Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (9): 1313-1320.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.09.001
Total knee arthroplasty for knee varus deformity: follow-up evaluation of femorotibial angle and range of motion
Li Guang-wei, Wang Hong-jun, Sun Xiao-zhi, Chen Lin-bin, Gao Yu-liang, Bai Zhong-xu, Cheng Xin-sheng
- Second Department of Orthopedics, the Second People’s Hospital of Zhengzhou, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China
-
Revised:2014-12-09Online:2015-02-26Published:2015-02-26 -
About author:Li Guang-wei, Master, Associate chief physician, Second Department of Orthopedics, the Second People’s Hospital of Zhengzhou, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Guang-wei, Wang Hong-jun, Sun Xiao-zhi, Chen Lin-bin, Gao Yu-liang, Bai Zhong-xu, Cheng Xin-sheng. Total knee arthroplasty for knee varus deformity: follow-up evaluation of femorotibial angle and range of motion[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(9): 1313-1320.
share this article
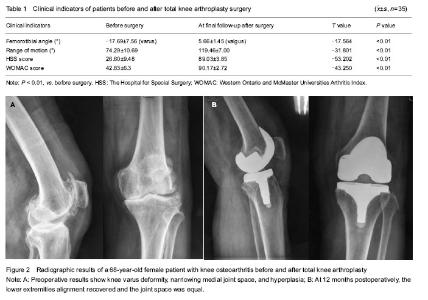
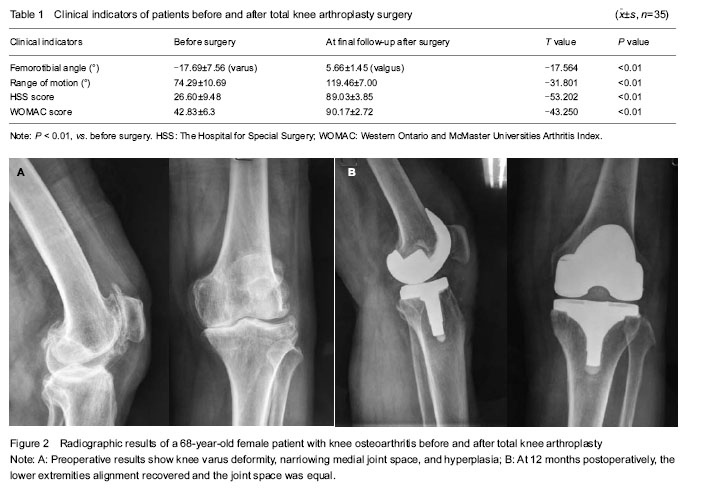
Quantitative analysis of participants According to the intention-to-treat analysis, 31 patients (35 knees) with knee varus deformity were involved in the final analysis, without drop-outs. Follow-up results All incisions were healing at I stage, no complications such as knee stiffness, blood vessels and nerve damage, prosthetic loosening and patellar fracture occurred. The average FTA was corrected from preoperative varus 17.69° (5°-30°) to postoperative 5.66° (2°-8°); knee ROM was improved from preoperative 74.29° (60°-95°) to 119.46° (105°-130°); the HSS score increased from preoperative 26.60 points (14-42 points) to postoperative 89.03 points (82-95 points), excellent in 28 cases and good in 7 cases; and the WOMAC score increased from preoperative 42.83 points (28-54 points) to postoperative 90.17 points (85-95 points). Statistical analysis results showed that, TKA surgery significantly improved the FTA, knee joint ROM, HSS score and WOMAC score in all involved patients (P < 0.01; Table 1). Typical case A 68-year-old female patient with knee osteoarthritis and knee varus flexion contracture deformity, received TKA surgery. There was no prosthetic loosening, no overhang and pain after 36 months of follow-ups, the clinical outcomes were satisfactory (Figure 2). Adverse events Two cases appeared anterior knee pain within 24 months postoperatively, the incidence was 6%. The pains were relieved to varying degrees after administration of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory antalgesic drugs and physical therapy."
| [1] Li S, Chen Y, Su W, et al. Systematic review of patellar resurfacing in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2011; 35(3): 305-316. [2] Radcliff KE, Orozco FR, Quinones D, et al. Preoperative risk stratification reduces the incidence of perioperative complications after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(8 Suppl):77-80.e8. [3] Zietz C, Bergschmidt P, Fritsche A, et al. Comparison of cross-sections of different femoral components for revision total knee replacement. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2012;20(1):32-36. [4] Wang X, Weng X, Lin J, et al. Surgical technique and clinical results of total knee arthroplasty in treating endstage gonarthrosis combined with valgus knee deformity. Zhongguo Xiufu Chongjian Waike Zazhi. 2012;26(5): 513-517. [5] Robertsson O, Dunbar M, Pehrsson T, et al. Patient satisfaction after knee arthroplasty: a report on 27, 372 knees operated on between 1981 and 1995 in Sweden. Acta Orthop Scand. 2000;71(3):262-267. [6] Gao W, Chen BC, Duan JT, et al. The anatomic research on the rotation relationship among the proximal tibia, distal femur and patella. Zhonghua Guke Zazhi. 2005;25(11): 687-691. [7] Li BW. Biomechanical alterations in total knee arthroplasty. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2008;12(17):3313-3316. [8] Zhou YX. Effect of artificial knee joint prosthesis design on patellofemoral joint function after total knee arthroplasty. Zhonghua Guke Zazhi. 2006;26(9):646-648. [9] Wang Y, Zhou YG, Wang JF, et al. Preliminary clinical outcome of mobile-bearing knee replacement. Zhonghua Guke Zazhi. 2002;22(5):276-279. [10] Kim YH, Yoon SH, Kim JS. Early outcome of TKA with a medial pivot fixed-bearing prosthesis is worse than with a PFC mobile-bearing prosthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467(2):493-503. [11] Wyss T, Schuster AJ, Christen B, et al. Tension controlled ligament balanced total knee arthroplasty: 5-year results of a soft tissue orientated surgical technique. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2008;128(2):129-135. [12] Lädermann A, Saudan M, Riand N, et al. Fixed-bearing versus mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomize clinical and radiological study. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 2008;94(3):247-251. [13] Karachalios TH, Sarangi PP, Newman JH. Severe varus and valgus deformities treated by total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg. 1994;76B:938-942. [14] Zhou DG, Lv HS, Du XK. Lower Extremity Alignment Analysis of Varus Knee with X-ray Image. Zhongguo Yixue Yingxiang Jishu. 2001;17(12):1222-1224. [15] Pan WJ, Jing K, He Y. Early clinical outcome of total knee arthroplasty for patients with knee of varus deformity and flexion contracture. Zhongguo Guyuguanjie Sunshang Zazhi. 2011;26(7):595-597. [16] Havet E, Gabrion A, Leiber-Wackenheim F, et al. Radiological study of the knee joint line position measured from the fibular head and proximal tibial landmarks. Surg Radiol Anat. 2007;29(4):285-289. [17] Hao SC, Jiang JN, Wang Y, et al. Effect of treatment of posterior stabilized total knee arthroplasty. Zhongguo Guyuguanjie Sunshang Zazhi. 2011;26(7):622-623. [18] Liu PF, Guo L, Tian FD, et al. Clinical analysis of total knee arthroplasty therapy for unilateral knee varus combined with flexion contracture deformity. Zhongguo Guyuguanjie Sunshang Zazhi. 2013;28(2):119-121. [19] Feng CL, Li ZS, Li AY, et al. Clinical research of total knee arthroplasty for patients with knee of varus deformity. Chongqing Yixue. 2013;42(11):1229-1230. [20] Lv HS, Yuan YL, Kou BL, et al. Clinic analysis of 1336 total knee arthroplasty. Beijing Daxue Xuebao (Yixueban). 2002; 34(5):618-622. [21] Li J, Zheng K, Hu PX, et al. Comparison of short-term result between high-flex and conventional posterior stabilized prosthesis in total knee arthroplasty. Zhongguo Xiufu Chongjian Waike Zazhi. 2010;24(3):278-281. [22] Kim YH, Sohn KS, Kim JS. Range of motion of standard and high flexion posterior stabilized total knee prosthese. A prospective, randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg (Am). 2005;87(7):1470-1475. [23] McCalden RW, MacDonald SJ, Bourne RB, et al. A randomized controlled trial comparing “high-flex” vs “standard” posterior cruciate substituting polyethylene tibial inserts in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2009; 24(6 Suppl):33-38. [24] Bao YJ, Dong JY, Xu DL. Application of fixed-bearing knee joint prosthesis in treatment of varus deformity in elderly osteoarthritis patients. Jiefangjun Yixueyuan Xuebao. 2013; 34(5):484-491. [25] Yamazaki J, Ishigami S, Nakmura T, et al. Hy-Flex II total knee system and range of motion. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2002;122(3):156-160. [26] Hsu RW. The management of the patella in total knee arthroplasty. Chang Gung Med J. 2006;29(5):448-457. [27] Zhang X, Wang ZW. Patella treatment in total knee arthroplasty. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(13):2421-2424. [28] Zou YG, Chen ZW, Feng ZQ, et al. Factors related to anterior knee pain after total knee arthroplasty. Nanfang Yike Daxue Xuebao. 2011;31(8):1428-1430. [29] Raviraj A, Prabhu A, Pai S, et al. Fixed vs mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasty: does it make a difference?--a prospective randomized study. J Arthroplasty. 2010;25(5): 835. [30] Chai W, Sun CJ, Ni M, et al. Case-control study on earlier medial tibial pain after total knee arthroplasty. Zhongguo Gushang. 2014;27(4):269-273. |
| [1] | Pu Xingyu, Luo Wenyuan, Qian Yaowen, Cai Liyang, Zhang Chao, Chen Shaolong, Wang Yue, Zhang Wei . Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty for medial compartmental knee osteoarthritis in young and middle-aged patients: a short-term follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1161-1166. |
| [2] | Chen Xiaokang, Wu Zhengjie, Zhou Bingxue, Zhou Jiansheng, Hong Shi. Semi-restrictive total elbow arthroplasty for complex distal humeral fractures in the older adults: one-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1168-1171. |
| [3] | Shi Jun-heng, Zhong De-gui, Hong Wei-wu, Huang Yong-quan. Meta-analysis of clinical outcomes of computer-navigated versus conventional opening wedge high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(31): 5077-5084. |
| [4] | Huang Chen-yu, Liu Shuai, Tian Shu-chang, Yao Qing-qiang, Wang Li-ming. Application of iASSIST-assisted total knee arthroplasty in the treatment of genu varum or genu valgus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(11): 1653-1658. |
| [5] | Song Qing-peng, Tian Wei, He Da, Han Xiao, Wang Jin-chao, Li Zu-chang, Feng Xiao. Influence of the artificial disc size on cervical artificial disc replacement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(11): 1665-1670. |
| [6] | Chen Qun-qun, Qiao Rong-qin, Duan Rui-qi, Hu Nian-hong, Li Zhao, Shao Min. Acu-Loc®2 volar distal radius bone plate system for repairing type C fracture of distal radius [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1025-1030. |
| [7] | Li Guo-qing, Mohetaer•Momin, Ma Jun. Short-term treatment outcome of the trabecular monoblock metal tibial components versus conventional cemented tibial components in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(35): 5589-5594. |
| [8] | Zhang Shu-fang, Chen Rong-chun, Guo Chao-yang, Ye Shu-xi. Three-dimensional printing-assisted atlantoaxial pedicle screw placement for type II C odontoid fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(31): 4951-4956. |
| [9] |
Geng Xiang, Huang Jia-zhang, Ma Xin, Wang Xu, Zhang Chao, Chen Li, Wang Chen.
A comparison between over-the-toe plaster slab and off-loading forefoot shoes following hallux valgus correction
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(26): 4234-4239.
|
| [10] | Sun Zhen-guo, Zhu Jia-jun, Cui Yan, Ni Sheng-hui, Zhang Zhi-yu . Three-dimensional printing technology-aided total knee arthroplasty for osteoarthritis with genu varum deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(15): 2395-2399. |
| [11] | He Sheng-hua, Lai Ju-yi, Wang Ye-guang, Sun Zhi-tao, Wang Jian, Feng Hua-long, Huang Fei-qiang. Zero-P anterior cervical fixation system for multilevel cervical myelopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(11): 1695-1700. |
| [12] | Qiu Hao, Lu Min-peng, Dong Jing, Zhang Zhong-zu, Chu Tong-wei, Wang Qun-bo, Quan Zheng-xue, Jiang Dian-ming. Subtotal corpectomy and reconstruction with titanium mesh cage implantation and pedicle screw fixation through posterior approach in treatment of thoracolumbar burst fracture or thoracolumbar fracture dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(53): 7932-7938. |
| [13] | Zhang Shu-fang, Zhong Hong-fa, Chen Rong-chun, Guo Zhao-yang, Ye Shu-xi, You Hui . Best choice of three-dimensional printing-assisted pedicle subtraction osteotomy for the treatment of kyphosis deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(53): 7966-7972. |
| [14] | Abudunaibi•Aili, Zhang Hong-qi, Huang Wei-min, Li Lei, Tian Hui-zhong. Special formed titanium mesh cages for treating spinal tuberculosis via one-stage posterior approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(48): 7192-7199. |
| [15] | Zhang Wei, Tang Zai-xiang, Geng De-chun, Zhu Feng, Dong Han-qing, Wang Yi-jun, Xu Yao-zeng. Multiple linear regression analysis of hip function and vitamin D levels before and after hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(44): 6557-6563. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||