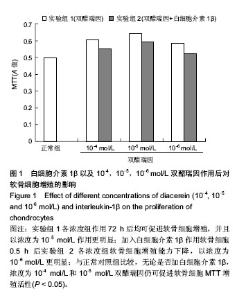
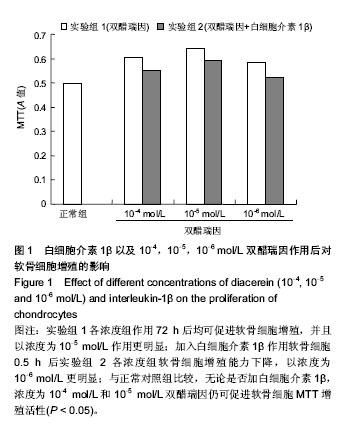
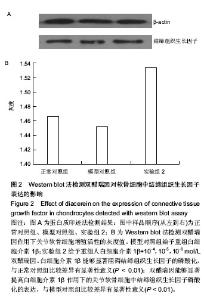
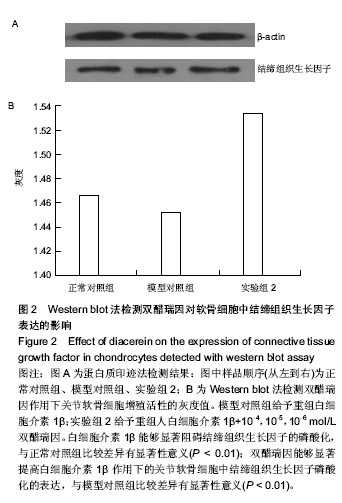
| [1] Daniels A, van Bilsen M, Goldschmeding R, et al. Connective tissue growth factor and cardiac fibrosis.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2009; 195(3): 321-338.
[2] The Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China. Guidance Suggestions for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 2006-09-30.
[3] 俞永林,任志伟,乔健,等.兔关节软骨细胞的分离培养及生物学特征[J].复旦学报:医学版,2006,33(6):753-756.
[4] Pelletier JP, McCollum R, Cloutier JM, et al. Synt hesis of metalloproteases and interleukin26(IL26)inhuman osteoart hriticsynovia membrance is an IL-l mediated process. J Rheumatol. 1995;43(suppl):109-114.
[5] Dozin B, Malpeti M, Camardella L, et al. Response of young, aged and oste- oarthritical human arricular condrrocytes to inflammatory cytokines:molecular and cellular aspects. Matrix Biol. 2002;21(4):449.
[6] James L, Cook C, Anderson C, et al.Effects of human recombinant interleukin-1 beta on canine articular chondrocytes in three-dimensional culture. AJVR. 2000;61: 766.
[7] Kubota S, Takigawa M. Role of CCN2/CTGF/Hcs 24 in bone growth. Int Rev Cytol. 2007; 257:1-41.
[8] Nakao K, Kubota S, Doi H, et al. Collaborative action of M-CSF and CTGF/CCN2 in articular chondrocytes: possible regenerative roles in articular cartilage metabolism. Bone. 2005; 36(5):884-892.
[9] 邵欣欣,田得祥,于长隆.一氧化氮抑制兔关节软骨细胞II型胶原的合成[J].中国运动医学杂志,2001,20(1):31-34.
[10] 彭程,林绵杯,肖涛.细胞因子与软骨损伤修复及研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2006,27(4):239-243.
[11] Toegel S, Wu SQ, Piana C, et al. Comparison between chondroprotective effects of glucosamine, curcumin, and diacerein in IL-1b-stimulated C-28/I2 chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2008;16:1205-1212. |