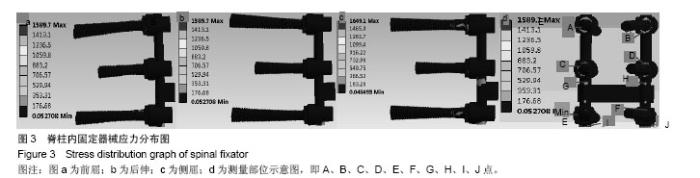
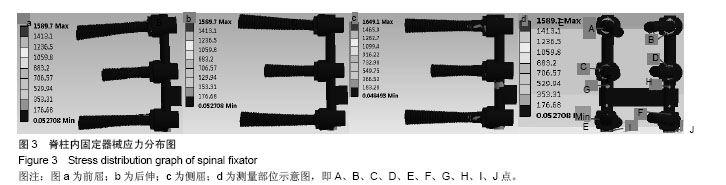
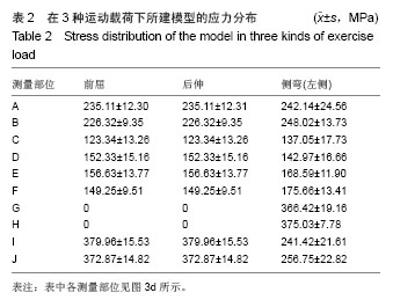
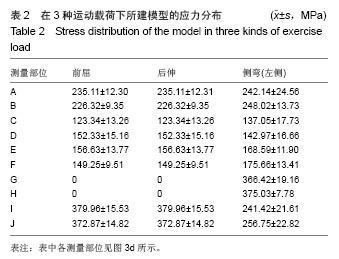
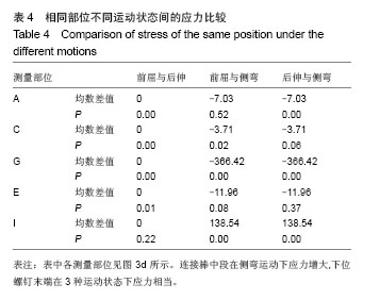
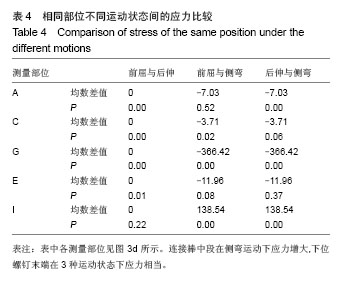
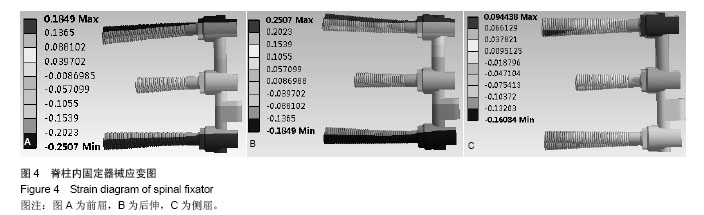
| [1]韦兴,何建军,侯树勋,等.胸椎椎弓根-肋骨复合体的解剖及影像学研究[J].中华外科杂志,2010,48(17):1313-1316.
[2]谢陶敢,陈其昕,李方才,等.胸椎椎弓根-肋骨单元与椎弓根的CT测量[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2008,18(9):665-668.
[3]徐荣明,刘观焱,赵红勇,等.胸椎关节突关节解剖学测量与经关节螺钉固定的关系[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2010,48(6):1115-1116.
[4]Lee GY, Massicotte EM, Ramperaaud YR, et al. Clinical accuracy of cervicothoracic pedicle screw placement:a comparison of the“open”lamino-foraminotomy and computer-assisted techniques.J Spinal Disord Tech. 2007; 20(1):25-32.
[5]Xu WX, Xu RM, Jiang WY,et al. Clinical study on surgical treatment for thoracolumbar burst fractures.Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2011;24(7):547-552.
[6]Lefranc M, Peltier J, Fichten A, et al.Dual, minimally invasive fixation in acute, double, thoracic spine fracture.Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 2011;54(5-6):253-256.
[7]Molina C, Sciubba DM, Chaput C,et al. A computed tomography-based feasibility study of translaminar screw placement in the pediatric thoracic spine. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2012;9(1):27-34.
[8]Kalani MY, Martirosyan NL, Little AS, et al.Tumoral calcinosis presenting as a deformity of the thoracic spine. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2011;8(6):584-587.
[9]Sun BF, Dong Y, Lü JY, et al.Expansive pedicle screws fixation combined with Wright artificial bone implantation for treatment of thoracolumbar burst fracture of the elderly patients.Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2011;24(7):544-546.
[10]Dvorak M, MacDonald S, Gurr KR, et al.An anatomical,radiographic,and biomechanical assessment of extrapedicular screw fixation in the thoracic spine. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 1993;18(12):1689-1694.
[11]Hussain M, Natarajan RN, Chaudhary G,et al.Simulation of inhomogeneous rather than homogeneous poroelastic tissue material properties within disc annulus and nucleus better predicts cervical spine response: a C3-T1 finite element model analysis under compression and moment loadings. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(4):245-255.
[12]郝志强,刘志斌.脊柱结核外科诊疗进展[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2013,7(15):7135-7137.
[13]Fei Q, Li QJ, Yang Y, et al.Three-dimensional finite element model of thoracolumbar spine with osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture. Zhong hua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2010;90(41): 2943-2946.
[14]He D, Wu L, Chi Y, et al.Facet joint plus interspinous process graft fusion to prevent postoperative late correction loss in thoracolumbar fractures with disc damage: finite element analysis and small clinical trials. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2011;26(3):229-237.
[15]Cheng FH, Shih SL, Chou WK, et al.Finite element analysis of the scoliotic spine under different loading conditions. Biomed Mater Eng. 2010;20(5):251-259.
[16]刘观鼓,徐荣明,赵红勇,等.胸椎后路经关节肋骨螺钉固定技术的提出及其解剖学研究[J].中华外科杂志,2010,48(14):1115-1116.
[17]胡哲,张少杰,王星,等.肋横突关节关节面的形态特点及其意义[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2014,5(32):538-543.
[18]李筱贺,李少华,由博,等.中下胸椎肋凹位置的研究及侧前方置钉数字化模拟[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2010,28(3): 251-254.
[19]He D,Wu L,Chi Y,et al.Facet joint plus interspinous process graft fusion to prevent postoperative late correction loss in thoracolumbar fractures with disc damage:finite element analysis and small clinical trials. Clin Biomech(Bristol,Avon). 2011;26(3):229-237.
[20]Woldtvedt DJ, Womack W, Gadomski BC. Finite element lumbar spine facet contact parameter predictions are affected by the cartilage thickness distribution and initial joint gap size. J Biomech Eng. 2011;133(6):061009.
[21]Galbusera F, Schmidt H, Neidlinger-Wilke C, et al. The effect of degenerative morphological changes of the intervertebral disc on the lumbar spine biomechanics: a poroelastic finite element investigation. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2011;14(8):729-739.
[22]Jackson AR, Huang CY, Gu WY. Effect of endplate calcification and mechanical deformation on the distribution of glucose in intervertebral disc: a 3D finite element study. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2011;14(2):195-204.
[23]Kim HJ, Chun HJ, Kang KT, et al. A Validated finite element analysis of never root stress in degenerative lumbar scoliosis. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2009;47(6):559-605.
[24]Li XF, Liu ZD, Dai LY, et al. Dynamic response of the idiopathic scoliotic spine to axial cyclic loads. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(7):521-528.
[25]Dall'Ara E, Schmidt R, Pahr D, et al. A nonlinear finite element model validation study based on a novel experimental technique for inducing anterior wedge-shape fractures in human vertebral bodies in vitro. J Biomech. 2010;43(12):2374-2380.
[26]Zeinali A, Hashemi B, Akhlaghpoor S.Noninvasive prediction of vertebral body compressive strength using nonlinear finite element method and an image based technique.Phys Med. 2010;26(2):88-97.
[27]Park WM, Park YS, Kim K,et al.Biomechanical comparison of instrumentation techniques in treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures:a finite element analysis. J Orthop Sci. 2009; 14(4):443-449.
[28]Mirzaei M, Zeinali A, Razmjoo A, et al.On prediction of the strength levels and failure patterns of human vertebrae using quantitative computed tomography (QCT)-based finite element method.J Biomech. 2009;42(11):1584-1591.
[29]Bottlang M, Helzel I, Long WB, et al. Anatomically contoured plates for fixation of rib fractures. J Trauma. 2010;68(3): 611-615.
[30]闫广辉,张庆胜,靳宪辉,等.经腰椎椎弓根动态内固定研究进展[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2012,9(6):31-34. |