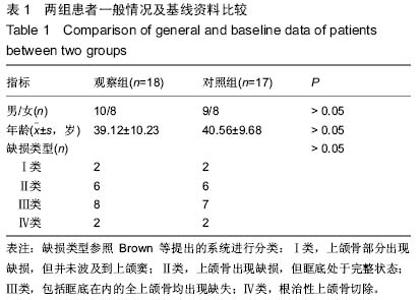
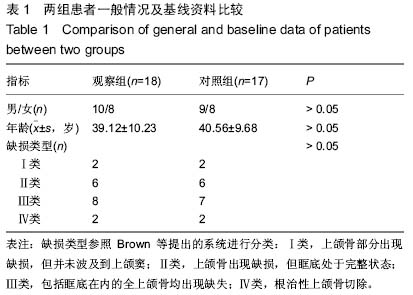
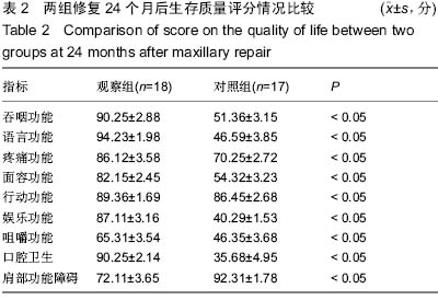
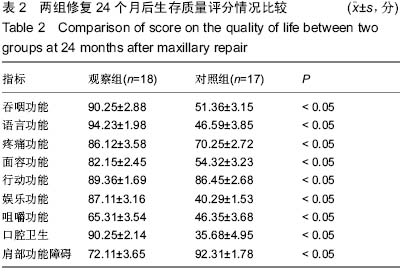
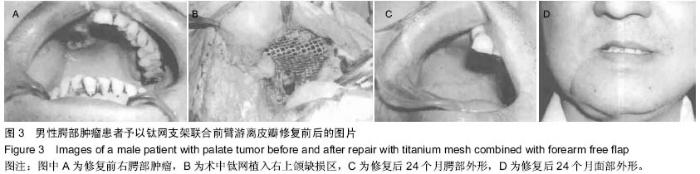
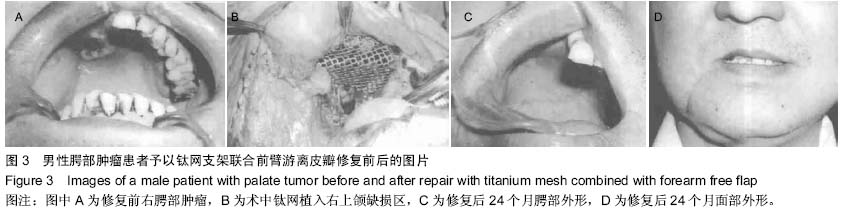
| [1] 张凯,徐涛,徐锦程,等.颞肌蒂下颌骨瓣联合前臂皮瓣一期修复腭上颌缺损[J].中华显微外科杂志,2012,35(4):272-275,后插2.
[2] 铁瑛,王冬梅,吴佚群,等.上颌骨缺损颧种植体功能设计及生物力学评价[J].上海交通大学学报,2006,40(8):1438-1443.
[3] 李建成,廖圣恺,陈永峰,等.游离前臂皮瓣、颊脂垫双重修复上颌缺损术后患者生存质量的评价[J].蚌埠医学院学报,2012,37(12): 1421-1423.
[4] 孙坚,李军,张志愿,等.上颌骨大型缺损的个体化三维闭合式功能性重建[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2003,1(1):3-7.
[5] 张森林,孟昭业,董震,等.游离前臂皮瓣与钛网联合修复上颌骨缺损[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2004,18(6):459-461.
[6] 张森林,孟昭业,曹罡,等.前臂皮瓣联合钛网和颊脂垫修复口腔癌术后的上颌骨缺损[J].口腔医学,2008,28(11):584-586.
[7] 李军,孙坚,马宏涛,等.个体化钛支架在构筑颌骨三维形态中的应用[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2003,13(1):17-20.
[8] Brown JS,Roger SN,McNally DN,et al.A modified classification for the maxillectomy defect.Head Neck.2000; 22(1):17.
[9] 朱良明,陶德韬,吴非非,等.钛网成形在颌骨缺损修复中的应用[J].皖南医学院学报,2010,29(5):365-366.
[10] 张森林,孟兆业,程娟,等.前臂皮瓣与钛网联合修复上颌骨缺损病人的术后护理[J].护理学杂志,2004,19(16):38-39.
[11] 胡晓光,雷德林.钛网加松质重建上颌骨及下颌骨缺损(跟踪报道2)[C].//第五届全国口腔颅颌面修复重建外科学术会议暨国际研讨会论文集,2013:152-153.
[12] 马宏涛,孙坚,李军,等.上颌骨三维重建术后患者咀嚼功能的评价[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2005,23(1):29-31.
[13] 羊书勇,郑维银,李晨军,等.3D 打印个性化钛网结合游离皮瓣修复上颌缺损的探索[J].西南国防医药,2014,24(10):1052-1055.
[14] 温立婷,乔莉,陈福权,等.赝复体钛网同期植入修复上颌骨切除后眶面部缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(21):3968-3974.
[15] 李俊,姚金光,陈海波,等.上颌骨大型缺损个体化三维闭合性功能重建[J].右江民族医学院学报,2005,27(4):453-456.
[16] 赵延峰,陆平,周晓南,等.成型钛网联合Medpor治疗严重颧上颌复合体骨折后眼球内陷畸形[J].中华整形外科杂志,2010, 26(2): 96-98.
[17] 张伟.改良面中翻径路同期钛网塑形重建全上颌骨切除术后缺损畸形[J].临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志,2007,21(12):564-565.
[18] 胡永杰,张陈平.应用钛网支架重建上颌骨肿瘤切除术后缺损畸形[J].上海口腔医学,2002,11(1):28-31.
[19] 王丽萍,张树标,范长斌,等.钛网连接固定种植体增强初期稳定性的临床应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(25): 4701-4705.
[20] 商洪涛,雷德林,刘彦普,等.颞肌瓣加预制钛网复合松质骨Ⅰ期重建上颌骨缺损[J].中国美容医学,2004,13(1):58-59.
[21] Bing-Yan Wang,Robin Weltman,Jared Abramian,等.钛网结合异体骨移植和人骨形成蛋白在上颌前牙种植前牙槽嵴骨增量中的应用研究(附1例报告)[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2014,7(1): 24-27.
[22] 沈毅,孙坚,李军,等.上颌骨功能性重建中用钛植入体重建颧上颌支柱的生物力学研究[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2011,9(3): 198-203.
[23] 严君烈,陈关福,刘雁鸣,等.预成钛网结合颊脂垫瓣和自体植骨修复上颌骨缺损[J].中华整形外科杂志,2007,23(6):469-472.
[24] 姜润松,胡蓉,赵雄,等.计算机辅助制作个性化钛网修复面斜裂骨缺损一例[J].中华整形外科杂志,2011,27(3):232-234.
[25] 董震,张森林,孟昭业,等.游离前臂皮瓣修复上颌部和腭部缺损[J].医学研究生学报,2004,17(5):474-475.
[26] 盛健峰.人工钛网修复上颌窦壁粉碎性骨折伴缺损的效果观察[J].实用医院临床杂志,2014,11(4):172-173.
[27] 孙坚,沈毅,李军,等.上颌骨功能性修复中骨性支柱重建的生物力学分析[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2010,8(1):34-39.
[28] 姚金光,李龙江,李俊,等.带蒂颊脂垫衬里与颞肌筋膜瓣联合钛网重建上颌骨缺损[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2006,24(1):57-59.
[29] 李建虎,孙沫逸,陆斌,等.新型三维钛网在眶底缺损重建整形手术中的应用[J].中国美容医学,2007,16(2):222-224.
[30] 孙坚,沈毅,李军,等.应用腓骨肌皮瓣结合钛网或颧种植体行单侧全上颌骨缺损重建[C].//2013年全国第五届口腔颌面外科修复重建学术会议暨国际研讨会论文集,2013:174-175.
[31] 孙坚,李军,张志愿,等.钛网与前臂游离皮瓣闭合式三维重建上颌骨缺损[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2002,18(4):291-293.
[32] 毕晓萍,范先群,施沃栋,等.三维眶底重建钛网在复合性眼眶骨折中的应用[J].中华眼科杂志,2011,47(8):683-687.
[33] 温立婷,石照辉,陈福权,等.同期钛网移植矫正上颌骨全切术后面部畸形[C].//第十四届全军耳鼻咽喉头颈外科学术大会论文集, 2011:212-212.
[34] 胡晓光,雷德林.钛网加松质重建上颌骨及下颌骨缺损(跟踪报道2)[C].//2013年全国第五届口腔颌面外科修复重建学术会议暨国际研讨会论文集,2013:28-29.
[35] 陈丹,杨凯,陈睿,等.两种游离皮瓣在口腔颌面部恶性肿瘤术后缺损修复中的应用[J].重庆医学,2014,43(12):1445-1447,1451.
[36] 李建成,廖圣恺,卢保全,等.颊脂垫与游离前臂皮瓣联合移植修复上颌缺损[J].中华显微外科杂志,2006,29(6):457-458.
[37] 于洪波,王旭东,张诗雷,等.计算机辅助导航技术在上颌骨肿瘤切除及缺损重建中的应用[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2013, 11(6): 472-476.
[38] 黄光磊,罗洪,赵科,等.钛网成形加游离组织瓣移植即刻修复上颌骨大部缺损[J].贵阳医学院学报,2003,28(4):373-374.
[39] 翁雁秋,孙坚,陈阳,等.上颌骨缺损手术重建与赝复体修复的语音功能评价[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2005,3(1):43-47.
[40] 孙国文,杨旭东,胡勤刚,等.应用钛网支架及前臂游离皮瓣修复上颌部肿瘤切除后洞穿缺损[J].中华整形外科杂志,2009,25(4): 251-254. |