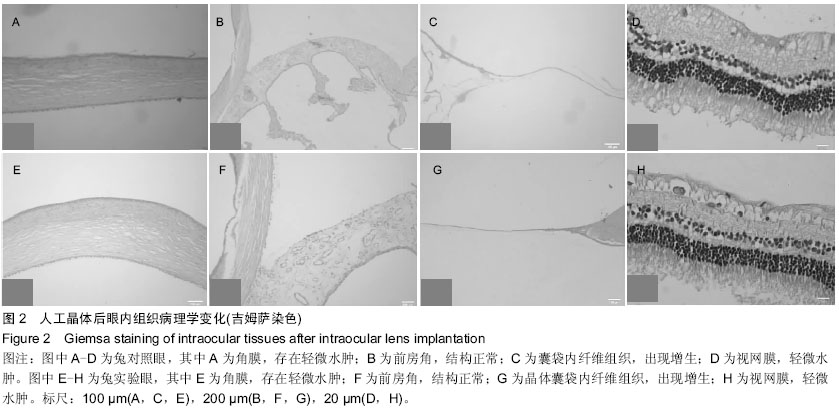
| [1] 林振德,李绍珍.小切口白内障手术[M].北京:北京人民卫生出版社,2002.
[2] 赵家良.“视觉2020”行动与我国防盲治盲工作[J].中华眼科杂志,2002,38(10):577-579.
[3] Kohnen T. Multifocal IOL technology: a successful step on the journey toward presbyopia treatment. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008;34(12):2005.
[4] Keates RH, Sall KN, Kreter JK. Effect of the Nd:YAG laser on polymethylmethacrylate, HEMA copolymer, and silicone intraocular materials. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1987;13(4): 401-409.
[5] 刘晓苏,徐美芳,郭梅清.人工晶体材料的特点及设计新进展[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(48):9793-9796.
[6] Luo M, Ji J, Zhao C, et al. Clinical study of Acrysof IQ aspheric intraocular lenses. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2010; 38(4):358-362.
[7] 中华人民共和国科学技术部.关于善待实验动物的指导性意见.2006-09-30.
[8] Mcdonald TO, Shadduck JA, Eye Irritation. In: Advances in Modern Toxicology. Volume 4: Dermatotoxicology and Pharmacology. Washington, DC: Hemisphere Publishing Corp, 1977.
[9] Gwow A. The rabbit in Cataract of IOL surgery. Anim Model Eye Res. 2008:184-206.
[10] Abela-Formanek C, Amon M, Schild G, et al. Uveal and capsular biocompatibility of hydrophilic acrylic, hydrophobic acrylic, and silicone intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002;28(1):50-61.
[11] Werner L, Mamalis N, Izak AM, et al. Posterior capsule opacification in rabbit eyes implanted with 1-piece and 3-piece hydrophobic acrylic intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005;31(4):805-811.
[12] Amon M, Menapace R. In vivo documentation of cellular reactions on lens surfaces for assessing the biocompatibility of different intraocular implants. Eye (Lond). 1994;8 ( Pt 6): 649-656.
[13] Apple DJ, Werner L. Complications of cataract and refractive surgery: a clinicopathological documentation. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 2001;99:95-107; discussion 107-109.
[14] Nishi O, Nishi K, Fujiwara T, et al. Effects of the cytokines on the proliferation of and collagen synthesis by human cataract lens epithelial cells. Br J Ophthalmol. 1996;80(1):63-68.
[15] Lee EH, Joo CK. Role of transforming growth factor-beta in transdifferentiation and fibrosis of lens epithelial cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1999;40(9):2025-2032.
[16] Nishi O, Nishi K, Wada K, et al. Expression of transforming growth factor (TGF)-alpha, TGF-beta(2) and interleukin 8 messenger RNA in postsurgical and cultured lens epithelial cells obtained from patients with senile cataracts. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1999;237(10):806-811.
[17] Shigemitsu T, Ishiguro K, Shimizu Y, et al. Immunocytochemical features of lens after cataract tissue--signalling molecules (growth factors, cytokines, other signalling molecules), cytoskeleton proteins, cellular and extracellular matrix proteins. Int Ophthalmol. 1999;23(3): 137-144.
[18] Hayashi Y, Kato S, Maeda T, et al. Immunohistologic study of interleukin-1, transforming growth factor-beta, and alpha-smooth muscle actin in lens epithelial cells in diabetic eyes. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005;31(11):2187-2192.
[19] Joo CK, Lee EH, Kim JC, et al. Degeneration and transdifferentiation of human lens epithelial cells in nuclear and anterior polar cataracts. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1999; 25(5):652-658.
[20] Gotoh N, Perdue NR, Matsushima H, et al. An in vitro model of posterior capsular opacity: SPARC and TGF-beta2 minimize epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in lens epithelium. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007;48(10): 4679-4687.
[21] Awasthi N, Wagner BJ. Suppression of human lens epithelial cell proliferation by proteasome inhibition, a potential defense against posterior capsular opacification. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006;47(10):4482-4489.
[22] Lee EH, Seomun Y, Hwang KH, et al. Overexpression of the transforming growth factor-beta-inducible gene betaig-h3 in anterior polar cataracts. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000; 41(7):1840-1845.
[23] Tognetto D, Toto L, Ballone E, et al. Biocompatibility of hydrophilic intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002; 28(4):644-651.
[24] Abela-Formanek C, Amon M, Schild G, et al. Uveal and capsular biocompatibility of hydrophilic acrylic, hydrophobic acrylic, and silicone intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002;28(1):50-61.
[25] Baillif S, Ecochard R, Hartmann D, et al. Intraocular lens and cataract surgery: comparison between bacterial adhesion and risk of postoperative endophthalmitis according to intraocular lens biomaterial. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2009;32(7):515-528.
[26] Macky TA, Pandey SK, Werner L, et al. Anterior capsule opacification. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 2001;41(3):17-31.
[27] Tognetto D, Sanguinetti G, Ravalico G. Tissue reaction to hydrophilic intraocular lenses. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2005;2(1):57-60.
[28] Saika S. Relationship between posterior capsule opacification and intraocular lens biocompatibility. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2004;23(3):283-305.
[29] Ursell PG, Spalton DJ, Pande MV, et al. Relationship between intraocular lens biomaterials and posterior capsule opacification. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1998;24(3):352-360.
[30] Yamada K, Nagamoto T, Yozawa H, et al. Effect of intraocular lens design on posterior capsule opacification after continuous curvilinear capsulorhexis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1995;21(6):697-700.
[31] Sacu S, Menapace R, Findl O, et al. Influence of optic edge design and anterior capsule polishing on posterior capsule fibrosis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004;30(3):658-662.
[32] Ollerton A, Werner L, Fuller SR, et al. Evaluation of a new single-piece 4% water content hydrophobic acrylic intraocular lens in the rabbit model. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012;38(10): 1827-1832.
[33] 姚克.复杂病例白内障手术学[M].北京:北京科学技术出版社, 2004:252.
[34] Hansen SO, Tetz MR, Solomon KD, et al. Decentration of flexible loop posterior chamber intraocular lenses in a series of 222 postmortem eyes. Ophthalmology. 1988;95(3): 344-349.
[35] Wagoner MD, Cox TA, Ariyasu RG, et al. Intraocular lens implantation in the absence of capsular support: a report by the American Academy of Ophthalmology. Ophthalmology. 2003;110(4):840-859. |