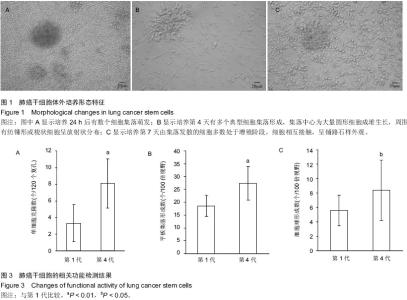
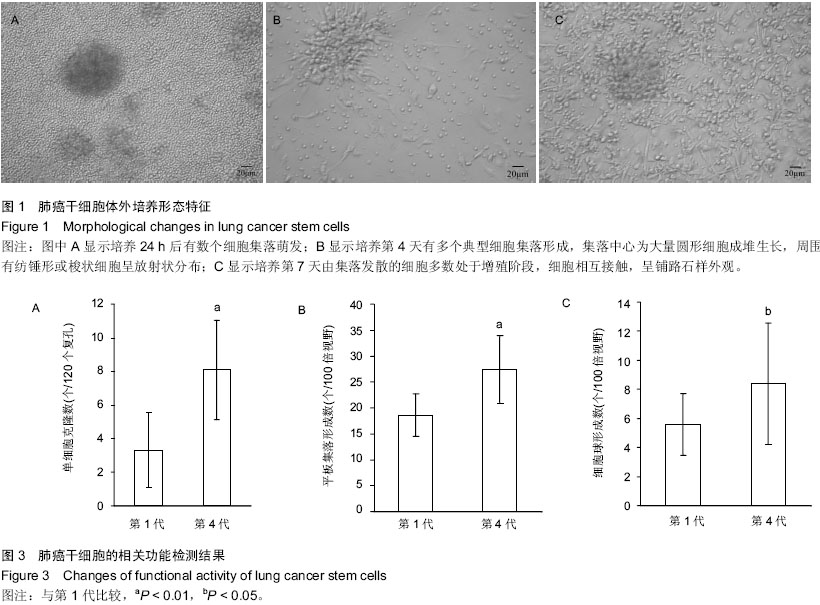
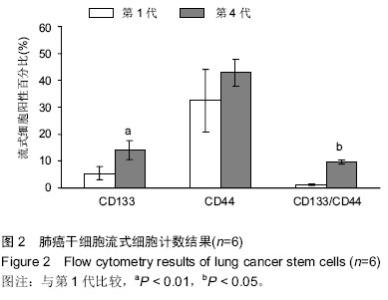
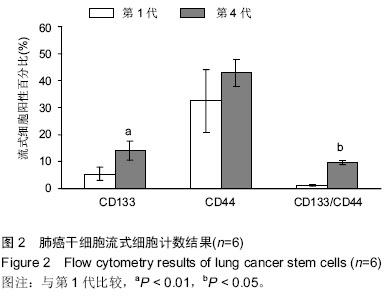
| [1] Proctor RN. Tobacco and the global lung cancer epidemic. Nat Rev Cancer. 2001;1(1):82-86.
[2] Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62(1):10-29.
[3] Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144(5):646-674.
[4] Jemal A, Thun MJ, Ries LA, et al. Annual report to the nation on the status of cancer, 1975-2005, featuring trends in lung cancer, tobacco use, and tobacco control. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008;100(23):1672-1694.
[5] Gentry SN, Jackson TL. A mathematical model of cancer stem cell driven tumor initiation: implications of niche size and loss of homeostatic regulatory mechanisms. PLoS One. 2013; 8(8):e71128.
[6] Visvader JE, Lindeman GJ. Cancer stem cells in solid tumours: accumulating evidence and unresolved questions. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8(10):755-768.
[7] Clarke MF, Dick JE, Dirks PB, et al. Cancer stem cells--perspectives on current status and future directions: AACR Workshop on cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 2006; 66(19):9339-9344.
[8] Tang DG. Understanding cancer stem cell heterogeneity and plasticity. Cell Res. 2012;22(3):457-472.
[9] Golebiewska A, Brons NH, Bjerkvig R, et al. Critical appraisal of the side population assay in stem cell and cancer stem cell research. Cell Stem Cell. 2011;8(2):136-147.
[10] Mizrak D, Brittan M, Alison M. CD133: molecule of the moment. J Pathol. 2008;214(1):3-9.
[11] Keysar SB, Jimeno A. More than markers: biological significance of cancer stem cell-defining molecules. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010;9(9):2450-2457.
[12] Chen YC, Hsu HS, Chen YW, et al. Oct-4 expression maintained cancer stem-like properties in lung cancer-derived CD133-positive cells. PLoS One. 2008;3(7):e2637.
[13] Hermann PC, Huber SL, Herrler T, et al. Distinct populations of cancer stem cells determine tumor growth and metastatic activity in human pancreatic cancer. Cell Stem Cell. 2007; 1(3):313-323.
[14] Ma S, Chan KW, Lee TK, et al. Aldehyde dehydrogenase discriminates the CD133 liver cancer stem cell populations. Mol Cancer Res. 2008;6(7):1146-1153.
[15] Miki J, Furusato B, Li H, et al. Identification of putative stem cell markers, CD133 and CXCR4, in hTERT-immortalized primary nonmalignant and malignant tumor-derived human prostate epithelial cell lines and in prostate cancer specimens. Cancer Res. 2007;67(7):3153-3161.
[16] Zhang Q, Shi S, Yen Y, et al. A subpopulation of CD133(+) cancer stem-like cells characterized in human oral squamous cell carcinoma confer resistance to chemotherapy. Cancer Lett. 2010;289(2):151-160.
[17] Matsumoto K, Arao T, Tanaka K, et al. mTOR signal and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha regulate CD133 expression in cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2009;69(18):7160-7164.
[18] Eramo A, Lotti F, Sette G, et al. Identification and expansion of the tumorigenic lung cancer stem cell population. Cell Death Differ. 2008;15(3):504-514.
[19] Du L, Wang H, He L, et al. CD44 is of functional importance for colorectal cancer stem cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2008; 14(21): 6751-6760.
[20] Shimada Y, Ishii G, Nagai K, et al. Expression of podoplanin, CD44, and p63 in squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. Cancer Sci. 2009;100(11):2054-2059.
[21] Leung EL, Fiscus RR, Tung JW, et al. Non-small cell lung cancer cells expressing CD44 are enriched for stem cell-like properties. PLoS One. 2010;5(11):e14062.
[22] Schulenburg A, Blatt K, Cerny-Reiterer S, et al. Cancer stem cells in basic science and in translational oncology: can we translate into clinical application. J Hematol Oncol. 2015; 8(1):16.
[23] Lathia JD, Venere M, Rao MS, et al. Seeing is believing: are cancer stem cells the Loch Ness monster of tumor biology. Stem Cell Rev. 2011;7(2):227-237.
[24] Park TS, Donnenberg VS, Donnenberg AD, et al. Dynamic Interactions Between Cancer Stem Cells And Their Stromal Partners. Curr Pathobiol Rep. 2014;2(1):41-52.
[25] Wang P, Gao Q, Suo Z, et al. Identification and characterization of cells with cancer stem cell properties in human primary lung cancer cell lines. PLoS One. 2013;8(3): e57020.
[26] Pacini N, Borziani F. Cancer stem cell theory and the warburg effect, two sides of the same coin. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(5): 8893-8930.
[27] Ciurea ME, Georgescu AM, Purcaru SO, et al. Cancer stem cells: biological functions and therapeutically targeting. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(5):8169-8185. |