Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (17): 2711-2718.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.17.016
Previous Articles Next Articles
Screw plate fixation, intramedullary fixation and artificial femoral head replacement in the repair of femoral intertrochanteric fractures in the elderly: choice and comparison
Zuo Jin-bu, Yu Lei, Liang Hong-wei, Wang Wei, Zhao Bin
- Department of Orthopedics, Beijing Municipal Corps Hospital of Chinese People’s Armed Police Forces, Beijing 100027, China
-
Online:2015-04-23Published:2015-04-23 -
Contact:Wang Wei, Chief physician, Associate professor, Department of Orthopedics, Beijing Municipal Corps Hospital of Chinese People’s Armed Police Forces, Beijing 100027, China -
About author:Zuo Jin-bu, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Beijing Municipal Corps Hospital of Chinese People’s Armed Police Forces, Beijing 100027, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zuo Jin-bu, Yu Lei, Liang Hong-wei, Wang Wei, Zhao Bin. Screw plate fixation, intramedullary fixation and artificial femoral head replacement in the repair of femoral intertrochanteric fractures in the elderly: choice and comparison[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(17): 2711-2718.
share this article
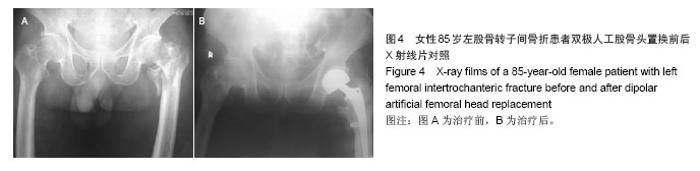
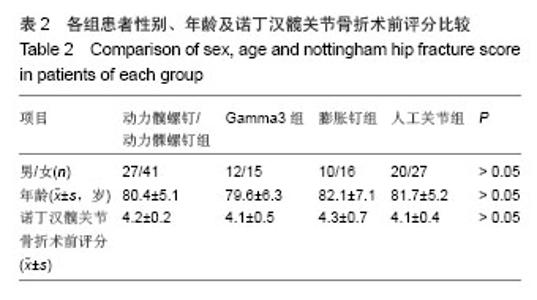
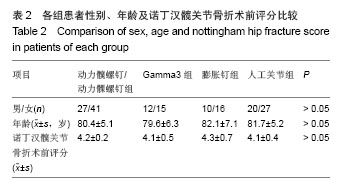
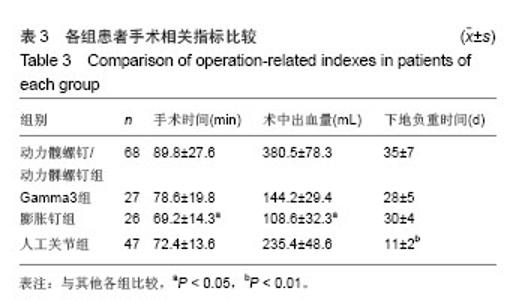
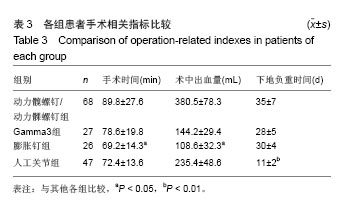
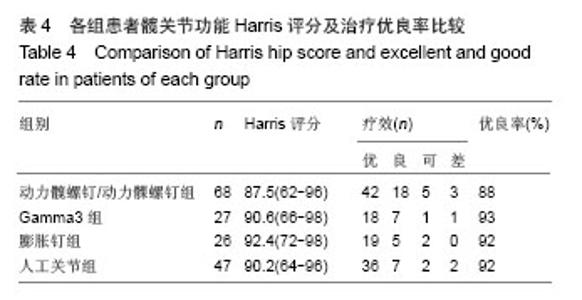
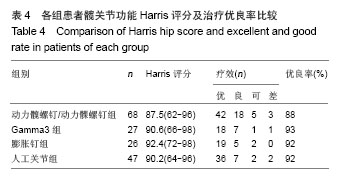
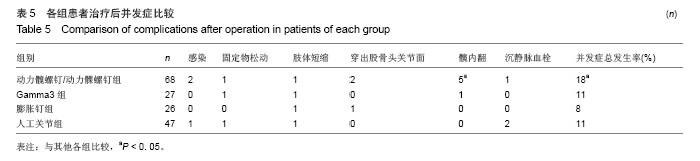
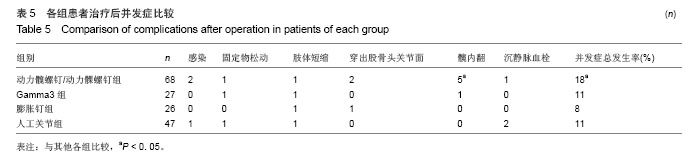
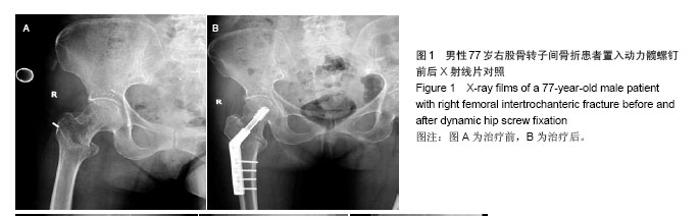
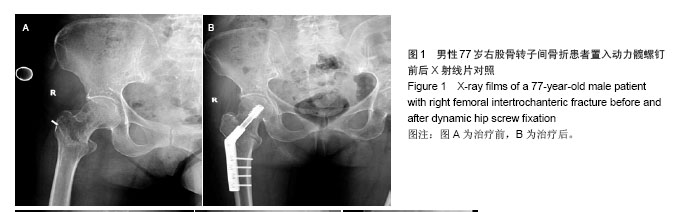
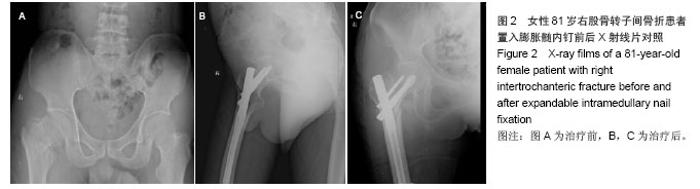
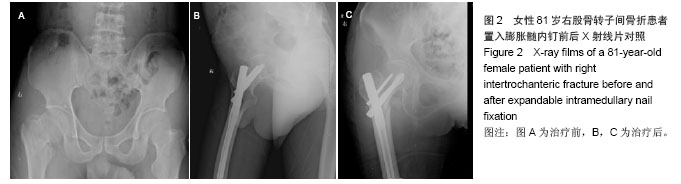
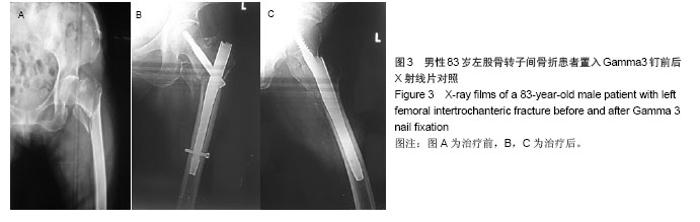
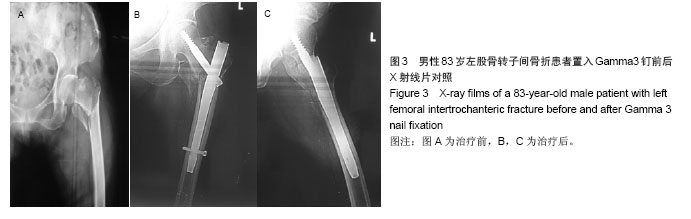
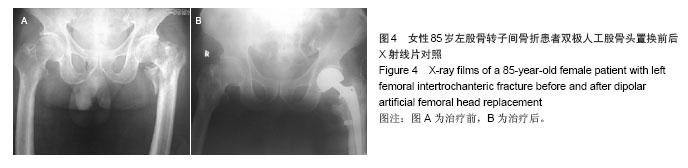
典型病例4:女性患者,85岁,因摔伤致左髋部肿痛、畸形9 h入院,诊断为左股骨转子间骨折。给予左下肢皮牵引,经术前常规准备,于伤后第5日在硬膜外麻醉下行人工双极股骨头置换,见图4。 2.7 不良事件 动力髋螺钉/动力髁螺钉组: 68例患者中2例发生浅表感染,1例内固定物松动,1例出现大于2 cm的肢体短缩,2例固定螺钉穿出股骨头关节面,5例出现髋内翻,1例患者术后1周出现深静脉血栓。并发症的总发生率为18%。 Gamma3组:27例患者中1例内固定物松动,1例出现大于2 cm肢体短缩,1例髋内翻,并发症的总发生率为11%。 膨胀钉组: 26例患者中1例出现大于2 cm肢体短缩,1例固定螺钉穿出股骨头关节面,并发症总发生率为8%。 人工关节组:47例患者中1例浅表感染,1例内固定物松动,1例出现大于2 cm肢体短缩,2例置换后出现深静脉血栓。并发症总发生率为11%。"
| [1]Xu YZ, Geng DC, Mao HQ, et al. A comparison of the proximal femoral nail antirotation device and dynamic hip screw in the treatment of unstable pertrochanteric fracture. J Int Med Res. 2010;38(4):1266-1275. [2]Simmermachera RKJ, Ljungqvist J, Bail H, et al. The new proximal femoral nail antirotation(PFNA) in daily practice: result of a multicentre clinical study. Injury Int J Care Injured. 2008;39:932-939. [3]O’Connor I, McDowell D, Barnes D.Hip Fractures: The St Ann's Bay Regional Hospital Experience. West Indian Med J. 2014; 63(2):142-145. [4]Cheng Q, Huang W, Gong X, et al.Minimally invasive percutaneous compression plating versus dynamic hip screw for intertrochanteric fractures: a randomized control trial. Chin J Traumatol. 2014;17(5):249-255. [5]Valera M, Bonifacio L, Basman S.Outcome of surgery for unstable intertrochanteric fractures in octogenarians. Malays Orthop J. 2014; 8(1):26-31. [6]DePalma AA, O'Halloran K, Shenoy K, et al.A novel technique for reducing intertrochanteric hip fractures. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2014;43(9):402-404. [7]王奔,葛振新,杨国跃,等.髓内与髓外固定修复股骨转子间骨折的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(4):736-743. [8]Elis J, Chechik O, Maman E, et al. Expandable proximal femoral nails versus 95° dynamic condylar screw-plates for the treatment of reverse oblique intertrochanteric fractures. Injury. 2012;43(8):1313-1317. [9]Hong JY, Suh SW, Park JH, et al. Comparison of soft-tissue serum markers in stable intertrochanteric fracture: dynamic hip screw versus proximal femoral nail-A preliminary study. Injury. 2011;42(2):204-208. [10]梁昌详,郑晓青,昌耘冰,等.精确定位防旋髓内钉置入治疗股骨转子间骨折[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(17):2685-2690. [11]Kim Y, Moon JK, Hwang KT, et al.Cementless bipolar hemiarthroplasty for unstable intertrochanteric fractures in octogenarians. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2014;48(4): 424-430. [12]Emami M, Manafi A, Hashemi B, et al.Comparison of intertrochanteric fracture fixation with dynamic hip screw and bipolar hemiarthroplasty techniques. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2013;1(1):14-17. [13]李军民,黎云冲,杨绍文.老年人股骨粗隆部骨折应用人工髋关节置换的效果观察[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2008,16(2):98-100. [14]左进步,余磊,梁宏伟,等.人工股骨头置换术治疗高龄股骨粗隆间骨折中股距重建的策略[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(2): 1602-1605. [15]Parvizi J, Tarity TD, Slenker N, et al. Proximal femoral replacement in Patients with non-neoplastic conditions. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(5):1036-1043. [16]高令军,裘世静,戴克戎.青年与老年股骨距的显微结构特征及其临床意义[J].中华骨科杂志,1999,19(7):393-395. [17]Leung WY, Tsang WL. Conventional muscle-reflection approach versus mini-incision muscle-splitting approach in dynamic hip screw fixation. J Orthop Surg(Hong Kong). 2008;16(2):156-161. [18]Said G,Farouk O,El-Sayed A,et al.Salvage of failed dynamic hip screw fixation of intertrochanteric fractures. Injury. 2006;37:194-202. [19]Little NJ, Verma V, Fernando C, et al. A prospective trial comparing the Holland nail with the dynamic hip screw in the treatment of intertrochanteric fractures of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008;90(8) : 1073-1078. [20]Calderón A, Ramos T, Vilchez F, et al. Proximal femoral intramedullary nail versus DHS plate for the treatment of intertrochanteric fractures. A prospective analysis. Acta Ortop Mex. 2013;27(4):236-239. [21]Gorodnichenko AI, Uskov ON, Platonov II. Intramedullary ostheosynthesis of femoral acetabular fractures in elderly patients. Khirurgiia (Mosk). 2013;(6):55-58. [22]Muller-Daniel SH. The Future: optimization of implants and instrumentation Gamma3(tm): the minimally invasive solution in hip fracture treatment. First Announcement Osteo Trauma Care. 2005;13:42-45. [23]陆凯,丁国明,李民,等. Gamma钉治疗股骨粗隆周围骨折常见并发症的原因分析及处理[J].骨与关节损伤杂志,2002,7(6): 467-468. [24]Heiney J,Battula S,Njus G,et al.Biomechanical comparison of three second-generation reconstruction nail in an unstable subtrochanteric femur fracture mode. Proc Inst Mech Eng. 2008;222(6):959-966. [25]Blumberg N, Tauber M,Dekel S. A preliminary clinical experience with the expandable intramedullary nail in traumatic humeurs,tibia, and femurfractures. Israel Orthopedic Association. Tel Aviv,Israel, 2001. [26]Franck WM, Olivieri M, Jannasch O. Expandable nail system for osteoporotic humeral shaft fractures: preliminary results. J Trauma. 2003;54:1152-1160. [27]Steinberg EL, Blumberg N, et al. The fixion proximal femur nailing system: biomechanical properties of the nail and a cadaveric study. J Biomech. 2005;38(1):63-68. [28]Tauber M. The biomechanical principles in the basis of long bone fractures fixation using the fixion system method. Biomedical Engineering Conference.Washington,DC,USA, 2002. [29]Haidukewych GJ, Berry DJ. Hip arthroplasty for salvage of failed treatment of intertrochanteric hip fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A(5):899-904. [30]Drobniewski M, Sibiński M, Plebański R, et al. Breakage of the prosthesis steam as a rare complication of total hip replacement. Chir Narzadow Ruchu Ortop Pol. 2010;75(1): 53-56. [31]岳建明,郝斌,杨亚军,等.股骨粗隆型人工股骨头置换术治疗高龄Evans-JensonⅢ型股骨粗隆间骨折临床探讨[J].宁夏医科大学学报,2011,33(9):872-874. [32]章玉冰,戎祖华,张俊德,等.G.T.F.柄人工髋关节置换治疗高龄股骨转子间骨折(Evans Ⅲ型)疗效分析[J].临床医学工程,2012, 19(11):1919-1920. [33]Hammad A,Abdel-Aal A,Said HG,et al.Total hip arthroplasty following failure of dynamic hip screw fixation of fractures of the proximal femur. Acta Orthop Belg. 2008;74(6): 788-792. [34]Tsiridis E, Pavlou G, Venkatesh R, et al. Periprosthetic femoral fractures around hip arthroplasty current conceps in their management. Hip Int. 2009;2:75-86. [35]左进步,余磊,梁宏伟,等.人工股骨头置换治疗高龄股骨转子间骨折与股骨颈骨折的比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011, 15(52):9774-9777. |
| [1] | Liu Pengran, Jiao Rui, Tao Jin, Chen Hui, Dai Jihang, Yan Lianqi. Comparison of the effects of total hip arthroplasty with different interface prostheses in the treatment of elderly hip diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2347-2351. |
| [2] | Fang Yi, Zhao Wenzhi, Pan Deyue, Han Xin, Zhang Lu, He Hongtao, Shi Feng, Tian Tingxiao. Acromioclavicular joint dislocation: how to achieve anatomical reduction, sustained stability and micro-motion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 796-802. |
| [3] | Fu Jiaxin, Xiao Lianping, Wang Shusen, Li Xiaodong, Han Liqiang, Wang Tonghao. Therapeutic effects of paraspinal approach combined with internal fixation through pedicle of fractured vertebra versus traditional AF screw-rod system for thoracolumbar fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1177-1181. |
| [4] | Qiu Zhongpeng, Li Ke, Li Gang, Liu Keyu, Du Xinhui, Meng Defeng, Shi Chenhui, Wang Weishan. Different treatments for two-part and three-part proximal humeral fractures by Neer classification: follow-up results analyzed using clinical economics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1188-1195. |
| [5] | Ke Wei, Li Ke, Wang Sibo, Du Xinhui, Qiu Zhongpeng, Kang Zhilin, Wang Weishan, Li Gang . Open reduction and plate fixation versus closed reduction and external fixation for distal radius fractures: scores and linear regression analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1196-1202. |
| [6] | Fan Zhirong, Peng Jiajie, Zhong Degui, Zhou Lin, Su Haitao, Huang Yongquan, Wu Jianglin, Liang Yihao. Suture anchor combined with open reduction and internal fixation versus open reduction and internal fixation for ankle fracture combined with deltoid ligament injury: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1307-1312. |
| [7] | Han Jie1, Chen Yueping1, Mo Jian1, Wang Dawei1, Su Bo1, Li Shuzhen1, Xia Tian2, Wang Shixin2. Ultrastructural evaluation of a rabbit model of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head after treatment with panax notoginseng saponins [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(7): 1035-1039. |
| [8] | Zhai Pei, Li Pengfei, Liang Zhenghui, Zeng Jianchun, Cai Guoxiong, Zeng Yirong, Fan Yueguang. Differential expression of miR-672-5p in rat osteoblasts after intervention by long-acting, intermediate-acting and short-acting hormones [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(5): 809-814. |
| [9] | Zhou Yu, Liu Yuehong, Liu Shuping, Chen Xi, Qin Wei, Li Qifeng. Spinal stability of intervertebral grafting reinforced by five or six augmenting screws versus transvertebral grafting reinforced by four augmenting screws for thoracolumbar vertebral fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(4): 505-511. |
| [10] | Li Xianzhou, Wang Qian, Zhang Cunxin . Lumbar spondylolisthesis: status and prospects of implant treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(4): 621-627. |
| [11] | Chen Yong, Zhang Bin. Three-dimensional printing technique-assisted total hip arthroplasty for developmental dysplasia of the hip in adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(36): 5772-5776. |
| [12] | Yin Hao, Zhou Enchang, Pan Zhengjun, Chen Guang, Jiang Hua. Finite element analysis of the four and three cannulated screws combined with buttress plate fixation for the treatment of Pauwels III femoral neck fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(32): 5133-5137. |
| [13] | Hu Liang1, Wang Junhai1, Wang Zhilie1, Xie Jinyuan1, Chen Deng1, Ding Fan2. Vascular endothelial growth factor combined with mutant hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha promotes angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(3): 378-383. |
| [14] |
Wang Lei, Li Zilong, Yuan Binbin, Wu Qingwei, Tang Fengming.
Clinical effect of locking plate versus anterograde intramedullary nail in the treatment of adult humeral shaft fractures: a meta-analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(24): 3924-3930.
|
| [15] | Su Lianbin, Feng Eryou, Zhang Yiyuan, Zhuo Youguang, Xiao Lili, Wang Wulian, Lin Feitai. Whether direct anterior approach for total hip arthroplasty is a risk factor of eccentric reaming to the anterior column of the acetabulum? [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(20): 3117-3123. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||