Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (18): 2874-2878.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.18.015
Previous Articles Next Articles
Expression of hepatic energy proteins following reduced-size liver transplantation in rats
Liu Jing, Li Li, Ran Jiang-hua, Zhang Sheng-ning, Li Lai-bang, Zhang Xi-bing, Gao Yang, Chen Yi-ming
- Department of Hepato-biliary-pancreatic Surgery, the First People’s Hospital of Kunming and the Ganmei Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650011, Yunnan Province, China
-
Received:2015-02-03Online:2015-04-30Published:2015-04-30 -
Contact:Li Li, Chief physician, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Hepato-biliary-pancreatic Surgery, the First People’s Hospital of Kunming and the Ganmei Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650011, Yunnan Province, China -
About author:Liu Jing, M.D., Department of Hepato-biliary-pancreatic Surgery, the First People’s Hospital of Kunming and the Ganmei Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650011, Yunnan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Jing, Li Li, Ran Jiang-hua, Zhang Sheng-ning, Li Lai-bang, Zhang Xi-bing, Gao Yang, Chen Yi-ming. Expression of hepatic energy proteins following reduced-size liver transplantation in rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(18): 2874-2878.
share this article
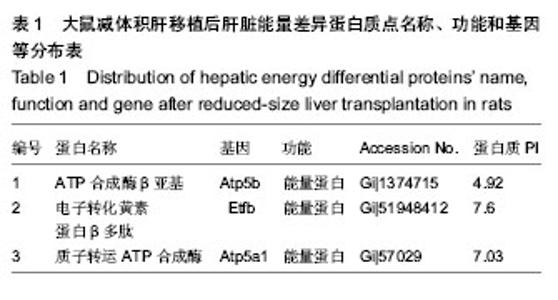
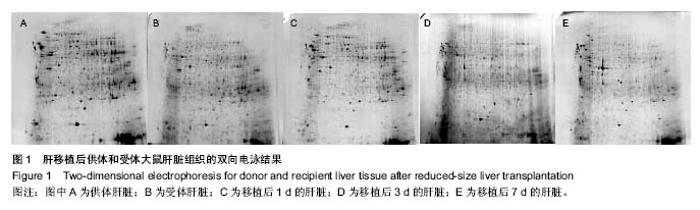
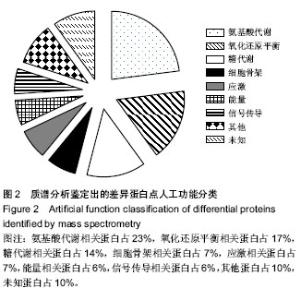
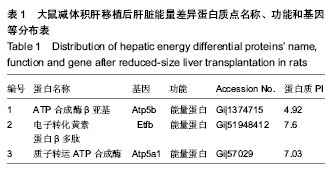
2.1 实验动物数量分析 构建大鼠减体积肝移植模型的过程中出现的死亡大鼠,都进行补足,最终共有供体和受体各12只大鼠进入结果分析。 2.2 大鼠减体积肝移植模型后肝脏能量差异蛋白的表达变化 双向电泳中平均从每张胶上可以检测到大约1 000个的蛋白点,以变化倍数大于10倍或小于0.1倍为标准进行差异蛋白点的选择,实验中总共发现了72个差异点,然后用MS-MS串联质谱分析鉴定,所有的差异点都得到了成功的鉴定(图1),共鉴定到了40个差异蛋白,其中功能比较明确的有32个蛋白质,功能并不是很明确有3个,还鉴定到了5个未知的蛋白质。初步鉴定到的差异蛋白质(以人工蛋白质功能分类为标准)中参与细胞能量过程的蛋白质主要有3种,其主要分布于肝移植后的第1,7天,占6%(图2,表1)。"
| [1] Brewis IA, Brennan P. Proteomics technologies for the global identification and quantification of proteins. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2010;80:1-44. [2] Woods AG, Ngounou Wetie AG, Sokolowska I, et al. Mass spectrometry as a tool for studying autism spectrum disorder. J Mol Psychiatry. 2013;1(1):6. [3] Woods AG, Wormwood KL, Wetie AG, et al. Autism spectrum disorder: An omics perspective. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2014. in press. [4] Mayer G, Jones AR, Binz PA, et al. Controlled vocabularies and ontologies in proteomics: overview, principles and practice. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1844(1 Pt A):98-107. [5] Dowling P, Hayes C, Ting KR, et al. Identification of proteins found to be significantly altered when comparing the serum proteome from Multiple Myeloma patients with varying degrees of bone disease. BMC Genomics. 2014; 15:904. [6] Pooladi M, Abad SK, Hashemi M. Proteomics analysis of human brain glial cell proteome by 2D gel. Indian J Cancer. 2014;51(2):159-162. [7] Hashemi M, Pooladi M, Razi Abad SK. The investigation of changes in proteins expression (Apolipoprotein A1 and albumin) in malignant astrocytoma brain tumor. J Cancer Res Ther. 2014;10(1):107-111. [8] Kienzl-Wagner K, Pratschke J, Brandacher G. Proteomics--a blessing or a curse? Application of proteomics technology to transplant medicine. Transplantation. 2011;92(5):499-509. [9] Kienzl-Wagner K, Pratschke J, Brandacher G. Biomarker discovery in transplantation--proteomic adventure or mission impossible? Clin Biochem. 2013;46(6):497-505. [10] Cohen Freue GV, Meredith A, Smith D, et al. Computational biomarker pipeline from discovery to clinical implementation: plasma proteomic biomarkers for cardiac transplantation. PLoS Comput Biol. 2013;9(4):e1002963. [11] Metzger J, Chatzikyrkou C, Broecker V, et al. Diagnosis of subclinical and clinical acute T-cell-mediated rejection in renal transplant patients by urinary proteome analysis. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2011;5(5-6):322-333. [12] Kim SC, Page EK, Knechtle SJ. Urine proteomics in kidney transplantation. Transplant Rev (Orlando). 2014;28(1): 15-20. [13] Halawa A. The early diagnosis of acute renal graft dysfunction: a challenge we face. The role of novel biomarkers. Ann Transplant. 2011;16(1):90-98. [14] Sigdel TK, Salomonis N, Nicora CD, et al. The identification of novel potential injury mechanisms and candidate biomarkers in renal allograft rejection by quantitative proteomics. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2014;13(2):621-631. [15] Pisitkun T, Gandolfo MT, Das S, et al. Application of systems biology principles to protein biomarker discovery: urinary exosomal proteome in renal transplantation. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2012;6(5-6):268-278. [16] Hossain MA, De Souza AI, Bagul A, et al. HSP70, Peroxiredoxin-3 and -6 are upregulated during renal warm ischaemia in a donation after circulatory death model. J Proteomics. 2014;108:133-145. [17] Kornasiewicz O, Bojarczuk K, Bugajski M, et al. Application of a proteomic approach to identify proteins associated with primary graft non-function after liver transplantation. Int J Mol Med. 2012;30(4):755-764. [18] Baker ES, Burnum-Johnson KE, Jacobs JM, et al. Advancing the high throughput identification of liver fibrosis protein signatures using multiplexed ion mobility spectrometry. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2014;13(4):1119-1127. [19] 刘静,李江,张升宁,等.改良法构建大鼠减体积肝移植模型[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复杂志,2010,14(18):3252-3257. [20] Jing L, Li L, Jiang-Hua R, et al. A causal analysis of intra- abdominal hemorrhage after reduced-size liver transplantation in rat. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2011;61(3):685-690. [21] Okayama A, Miyagi Y, Oshita F, et al. Proteomic analysis of proteins related to prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma. J Proteome Res. 2014;13(11):4686-4694. [22] Kim MS, Pinto SM, Getnet D, et al. A draft map of the human proteome. Nature. 2014;509(7502):575-581. [23] Wilhelm M, Schlegl J, Hahne H, et al. Mass-spectrometry- based draft of the human proteome. Nature. 2014;509(7502): 582-587. [24] Rigbolt KT, Prokhorova TA, Akimov V, et al. System-wide temporal characterization of the proteome and phosphoproteome of human embryonic stem cell differentiation. Sci Signal. 2011;4(164):rs3. [25] Mardinoglu A, Kampf C, Asplund A, et al. Defining the human adipose tissue proteome to reveal metabolic alterations in obesity. J Proteome Res. 2014;13(11):5106-5119. [26] Martins-de-Souza D. Proteomics, metabolomics, and protein interactomics in the characterization of the molecular features of major depressive disorder. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2014; 16(1):63-73. [27] Sleddering MA, Markvoort AJ, Dharuri HK, et al. Proteomic Analysis in Type 2 Diabetes Patients before and after a Very Low Calorie Diet Reveals Potential Disease State and Intervention Specific Biomarkers. PLoS One. 2014;9(11): e112835. [28] Jov?evska I, Zupanec N, Ko?evar N, et al. TRIM28 and β-Actin Identified via Nanobody-Based Reverse Proteomics Approach as Possible Human Glioblastoma Biomarkers. PLoS One. 2014;9(11):e113688. [29] Webb-Robertson BJ, Matzke MM, Datta S, et al. Bayesian proteoform modeling improves protein quantification of global proteomic measurements. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2014;13(12): 3639-3646. [30] Dallas DC, Guerrero A, Parker EA, et al. Current peptidomics: Applications, purification, identification, quantification and functional analysis. Proteomics. 2014. in press. [31] Dong Y, Cai J, Chen S. Proteomics of drug-resistant cancer biomarkers. Bioanalysis. 2014;6(19):2519-2521. [32] Tang B, Li Y, Zhao L, et al. Stable isotope dimethyl labeling combined with LTQ mass spectrometric detection, a quantitative proteomics technology used in liver cancer research. Biomed Rep. 2013;1(4):549-554. [33] Sharma S, Ray S, Mukherjee S, et al. Multipronged quantitative proteomic analyses indicate modulation of various signal transduction pathways in human meningiomas. Proteomics. 2014. in press. [34] Hirokawa S, Shimanuki T, Kitajima H, et al. Knockdown of electron transfer flavoprotein β subunit reduced TGF-β-induced α-SMA mRNA expression but not COL1A1 in fibroblast-populated three-dimensional collagen gel cultures. J Dermatol Sci. 2012;68(3):179-186. [35] Malecki J, Ho AY, Moen A, et al. Human METTL20 is a Mitochondrial Lysine Methyltransferase that Targets the Beta Subunit of Electron Transfer Flavoprotein (ETFβ) and Modulates Its Activity. J Biol Chem. 2014. in press. [36] Rhein VF, Carroll J, He J, et al. Human METTL20 methylates lysine residues adjacent to the recognition loop of the electron transfer flavoprotein in mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 2014;289 (35): 24640-24651. [37] Kasumov EA, Kasumov RE, Kasumova IV. A mechano- chemiosmotic model for the coupling of electron and proton transfer to ATP synthesis in energy-transforming membranes: a personal perspective. Photosynth Res. 2014. in press. [38] Schertl P, Braun HP. Respiratory electron transfer pathways in plant mitochondria. Front Plant Sci. 2014;5:163. [39] Morelli AM, Ravera S, Calzia D, et al. Hypothesis of lipid-phase-continuity proton transfer for aerobic ATP synthesis. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2013;33(12):1838-1842. [40] Koumandou VL, Kossida S. Evolution of the F0F1 ATP synthase complex in light of the patchy distribution of different bioenergetic pathways across prokaryotes. PLoS Comput Biol. 2014;10(9):e1003821. [41] Falk G, Walker JE. DNA sequence of a gene cluster coding for subunits of the F0 membrane sector of ATP synthase in Rhodospirillum rubrum. Support for modular evolution of the F1 and F0 sectors. Biochem J. 1988;254(1):109-122. [42] von Ballmoos C, Wiedenmann A, Dimroth P. Essentials for ATP synthesis by F1F0 ATP synthases. Annu Rev Biochem. 2009;78:649-672. [43] Dimroth P, Kaim G, Matthey U. Crucial role of the membrane potential for ATP synthesis by F(1)F(o) ATP synthases. J Exp Biol. 2000;203(Pt 1):51-59. [44] Arakaki N, Nagao T, Niki R, et al. Possible role of cell surface H+ -ATP synthase in the extracellular ATP synthesis and proliferation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Mol Cancer Res. 2003;1(13):931-99. [45] Fillingame RH. Coupling H+ transport and ATP synthesis in F1F0-ATP synthases: glimpses of interacting parts in a dynamic molecular machine. J Exp Biol. 1997;200(Pt 2):217-224. [46] Deshpande M, Notari L, Subramanian P, et al. Inhibition of tumor cell surface ATP synthesis by pigment epithelium -derived factor: implications for antitumor activity. Int J Oncol. 2012;41(1):219-227. [47] Wang J, Li R, Zhang G. Research on relevance between mitochondrial ATP synthase and malignant tumor. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2014;31(3):714-717. [48] Sánchez-Aragó M, Formentini L, Cuezva JM. Mitochondria-mediated energy adaption in cancer: the H(+)-ATP synthase-geared switch of metabolism in human tumors. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013;19(3):285-298. [49] Bockenhauer SD, Duncan TM, Moerner WE, et al. The regulatory switch of F1-ATPase studied by single-molecule FRET in the ABEL Trap. Proc Soc Photo Opt Instrum Eng. 2014;8950:89500H. [50] Duncan TM, Düser MG, Heitkamp T, et al. Regulatory conformational changes of the ε subunit in single FRET-labeled FoF1-ATP synthase. Proc Soc Photo Opt Instrum Eng. 2014;8948:89481J. [51] Börsch M, Duncan TM. Spotlighting motors and controls of single FoF1-ATP synthase. Biochem Soc Trans. 2013;41(5): 1219-1226. [52] Fu Y, Zhu Y. Ectopic ATP synthase in endothelial cells: a novel cardiovascular therapeutic target. Curr Pharm Des. 2010; 16(37): 4074-4079. [53] Krysko DV, Vandenabeele P. From regulation of dying cell engulfment to development of anti-cancer therapy. Cell Death Differ. 2008;15(1):29-38. [54] Subramanian K, Naik VD, Sathishkumar K, et al. Interactive effects of in vitro binge-like alcohol and ATP on umbilical endothelial nitric oxide synthase post-translational modifications and redox modulation. Reprod Toxicol. 2014;43:94-101. [55] Barker RN, Erwig LP, Hill KS, et al. Antigen presentation by macrophages is enhanced by the uptake of necrotic, but not apoptotic, cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 2002;127(2):220-225. [56] Oh YS, Lee YJ, Park K, et al. Treatment with glucokinase activator, YH-GKA, increases cell proliferation and decreases glucotoxic apoptosis in INS-1 cells. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2014;51: 137-145. [57] De Marchi U, Thevenet J, Hermant A, et al. Calcium co-regulates oxidative metabolism and ATP synthase- dependent respiration in pancreatic beta cells. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(13):9182-9194. |
| [1] | Lin Haiqi, Chen Liang, Tang Lu, Weng Xiquan, Lin Wentao. Significance of urinary proteomics assessing pathological changes in the body [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3259-3266. |
| [2] | Hu Wandong, He Jialin, Zhang Longsheng, Liao Wenbo. Differential proteomics study of patients with sternal ossification of the ligamentum flavum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2625-2629. |
| [3] | Li Liqiang, Jiao Longxing, Zhang Wu, Yan Wentao, Li Jian, Li Minghao. Effect of immature dendritic cells derived from bone marrow on rejection of orthotopic liver transplantation in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 2025-2029. |
| [4] | Li Shengqiang, Xie Bingying, Chen Juan, Xie Lihua, Huang Jingwen, Ge Jirong. Interaction proteomics of long noncoding RNA uc431+ gene in postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1641-1646. |
| [5] | Yang Feng, Chang Lipu, Huang Changshan, Gong Xiaoguang, Chang Shunwu. Macrolide antibiotics protects against ischemia-reperfusion injury after liver transplantation in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(26): 4176-4182. |
| [6] | Qin Danying, Zhang Yuheng, Li Xueyong, Yang Wenxian. Proteomics analysis of exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells in skin damage repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(13): 2011-2019. |
| [7] | Liu Mengyuan1, Fang Fang2. Risk factors for multi-drug resistant organisms infection after liver transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(7): 1109-1114. |
| [8] | Liu Sijie, E Xiaoqiang, Pan Qi, Yao Guijun. Standardized treatment of infection around the prosthesis after joint replacement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(32): 5195-5202. |
| [9] | Gao Hongqiang, Liu Jing, Li Zhiqiang, Wang Hailei, Zhao Xiongqi, Zhang Shengning, Ran Jianghua, Li Li . Ulinastatin improves rat liver metabolism after reduced-size liver transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(3): 435-440. |
| [10] | Fan Siqi1, Zeng Ping2, Zhou Yi3, Qin Gang2, Liao Xiaobo2, He Kaiyi2. Screening differentially expressed proteins in the serum of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus combined with osteonecrosis of the femoral head by iTRAQ technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(3): 476-481. |
| [11] | Cai Qiucheng, Fan Hongkai, Xiong Rihui, Jiang Yi. Intravenous administration of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells protects liver function following fatty liver transplantation from donors after cardiac death [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(17): 2625-2629. |
| [12] | Zhao Ying-peng, Li Li, Chen Gang, Bai Jian-hua, Liu Qi-yu. Reduced-size liver transplantation with fatty liver donors in a rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(4): 582-586. |
| [13] | Ding Chen1, Jiang Yi2, Pan Fan2, Cai Qiucheng2. Lipid metabolism after autologous orthotopic liver transplantation in rat models of fatty liver [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(36): 5821-5827. |
| [14] | Liu Li-ye1, Zhao De-fang2, Gao Fei1, Zhang Tong2, Dong Qin2. Schisandra extract regulates Th17 cells and regulatory T cell imbalance in dogs undergoing liver transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(20): 3213-3217. |
| [15] | Gui Yu-chang1, Xu Jian-wen2, Tai Zhi-hong1, Rao Yuan-sen1, Cao Yu-ju1, Yin Li-jun3. Non-surgical treatment of lumbar intervertebral disc protrusion without blood stasis: a serum proteomic analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(16): 2570-2576. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||