Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (15): 2405-2409.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.15.021
Previous Articles Next Articles
The role and mechanism of parathyroid hormone in promoting bone formation
Wang Min-jiao, Si Jia-wen, Shen Guo-fang
- Department of Oral and Craniomaxillofacial Science, Shanghai Ninth People’s Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai Key Laboratory of Stomatology, Shanghai 200011, China
-
Revised:2015-02-14Online:2015-04-09Published:2015-04-09 -
Contact:Shen Guo-fang, M.D., Chief physician, Department of Oral and Craniomaxillofacial Science, Shanghai Ninth People’s Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai Key Laboratory of Stomatology, Shanghai 200011, China -
About author:Wang Min-jiao, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Oral and Craniomaxillofacial Science, Shanghai Ninth People’s Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai Key Laboratory of Stomatology, Shanghai 200011, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81271122
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Min-jiao, Si Jia-wen, Shen Guo-fang. The role and mechanism of parathyroid hormone in promoting bone formation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(15): 2405-2409.
share this article
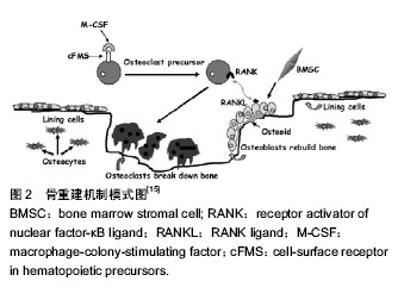
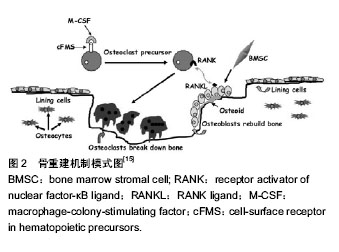
2.1 骨质疏松与甲状旁腺激素 甲状旁腺激素是由84个氨基酸组成的钙调节激素,由甲状旁腺释放,主要作用于肾脏和骨组织。其活性片段(甲状旁腺激素1-34),亦具有甲状旁腺激素相同的生理作用。甲状旁腺激素作为临床用药,间断使用促进骨质形成以及预防骨折的效果已经得到广泛证实。为评价人甲状旁腺素预防骨质疏松性骨折的安全性和有效性,加拿大骨质疏松临床指南委员会Cranney等检索了Medline、Embase、HTA、Current Contents和Cochrane对照临床试验注册数据库中自1966至2005年2月的相关随机对照研究,并进行了系统评价。共有12项随机、安慰剂或活性药物对照的临床研究被纳入分析,治疗时间均≥1年。结果显示,人甲状旁腺激素(1-34)显著增加了腰椎骨密度,轻度增加了股骨颈和全髋骨密度;人甲状旁腺激素(1-84)也显著增加了腰椎骨密度。对于有脊椎骨折史的绝经后妇女,人甲状旁腺激素(1-34)显著降低了再发生脊柱和非脊柱骨折的危险[7]。研究显示治疗20个月后停用甲状旁腺激素,骨折风险还在持续降低,并可维持50个月以上,中国SFDA批准甲状旁腺激素使用24个月,目前考虑其安全性与不良反应的因素,常用剂量为20 μg/d,一般使用时间不超过2年[8]。 甲状旁腺激素造成的骨质变化时一个复杂的过程,它既能刺激成骨细胞调节的骨形成,亦可以刺激破骨细胞调节的骨吸收,间歇性的甲状旁腺激素注射已经被广泛的证实可以刺激骨质的形成[9-10]。Lindsay等[11]比较每日甲状旁腺激素间歇性给药的患者1个月前后的骨密度,发现给药后的骨密度明显增加。研究表明,间歇性的甲状旁腺激素 给药主要作用于四肢骨中的骨小梁以及密质骨表面,少量作用于骨膜表面,通过刺激成骨细胞增殖,抑制成骨细胞凋亡,同时激活衬里细胞,从而促进骨质形成[12-13]。 2.2 作用机制 甲状旁腺激素作用于甲状旁腺激素Ⅰ型受体(PPR),PPR是一种在肾脏和骨组织中广泛分布的经典的Ⅱ型G蛋白偶联受体,该受体有7个跨膜区,触发经典的G蛋白信号通路,一种是蛋白激酶A 信号通路(protein kinase A pathway,PKA pathwav),另一种是蛋白激酶C信号通路(protein kinase C pathway,PKC pathway)。甲状旁腺激素主要通过PKA信号通路调节其下游反应蛋白。cAMP-PKA信号通路被认为是传导甲状旁腺激素信号的主要路径[14]。Datta等[15]研究提示MAPKs/ERKs通路也参与PPR的骨形成调节,骨重建机制模式图见图2[15]。MAPKs/ERKs通路主要依赖于PKC通路[14]。"
| [1] Harvey N,Dennison E, Cooper C.Osteoporosis: impact on health and economics. Nat Rev Rheumatol.2010;6(2):99-105. [2] Anil S. Preethanath RS, AlMoharib HS, et al.Impact of osteoporosis and its treatment on oral health. Am J Med Sci. 2013;346(5):396-401. [3] Dervis E.Oral implications of osteoporosis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod.2005;100(3):349-56. [4] Cheung A, Seeman E.Teriparatide therapy for alendronate-associated osteonecrosis of the jaw. N Engl J Med.2010;363(25):2473-2474. [5] Tang ZL, Zhang WJ, Wang DX, et al.An experimental study addressing the promotion of mandibular defect repair through the intermittent subcutaneous injection of parathyroid hormone. J Oral Maxillofac Surg.2014;72(2):419-430. [6] Tokunaga K, Seto H, Ohba H, et al. Topical and intermittent application of parathyroid hormone recovers alveolar bone loss in rat experimental periodontitis. J Periodontal Res. 2011; 46(6):655-662. [7] Cranney, A, Papaioannou A, Zytaruk N, et al. Parathyroid hormone for the treatment of osteoporosis: a systematic review. CMAJ, 2006;175(1):52-59. [8] Neer RM, Arnaud CD, Zanchetta JR et al. Effect of parathyroid hormone (1-34) on fractures and bone mineral density in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. N Engl J Med.2001; 344(19):1434-1441. [9] Jilka RL.Molecular and cellular mechanisms of the anabolic effect of intermittent PTH. Bone. 2007;40(6):1434-1446. [10] Silva BC, Costa AG, Cusano NE et al. Catabolic and anabolic actions of parathyroid hormone on the skeleton. J Endocrinol Invest. 2011;34(10):801-810. [11] Lindsay R, Cosman F, Zhou H,et al. A novel tetracycline labeling schedule for longitudinal evaluation of the short-term effects of anabolic therapy with a single iliac crest bone biopsy: early actions of teriparatide. J Bone Miner Res. 2006; 21(3):366-373. [12] Compston JE. Skeletal actions of intermittent parathyroid hormone: effects on bone remodelling and structure. Bone. 2007;40(6):1447-1452. [13] Kneissel M, Boyde A, Gasser JA. Bone tissue and its mineralization in aged estrogen-depleted rats after long-term intermittent treatment with parathyroid hormone (PTH) analog SDZ PTS 893 or human PTH(1-34). Bone. 2001;28(3): 237-250. [14] Swarthout JT,D'Alonzo RC,Selvamurugan N,et al.Parathyroid hormone-dependent signaling pathways regulating genes in bone cells. Gene. 2002;282(1-2):1-17. [15] Datta NS, Abou-Samra AB. PTH and PTHrP signaling in osteoblasts. Cell Signal. 2009;(8):1245-1254. [16] Nishida S, Yamaguchi A,Tanizawa T, et al.Increased bone formation by intermittent parathyroid hormone administration is due to the stimulation of proliferation and differentiation of osteoprogenitor cells in bone marrow. Bone.1994;15(6): 717-723. [17] Ogita M, Rached MT, Dworakowski E et al.Differentiation and proliferation of periosteal osteoblast progenitors are differentially regulated by estrogens and intermittent parathyroid hormone administration. Endocrinology. 2008; 149(11):5713-5723. [18] de Castro LF, Lozano D, Portal-Núñez S, et al.Comparison of the skeletal effects induced by daily administration of PTHrP (1-36) and PTHrP (107-139) to ovariectomized mice. J Cell Physiol.2012; 227(4):1752-1760. [19] de Gortazar AR, Alonso V, Alvarez-Arroyo MV, et al.Transient exposure to PTHrP (107-139) exerts anabolic effects through vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 in human osteoblastic cells in vitro. Calcif Tissue Int. 2006;79(5):360-9. [20] Krishnan V, Moore TL, Ma YL, et al. Parathyroid hormone bone anabolic action requires Cbfa1/Runx2-dependent signaling. Mol Endocrinol.2003;17(3):423-435. [21] Stewart, AF, Cain RL, Burr DB, et al.Six-month daily administration of parathyroid hormone and parathyroid hormone-related protein peptides to adult ovariectomized rats markedly enhances bone mass and biomechanical properties: a comparison of human parathyroid hormone 1-34, parathyroid hormone-related protein 1-36, and SDZ-parathyroid hormone 893. J Bone Miner Res.2000;15(8):1517-1525. [22] Rickard DJ, Wang FL, Rodriguez-Rojas AM, et al. Intermittent treatment with parathyroid hormone (PTH) as well as a non-peptide small molecule agonist of the PTH1 receptor inhibits adipocyte differentiation in human bone marrow stromal cells. Bone.2006; 39(6):1361-1372. [23] Dobnig H, Turner RT.Evidence that intermittent treatment with parathyroid hormone increases bone formation in adult rats by activation of bone lining cells. Endocrinology.1995;136(8): 3632-3638. [24] 唐雯菁,杜艳萍,洪维,等.甲状旁腺素对骨髓间充质干细胞增殖、分化和旁分泌功能的影响[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志, 2014;7(01):42-47. [25] 徐峰,董进. rhPTH1-34对成骨细胞增殖及BMP-7、BMP-9基因表达的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2011;17(06):489-492. [26] Datta NS,Pettway GJ,Chen C,et al.Cyclin D1 as a target for the proliferative effects of PTH and PTHrP in early osteoblastic cells. J Bone Miner Res. 2007;22(7):951-964. [27] Portal-Nunez S,Lozano D,de Castro LF,et al.Alterations of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway and its target genes for the N- and C-terminal domains of parathyroid hormone-related protein in bone from diabetic mice. FEBS Lett.2010;584(14):3095-100. [28] Weinstein RS, Jilka RL, Almeida M,et al. Intermittent parathyroid hormone administration counteracts the adverse effects of glucocorticoids on osteoblast and osteocyte viability, bone formation, and strength in mice. Endocrinology.2010; 151(6):2641-2649. [29] Endo I.[Glucocorticoid and Bone. The effect of glucocorticoid and PTH in osteoblast apoptosis and differentiation via interleukin 11 expression]. Clin Calcium.2014; 24(9):1321-1328. [30] Bellido T, Ali AA, Plotkin LI, et al.Proteasomal degradation of Runx2 shortens parathyroid hormone-induced anti-apoptotic signaling in osteoblasts. A putative explanation for why intermittent administration is needed for bone anabolism. J Biol Chem.2003; 278(50):50259-50272. [31] Chen HL, Demiralp B, Schneider A, et al. Parathyroid hormone and parathyroid hormone-related protein exert both pro- and anti-apoptotic effects in mesenchymal cells. J Biol Chem.2002; 277(22):19374-19381. [32] Manolagas SC. From estrogen-centric to aging and oxidative stress: a revised perspective of the pathogenesis of osteoporosis. Endocr Rev.2010;31(3):266-300. [33] Schnoke M, Midura SB, Midura RJ. Parathyroid hormone suppresses osteoblast apoptosis by augmenting DNA repair. Bone.2009;45(3):590-602. [34] Glass DA, 2nd, Karsenty G. In vivo analysis of Wnt signaling in bone. Endocrinology.2007;148(6):2630-2634. [35] Kulkarni NH, Halladay DL, Miles RR, et al. Effects of parathyroid hormone on Wnt signaling pathway in bone. J Cell Biochem.2005; 95(6):1178-1190. [36] Wan M, Yang C, Li J, et al. Parathyroid hormone signaling through low-density lipoprotein-related protein 6. Genes Dev. 2008;22(21):2968-2979. [37] Uyama M,Kawanami M,Tamura M.Wasf2: a novel target of intermittent parathyroid hormone administration. Int J Mol Med. 2013;31(5):1243-1247. [38] Bouleftour W, Bouet G, Granito RN, et al. Blocking the expression of both bone sialoprotein (BSP) and osteopontin (OPN) impairs the anabolic action of PTH in mouse calvaria bone.J Cell Physiol. 2015;230(3):568-577. [39] Sowa H,Kaji H,Iu MF,et al.Parathyroid hormone-Smad3 axis exerts anti-apoptotic action and augments anabolic action of transforming growth factor beta in osteoblasts. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(52):52240-52252. [40] Sabbieti MG, Agas D, Xiao L, et al. Endogenous FGF-2 is critically important in PTH anabolic effects on bone. J Cell Physiol. 2009;219(1):143-151. [41] Standal T, Johnson R, McGregor N, et al.gp130 in late osteoblasts and osteocytes is required for PTH-induced osteoblast differentiation.J Endocrinol. 2014;223(2):181-190. |
| [1] | Huo Hua, Cheng Yuting, Zhou Qian, Qi Yuhan, Wu Chao, Shi Qianhui, Yang Tongjing, Liao Jian, Hong Wei. Effects of drug coating on implant surface on the osseointegration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3558-3564. |
| [2] | Wei Qin, Zhang Xue, Ma Lei, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Duan Mingjun, Wu Shuo, Jia Qiyu, Ma Chuang. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB induces the differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2953-2957. |
| [3] | Guo Zhibin, Wu Chunfang, Liu Zihong, Zhang Yuying, Chi Bojing, Wang Bao, Ma Chao, Zhang Guobin, Tian Faming. Simvastatin stimulates osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2963-2968. |
| [4] | Li Xiangze, Bu Xianmin, Li Dongmei, Chi Yulei, Su Qiang, Jin Xintong, Zhao Jian, Zhang Gaotian, Wu Bin, Meng Chunyang . Stem cells, cytokines, hormones, neuropeptides and genes in traumatic brain trauma to promote fracture healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3057-3063. |
| [5] | Wu Yukun, Han Jie, Wen Shuaibo. Mechanism of Runx2 gene in fracture healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2274-2279. |
| [6] | Yu Chenghao, Zhang Yi, Qi Chao, Chen Jinli, Gao Jiake, Yu Tengbo. Effect of cytokines and platelet-rich plasma on tendon derived stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 133-140. |
| [7] | Chen Qiang, Zhuo Hongwu, Xia Tian, Ye Zhewei . Toxic effects of different-concentration isoniazid on newborn rat osteoblasts in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(8): 1162-1167. |
| [8] | Li Jinyu, Yu Xing, Jiang Junjie, Xu Lin, Zhao Xueqian, Sun Qi, Zheng Chenying, Bai Chunxiao, Liu Chuyin, Jia Yusong. Promoting effect of osteopractic total flavone combined with nano-bone materials on proliferation and differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1030-1036. |
| [9] | Qiao Jiutao, Guan Dehong, Wang Dongyan, Liu Aiyun. Zuogui Pill has protective effect against oxidative stress injury in osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1052-1056. |
| [10] | Ge Juncheng, Ma Jinhui, Wang Bailiang, Yue Debo, Sun Wei, Wang Weiguo, Guo Wanshou, Li Zirong. Application of bisphosphonates in avascular necrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 753-759. |
| [11] | Zhang Chao, Li Xingyong, Ma Guifu, Pu Xingyu, Luo Wenyuan. Hoxa9 silencing promotes tibial fracture healing by regulating osteogenic differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(35): 5600-5606. |
| [12] | Wei Jianghong, Jia Aijun, Ma Libing, Wang Yueling, Qiu Lulu, Xiao Bing. Th-17 regulatory cytokines promote interleukins-17A and 17F production by neutrophils during asthma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(31): 5044-5051. |
| [13] | Wang Wenhong, Li Yanjun, Cui Caiyun. Factors influencing differentiation of stem cells from the apical papilla into odontoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(31): 5071-5078. |
| [14] | Song Shilei, Chen Yueping, Zhang Xiaoyun. Mechanism of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway regulating osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(3): 408-415. |
| [15] | He Qiang, Qian Weiqing, Yao Nianwei, Zhou Mengling, Liu Yixin, Yin Hong. Protection of inflammatory osteoblasts in neonatal rats using catalpol from the root of Rehmannia glutinosa [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(29): 4626-4631. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||