Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (9): 1345-1351.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.09.006
Previous Articles Next Articles
Cement and cementless hemi-hip replacement for the repair of femoral neck fracture in the elderly
Wang Ben-jie1, 2, Zhao De-wei1, 2, Xie Hui1, 2, Yang Lei1, Fu Wei-min1, Liu Bao-yi1, Qiu Xing1
- 1Faculty of Electronic Information and Electronic Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024, Liaoning Province, China
2Department of Orthopedics, Zhongshan Hospital of Dalian University, Dalian 116001, Liaoning Province, China
-
Revised:2015-02-08Online:2015-02-26Published:2015-02-26 -
Contact:Zhao De-wei, M.D., Chief physician, Faculty of Electronic Information and Electronic Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024, Liaoning Province, China; Department of Orthopedics, Zhongshan Hospital of Dalian University, Dalian 116001, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Wang Ben-jie, Studying for doctorate, Associate chief physician, Faculty of Electronic Information and Electronic Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024, Liaoning Province, China; Department of Orthopedics, Zhongshan Hospital of Dalian University, Dalian 116001, Liaoning Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Ben-jie, Zhao De-wei, Xie Hui, Yang Lei, Fu Wei-min, Liu Bao-yi, Qiu Xing . Cement and cementless hemi-hip replacement for the repair of femoral neck fracture in the elderly[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(9): 1345-1351.
share this article
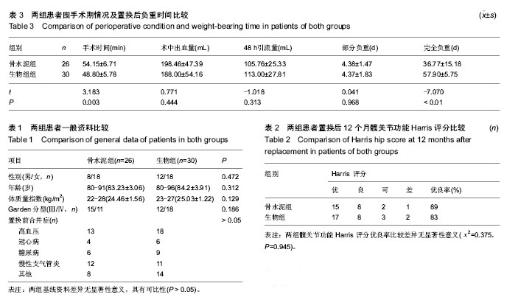
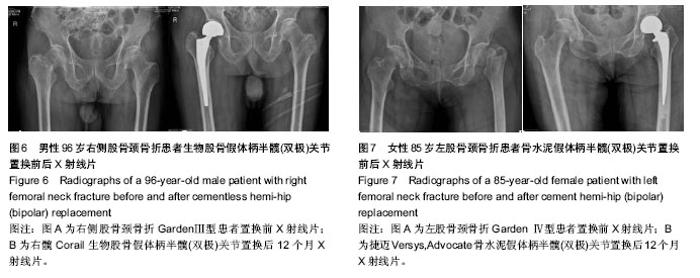
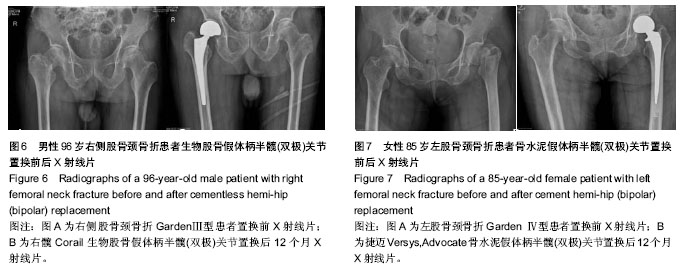
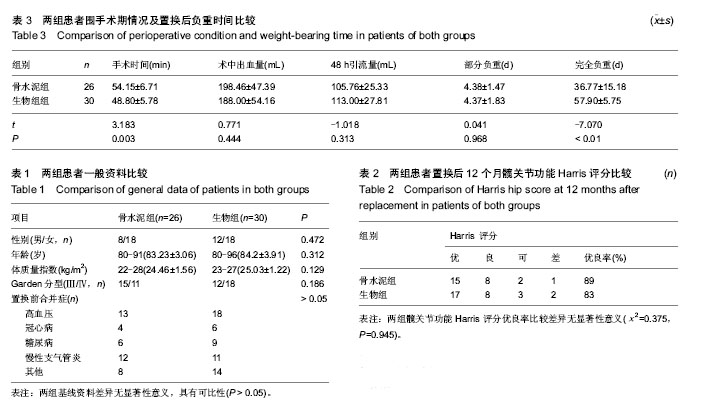
2.2 基线资料比较 两组患者一般资料相比,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),具有可比性,见表1。 2.3 随访结果 骨水泥组中置换后7 d出现脑血管栓塞1例,并出现单侧肢体瘫痪,经相应治疗后恢复肢体运动;腔隙性脑梗死2例,无肢体瘫痪症状;肺部感染2例,经抗生素治疗后痊愈。1例患者于置换后26个月死亡,死亡原因为急性心肌梗死。生物组置换后2-7 d出现腔隙性脑梗死1例,无偏瘫症状;下肢深静脉栓塞1例,抗血栓治疗后痊愈;肺部感染1例,抗生素治疗后痊愈。3例患者死亡,分别于置换后14,26和32个月,死亡原因为肺内感染(1例)和急性心肌梗死(2例)。两组无切口感染,深部感染发生。随访期内两组无关节脱位,无假体松动、下沉,及假体周围骨折等假体相关并发症发生。 2.4 关节功能和生活质量评价 随访12个月,关节功能评价统一采用Harris评分,骨水泥组髋关节功能Harris评分优良率较生物组高,但两组比较差异无显著性意义 (χ2=0.375,P=0.945),见表2。 2.5 两组手术相关指标比较 骨水泥组手术时间较生物型组延长,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01);两组术中出血量及置换后引流量差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。两组老年患者置换后负重时间比较,下床部分负重时间两组差异无显著性意义;完全负重时间骨水泥组早于生物组,差异有显著性意义(t=-7.07,P < 0.01),见表3。 2.6 典型病例 见图6,7。"
| [1] Holt G, Smith R, Duncan K, et al. Changes in population demographics and the future incidence of hip fracture. Injury.2009;40:722-726. [2] Parker M, Johansen A. Hip fracture. BMJ.2006;333:27-30. [3] Davison JN, Calder SJ, Anderson GH, et al. Treatment for displaced intracapsular fracture of the proximal femur. A prospective, randomised trial in patients aged 65 to 79 years. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001;83(2):206-212. [4] Heetveld MJ, Rogmark C, Frihagen F, et al. Internal fixation versus arthroplasty for displaced femoral neck fractures: what is the evidence? J Orthop Trauma. 2009;23(6):395-402. [5] Johansson T, Jacobsson SA, Ivarsson I, et al. Internal fixation versus total hip arthroplasty in the treatment of displaced femoral neck fractures: a prospective randomized study of 100 hips. Acta Orthop Scand. 2000;71(6):597-602. [6] No authors listed. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Guideline CG124 Hip Fracture: the management of hip fracture in adults, 2011. [7] Costain DJ, Whitehouse SL, Pratt NL, et al. Perioperative mortality after hemiarthroplasty related to fixation method. Acta Orthop. 2011;82:275-281. [8] Talsnes O, Vinje T, Gjertsen JE, et al. Perioperative mortality in hip fracture patients treated with cemented and uncemented hemiprosthesis: a register study of 11,210 patients. Int Orthop. 2013;37:1135-1140. [9] Middleton RG, Uzoigwe CE, Young PS, et,al. Peri-operative mortality after hemiarthroplasty for fracture of the hip does cement make a difference? Bone Joint J. 2014;96-B(9): 1185-1191. [10] Jamsen E, Eskelinen A, Peltola M, et al. High early failure rate after cementless hip replacement in the Octogenarian. Clin Orthop Relate Res. 2014;472:2779-2789. [11] Middleton RG, Uzoigwe CE, Young PS, et al. Peri-operative mortality after hemiarthroplasty for fracture of the hip: does cement make a difference? Bone Joint J. 2014;96-B: 1185-1191. [12] Dalury D, Kelley T, Adams M. Modern Proximally Tapered Uncemented Stems Can Be Safely Used in Dorr Type C Femoral Bone. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(6):1014-1018. [13] Pentlow AK, Heal JS.Subsidence of collarless uncemented femoral stems in total hips replacements performed for trauma. Injury. 2012;43(6):882-885. [14] Makela KT, Eskelinen A, Pulkkinen P, et al.Total hip arthroplasty for primary osteoarthritis in patients fiftyfive years of age or older: an analysis of the Finnish arthroplasty registry. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90:2160-2170. [15] Troelsen A, Malchau E, Sillesen N, et al.Areview of current fixation use and registry outcomes in total hip arthroplasty: the uncemented paradox. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471: 2052-2059. [16] Dorr LD, Faugere MC, Mackel AM, et al. Structural and cellular assessment of bone quality of proximal femur. Bone. 1993;14:231-242. [17] Harris WH. Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures: treatment by mold arthroplasty An end-result study using a new method of result evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1969;51:737-755. [18] Gruen TA, McNeice GM, Amstutz HC. “Modes of failure” of cemented stem-type femoral components: a radiographic analysis of loosening. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979;141:17-27. [19] Hossain M, Andrew JG. There a difference in perioperative mortality between cemented and uncemented implants in hip fracture surgery? Injury. 2012;43(12):2161-2164. [20] Rutter PD, Panesar SS, Darzi A, et al. What is the risk of death or severe harm due to bone cement implantation syndrome among patients undergoing hip hemiarthroplasty for fractured neck of femur? A patient safety surveillance study. BMJ Open. 2014;4(6):e004853. [21] Donaldson AJ, Thomson HE, Harper NJ, et al. Bone cement implantation syndrome. Br J Anaesth. 2009;102:12-22. [22] Rothberg DL, Kubiak EN, Peters CL, et al. Reducing the risk of bone cement implantation syndrome during femoral arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2013;36:463-467. [23] Azegami S, Gurusamy KS, Parker MJ. Cemented versus uncemented hemiarthroplasty for hip fractures: a systematic review of randomised controlled trials. Hip Int. 2011;21:509-517. [24] Parker MJ, Pryor G, Gurusamy K. Cemented versus uncemented hemiarthroplasty for intracapsular hip fractures: a randomised controlled trial in 400 patients. J Bone Joint Surg [Br]. 2010;92-B:116-122. [25] Taylor F, Wright M, Zhu M. Hemiarthroplasty of the hip with and without cement: a randomized clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg [Am]. 2012;94-A:577-583. [26] Figved W, Opland V, Frihagen F, et al. Cemented versus uncemented hemiarthroplasty for displaced femoral neck fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2009;467:2426-2435. [27] Capello WN, D’Antonio JA, Jaffe WL, et al. Hydroxyapatite- coated femoral components: 15-year minimum followup. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;453:75-80. [28] Capello WN, D’Antonio JA, Manley MT, et al. Hydroxyapatite in total hip arthroplasty: clinical results and critical issues. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998;355:200-211. [29] Cook SD, Thomas KA, Dalton JE, et al. Hydroxyapatite coating of porous implants improves bone ingrowth and interface attachment strength. J Biomed Mater Res. 1992;26:989-1001. [30] D’Antonio JA, Capello WN, Crothers OD, et al. Early clinical experience with hydroxyapatite-coated femoral implants.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1992;74:995-1008. [31] Jameson SS, Jensen CD, Elson DW, et al. Cemented versus cementless hemiarthroplasty for intracapsular neck of femur fracture: a comparison of 60,848 matched patients using national data. Injury.2013;44:730-734. [32] Uzoigwe CE, Burnand HG, Cheesman CL, et al. Early and ultra-early surgery in hip fracture patients improves survival. Injury.2013;44:726-729. [33] Abdulkarim A, Ellanti P, Motterlini N, et al.Cemented versus uncemented fixation in total hip replacement: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Orthop Rev (Pavia). 2013;5:e8. [34] Jameson SS, Baker PN, Mason J, et al. Independent predictors of failure up to 7.5 years after 35 386 single-brand cementless total hip replacements: a retrospective cohort study using National Joint Registry data. Bone Joint J. 2013;95:747-757. [35] Grammatopoulos G, Wilson HA, Kendrick BJ, et al. Hemiarthroplasty using cemented or uncemented stems of proven design: a comparative study. Bone Joint J. 2015; 97-B(1):94-99. [36] Jamsen E, Puolakka T, Eskelinen A, et al. Predictors of mortality following primary hip and knee replacement in the aged: a single-center analysis of 1,998 primary hip and knee replacements for primary osteoarthritis. Acta Orthop. 2013; 84:44-53. [37] Pieringer H, Labek G, Auersperg V, et al. Cementless total hip arthroplasty in patients older than 80 years of age. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003;85:641-645. [38] Puolakka TJ, Pajama¨ki KJ, Halonen PJ, et al. The Finnish Arthroplasty Register: report of the hip register. Acta Orthop Scand. 2001;72:433-441. [39] Ranstam J, Kärrholm J, Pulkkinen P, et al. Statistical analysis of arthroplasty data: II. Guidelines. Acta Orthop.2011;82:258-267. [40] Toossi N, Adeli B, Timperley AJ, et al. Acetabular components in total hip arthroplasty: is there evidence that cementless fixation is better? J Bone Joint Surg Am.2013;95:168-174. |
| [1] | Tang Hui, Yao Zhihao, Luo Daowen, Peng Shuanglin, Yang Shuanglin, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. High fat and high sugar diet combined with streptozotocin to establish a rat model of type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1207-1211. |
| [2] | Li Zhongfeng, Chen Minghai, Fan Yinuo, Wei Qiushi, He Wei, Chen Zhenqiu. Mechanism of Yougui Yin for steroid-induced femoral head necrosis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1256-1263. |
| [3] | Hou Guangyuan, Zhang Jixue, Zhang Zhijun, Meng Xianghui, Duan Wen, Gao Weilu. Bone cement pedicle screw fixation and fusion in the treatment of degenerative spinal disease with osteoporosis: one-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 878-883. |
| [4] | Li Shibin, Lai Yu, Zhou Yi, Liao Jianzhao, Zhang Xiaoyun, Zhang Xuan. Pathogenesis of hormonal osteonecrosis of the femoral head and the target effect of related signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 935-941. |
| [5] | Xiao Fangjun, Chen Shudong, Luan Jiyao, Hou Yu, He Kun, Lin Dingkun. An insight into the mechanism of Salvia miltiorrhiza intervention on osteoporosis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 772-778. |
| [6] | Liu Bo, Chen Xianghe, Yang Kang, Yu Huilin, Lu Pengcheng. Mechanism of DNA methylation in exercise intervention for osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 791-797. |
| [7] | Nie Shaobo, Li Jiantao, Sun Jien, Zhao Zhe, Zhao Yanpeng, Zhang Licheng, Tang Peifu. Mechanical stability of medial support nail in treatment of severe osteoporotic intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 329-333. |
| [8] | Zhong Yuanming, Wan Tong, Zhong Xifeng, Wu Zhuotan, He Bingkun, Wu Sixian. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of percutaneous curved vertebroplasty and unilateral pedicle approach percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 456-462. |
| [9] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| [10] | Feng Guancheng, Fang Jianming, Lü Haoran, Zhang Dongsheng, Wei Jiadong, Yu Bingbing. How does bone cement dispersion affect the early outcome of percutaneous vertebroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3450-3457. |
| [11] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [12] | Cai Qunbin, Yang Lijuan, Li Qiumin, Chen Xinmin, Zheng Liqin, Huang Peizhen, Lin Ziling, Jiang Ziwei . Feasibility of internal fixation removal of intertrochanteric fractures in elderly patients based on fracture mechanics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3313-3318. |
| [13] | Liu Yulin, Li Guotai. Combined effects of hyperbaric oxygen, vibration training and astaxanthin on bone mineral density, glucose metabolism and oxidative stress in diabetic osteoporosis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3117-3124. |
| [14] | Lin Haishan, Mieralimu Muertizha, Li Peng, Ma Chao, Wang Li. Correlation between skeletal muscle fiber characteristics and bone mineral density in postmenopausal women with hip fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3144-3149. |
| [15] | Hu Guang, Guan Zhiyu, Zhang Kaiwei . Mechanism underlying the interventional effect of Panax Notoginsenosides on ovariectomized osteoporotic fracture rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 172-177. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||