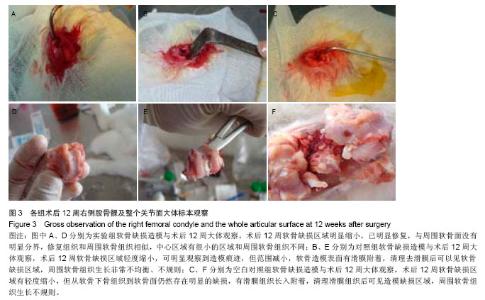
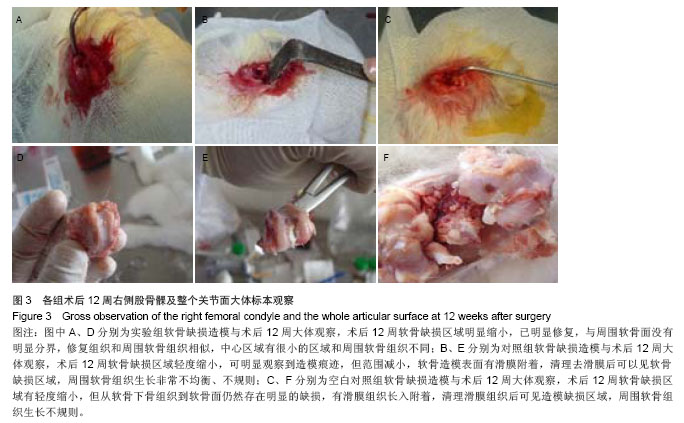
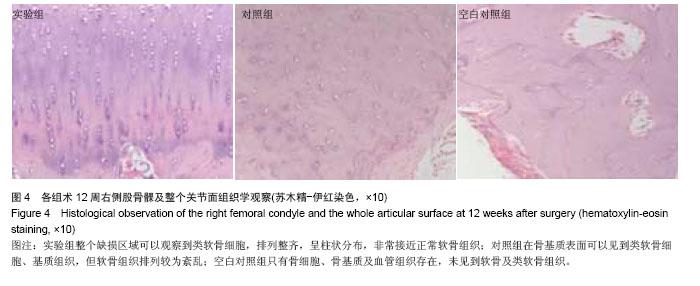
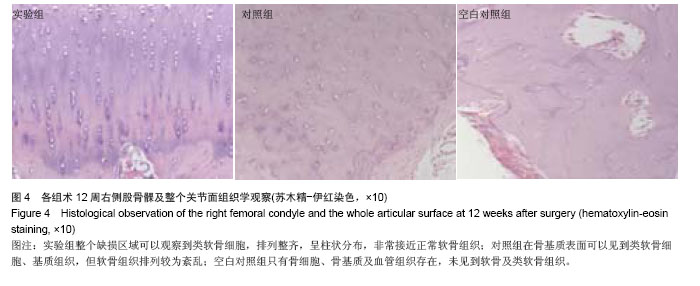
| [1]O’Driscoll SW.The healing and regeneration of articular cartilage.Bone Joint Surg Am.1998;80(12): 1795-1812.
[2]康健,袁文.富血小板凝胶制备方法的比较与优选[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(3):476-481.
[3]Alsousou J,Thompson M,Hulley P,et al.The biology of platelet-rich plasma and its application in trauma and orthopaedic surgery: a review of the literature. J Bone Joint Surg Br.2009;91(8):987-996.
[4]De Almeida AM,Demange MK,Sobrado MF,et al.Patellar tendon healing with platelet-rich plasma: a prospective randomized controlled trial.Am J Sports Med.2012;40(6): 1282-1288.
[5]刘骥,袁霆,张长青.富血小板血浆治疗慢性组织损伤的研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2010,24(6):754-757.
[6]Randelli P,Arrigoni P,Ragone V,et al.Platelet rich plasma in arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: a prospective RCT study, 2-year follow-up. Aliprandi A, Cabitza P.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011; 20(4):518-528.
[7]Wei LC,Lei GH,Sheng PY,et al.Efficacy of platelet-rich plasma combined with allograft bone in the management of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures: a prospective cohort study. J Orthop Res.2012;30(10):1570-1576.
[8]Hartmann EK,Heintel T,Morrison RH,et al.Influence of platelet-rich plasma on the anterior fusion in spinal injuries: a qualitative and quantitative analysis using computer tomography. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2010;130(7):909-914.
[9]Liu J,Song W,Yuan T,et al.A Comparison between Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) and Hyaluronate Acid on the Healing of Cartilage Defects.PLoS One.2014;9(5):e97293P.
[10]Lundquist W,Stanford R.Chronic Pain Perspectives: Targeting systemic inflammation in patients with obesity-related pain: One practice's success with platelet-rich plasma therapy.J Fam Pract.2013;62(9):S10-15.
[11]Gandhi A,Bibbo C,Pinzur M,et al.The role of platelet-rich plasma in foot and ankle surgery. Foot Ankle Clin.2005;10(4): 621-637.
[12]Vogrin M,Rupreht M,Dinevski D,et al.Effects of a platelet gel on early graft revascularization after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a prospective, randomized, double-blind, clinical trial.Eur Surg Res. 2010;45(2):77-85.
[13]Sheth U,Simunovic N,Klein G,et al.Efficacy of autologous platelet-rich plasma use for orthopaedic indications: a meta-analysis.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(4):298-307.
[14]Sheth U, Simunovic N, Klein G,et al.Efficacy of autologous platelet-rich plasma use for orthopaedic indications:a meta-analysis.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(4):e25.
[15]Mnaymneh W, Mailinin T. Massive allografts in surgery of bone tumors.Orthop Clin North Am.1989;20(3):455-467.
[16]Johnson EE,Urist MR,Schmalzried TP,et al.Autogenic cancellous bone grafts in extensive segmental ulnar defects in dogs. Effects of xenogenic bovine bone morphogentic protein without and with interposition of soft tissues and interruption of blood supply.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1989; (243):254-265.
[17]郝永壮,张宇明,苏云星,等.组织工程化软骨对兔膝关节全层软骨缺损的修复效果[J].山西医科大学学报,2013,44(10):791-836.
[18]Haider A,Gupta KC,Kang IK.PLGA/nHA hybrid nanofiber scaffold as a nanocargo carrier of insulin for accelerating bone tissue regeneration. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2014;9(1):314.
[19]张长青,袁霆.富血小板血浆制作技术和临床应用[M].上海:科学技术出版社,2011.
[20]周蔚,吴海涛,李采.海螺峭作为组织工程支架材料的实验研究[J].复旦学报:医学版,2007,34(3):438-441.
[21]陶凯,毛天球,陈富林,等.一种新型羟基磷灰石材料的制备及其细胞相容性探讨[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2006,23(4):887-890.
[22]Madry H,Kaul G,Zurakowski D,et al.Cartilage constructs engineered from chondrocytes overexpressing IGF-I improve the repair of osteochondral defects in a rabbit model.Eur Cell Mater.2013;25:229-247.
[23]Ivkovic A,Marijanovic I,Hudetz D,et al.Regenerative medicine and tissue engineering in orthopaedic surgery. Front Biosci. 2011;3:923-944.
[24]Numano T,Homma K,Tateishi T,et al.Feasibility of noninvasive evaluation of biophysical properties of tissue-engineered cartilage by using quantitative MRI.J Biomech.2007;40:2990.
[25]Cui JH,Park SR,Choi BH,et al.Preconditioning of rabbit mesenchymal stem cells in polyglycolic acid (PGA) scaffold using low-intensity ultrasound improved regeneration of cartilage in rabbit articular cartilage defect model. Tissue Eng Regen Med.2010;7:24.
[26]Hong HH, Kim SJ, Kim SH, et al.Effect of PLGA scaffold penetrated demineralized bone solution for chondrogenesis: In vitro test.Tissue Eng Regen Med.2010;7:142.
[27]裴雪涛.再生医学—理论与技术[M].北京:科学出版社,2010: 260-261.
[28]Mike AG,Sarakinos G,Lyman MD,et al.Sagittal ramus Osteotomis fixed with biodegradable screws:a preliminary report.J Cell Biochem.1994;56(4):192-195.
[29]Sittinger M,Bujia J,Rotter N,et al.Tissue engineering and autologous transplant formation:practical approaches with resorbable biomaterials and new cell culture techniques. Biomat.1996;17:237-242.
[30]刘艺,张安祯,王和鸣,等.海缥峭接骨动物实验研究[J].福建医药, 1998,19(3):49.
[31]刘源,于江,白洁,等.海螵蛸-骨形态发生蛋白复合材料对骨缺损大鼠成骨及再血管化的影响[J].中华烧伤杂志,2013,29(6): 548-553.
[32]付小兵,王正国,吴祖泽.再生医学基础与临床[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2013:491. |