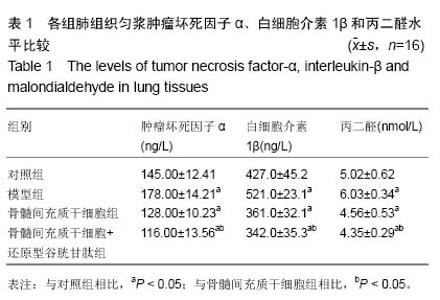
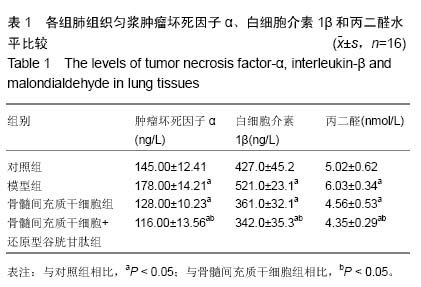
| [1] Tsoutsou PG, Koukourakis MI. Radiation pneumonitis and fibrosis: mechanisms underlying its pathogenesis and implications for future research. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006;66(5):1281-1293.
[2] Chen Y, Williams J, Ding I, et al. Radiation pneumonitis and early circulatory cytokine markers. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2002; 12(1 Suppl 1):26-33.
[3] Krause DS, Theise ND, Collector MI, et al. Multi-organ, multi-lineage engraftment by a single bone marrow-derived stem cell. Cell. 2001;105(3):369-377.
[4] Kotton DN, Ma BY, Cardoso WV, et al. Bone marrow-derived cells as progenitors of lung alveolar epithelium. Development. 2001;128(24):5181-5188.
[5] 王莉,方妮,张伟京,等.骨实质来源间质干细胞对博莱霉素诱导小鼠肺损伤的保护作用[J].解放军医学杂志,2008,33(10): 1220-1224.
[6] Dillioglugil MO, Ilgazli A, Maral H, et al. Protective effects of N-acetylcysteine on the peroxidative changes of rat lungs exposed to inhalation of thinners. Respirology. 2005;10(5):615-619.
[7] Ritter C, da Cunha AA, Echer IC, et al. Effects of N-acetylcysteine plus deferoxamine in lipopolysaccharide- induced acute lung injury in the rat. Crit Care Med. 2006;34(2): 471-477.
[8] Usuki J, Matsuda K, Azuma A, et al. Sequential analysis of myofibroblast differentiation and transforming growth factor-β1/Smad pathway activation in murine pulmonary fibrosis. J Nippon Med Sch. 2012;79(1):46-59.
[9] Zhao F, Zhang YF, Liu YG, et al. Therapeutic effects of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells engraftment on bleomycin-induced lung injury in rats. Transplant Proc. 2008; 40(5):1700-1705.
[10] Shi Y, Su J, Roberts AI, et al. How mesenchymal stem cells interact with tissue immune responses. Trends Immunol. 2012; 33(3):136-143.
[11] Rojas M, Xu J, Woods CR, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in repair of the injured lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2005;33(2):145-152.
[12] Aslam M, Baveja R, Liang OD, et al. Bone marrow stromal cells attenuate lung injury in a murine model of neonatal chronic lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009; 180(11): 1122-1130.
[13] Gomez-de-Antonio D, Zurita M, Santos M, et al. Stem cells and bronchial stump healing. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2010; 140(6):1397-1401.
[14] Wang L, Tu XH, Zhao P, et al. Protective effect of transplanted bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells on pancreatitis-associated lung injury in rats. Mol Med Rep. 2012; 6(2):287-292.
[15] 康新勤,藏伟进,宋土生,等.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞分离培养及其形态观察[J].西安交通大学学报:医学版,2003,24(5):518-519.
[16] Haddad JJ, Olver RE, Land SC. Antioxidant/pro-oxidant equilibrium regulates HIF-1alpha and NF-kappa B redox sensitivity. Evidence for inhibition by glutathione oxidation in alveolar epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(28):21130- 21139.
[17] Slater AF, Stefan C, Nobel I, et al. Signalling mechanisms and oxidative stress in apoptosis. Toxicol Lett. 1995;82-83: 149-153.
[18] 金婧,董淑红,苏力,等.新生大鼠内毒素性急性肺损伤肺组织 MDA、SOD和IL-10、IL-18的改变[J].新生儿科杂志, 2004,19(2): 69-72. |