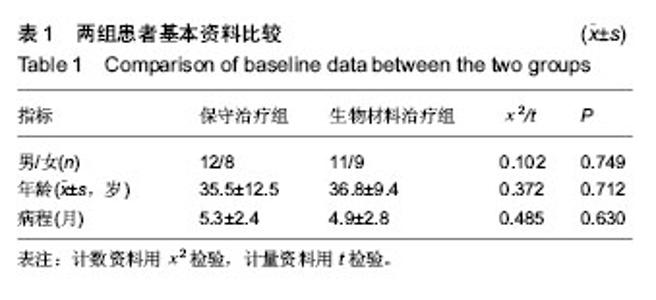
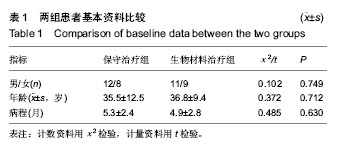
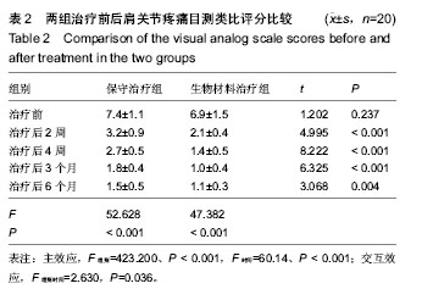
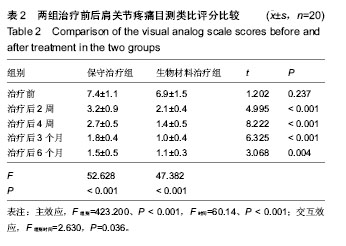
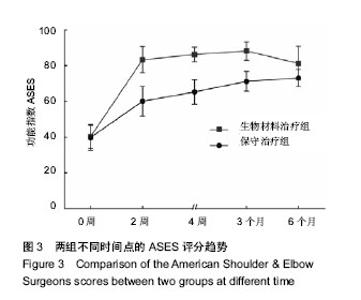
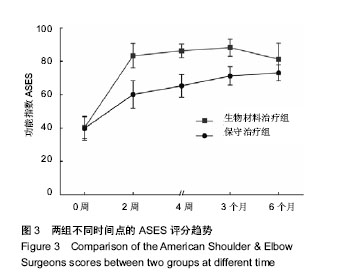
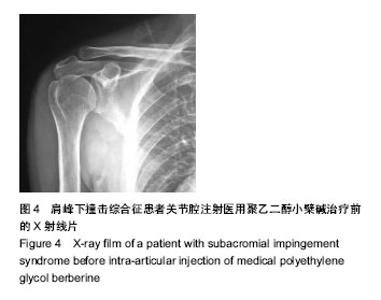
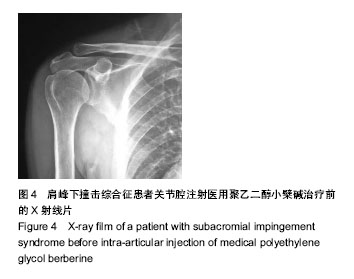
| [1] Erasmo R,Guerra G,Guerra L.Fractures and fracture- dislocations of the proximal humerus: A retrospective analysis of 82 cases treated with the Philos(®) locking plate.Injury.2014; 45 Suppl 6:S43-48.
[2] Singh HP,Mehta SS,Pandey R.A preoperative scoring system to select patients for arthroscopic subacromial decompression. J Shoulder Elbow Surg.2014;23(9): 1251-1256.
[3] 杜欢.保守治疗肩峰下撞击综合征30例[J].南京中医药大学学报, 2011,27(5):487-488.
[4] 费文勇,章洪喜,谢军,等.关节镜下肩峰下减压术微创治疗肩峰撞击征的临床疗效观察[J].中国内镜杂志,2013,19(12): 1263-1267.
[5] 傅中国,姜保国,张殿英,等.肩峰撞击征合并肩袖损伤的治疗[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2005,7(9):817-819.
[6] Blume C,Wang SS.Comparison of changes in supraspinatus muscle thickness in persons with subacromial impingement syndrome and asymptomatic adults. Physiother Theory Pract. 2014;30(8):544-551.
[7] Haik MN,Alburquerque-Sendín F,Camargo PR.Reliability and minimal detectable change of 3-dimensional scapular orientation in individuals with and without shoulder impingement.J Orthop Sports Phys Ther.2014;44(5):341-349.
[8] Haldorsen B,Svege I,Roe Y,et al.Reliability and validity of the Norwegian version of the Disabilities of the Arm,Shoulder and Hand questionnaire in patients with shoulder impingement syndrome.BMC Musculoskelet Disord.2014;15:78.
[9] Hoenecke HR Jr,Flores-Hernandez C,D'Lima DD.Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty component center of rotation affects muscle function.J Shoulder Elbow Surg.2014;23(8): 1128-1135.
[10] Lee YL,Sagare AP,Lee CY,et al. Formation of protoberberine- type alkaloids by the tubers of somatic embryo-derived plants of Corydalis yanhusuo.Planta Med. 2001;67(9):839-842.
[11] Lin YC,Kuo JY,Hsu CC,et al.Optimizing manufacture of liposomal berberine with evaluation of its antihepatoma effects in a murine xenograft model.Int J Pharm. 2013; 441(1-2):381-388.
[12] 靳安民,闵少雄,高艳杰,等. 医用聚乙二醇小檗碱液预防腰椎管术后硬膜外粘连的临床研究[J].黑龙江医学,2007,31(3):201-203.
[13] Wilson RD,Harris MA,Gunzler DD,et al.Percutaneous peripheral nerve stimulation for chronic pain in subacromial impingement syndrome: a case series. Neuromodulation. 2014;17(8):771-776.
[14] de Witte PB, Henseler JF, van Zwet EW,et al.Cranial humerus translation, deltoid activation, adductor co-activation and rotator cuff disease - different patterns in rotator cuff tears, subacromial impingement and controls.Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon).2014;29(1):26-32.
[15] Marzetti E,Rabini A,Piccinini G,et al.Neurocognitive therapeutic exercise improves pain and function in patients with shoulder impingement syndrome: a single-blind randomized controlled clinical trial.Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2014;50(3):255-264.
[16] Park SI,Choi YK,Lee JH,et al.Effects of shoulder stabilization exercise on pain and functional recovery of shoulder impingement syndrome patients.J Phys Ther Sci.2013;25(11): 1359-1362.
[17] Tucci HT,Martins J,Sposito Gde C,et al.Closed Kinetic Chain Upper Extremity Stability test (CKCUES test): a reliability study in persons with and without shoulder impingement syndrome.BMC Musculoskelet Disord.2014;15:1.
[18] 朱江龙,苏波,王大伟.健骨注射液肩峰下注射治疗肩峰下撞击综合征的临床疗效观察[J].中医正骨,2012,24(5):60-64.
[19] 戴祝,华英汇,陈世益,等.原发性冷冻肩与肩峰撞击征的鉴别诊断及治疗[J].实用骨科杂志,2012,18(1):50-52.
[20] Gebremariam L,Hay EM,van der Sande R,et al.Subacromial impingement syndrome--effectiveness of physiotherapy and manual therapy. Br J Sports Med. 2014;48(16):1202-1208.
[21] van Kampen DA,Willems WJ,van Beers LW,et al. Determination and comparison of the smallest detectable change (SDC) and the minimal important change (MIC) of four-shoulder patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs). J Orthop Surg Res. 2013;8:40.
[22] Neviaser A,Braman J,Parsons B.What's new in shoulder and elbow surgery.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2013;95(20):1896-1901.
[23] 徐海栋,付强,赵建宁.数字技术在脊柱微创外科中的应用进展[J].医学研究生学报,2014,27(2):207-210.
[24] 眭杰,汪滋民.肩峰下滑囊切除在肩峰下撞击综合征手术治疗的应用价值[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2013,21(1):37-40.
[25] 徐海栋,陈勇,卢俊浩,等.带线锚钉Krackow缝合法修复急性跟腱断裂的临床研究[J].医学研究生学报,2013,26(3):156-159. |