Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (53): 8685-8692.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.53.029
Meta-analysis of posterolateral fusion versus 360° circumferential fusion in lumbar spondylolisthesis
Wang Zhan, Wang Wen-ji
- The First Clinical Medical College, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China
-
Revised:2014-10-30Online:2014-12-24Published:2014-12-24 -
Contact:Wang Wen-ji, M.D., Master’s supervisor, Chief physician, The First Clinical Medical College, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China -
About author:Wang Zhan, Studying for master’s degree, The First Clinical Medical College, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Zhan, Wang Wen-ji. Meta-analysis of posterolateral fusion versus 360° circumferential fusion in lumbar spondylolisthesis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(53): 8685-8692.
share this article
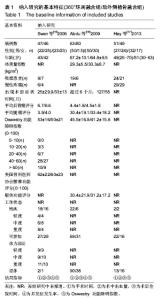
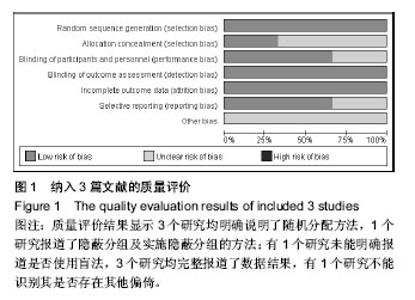
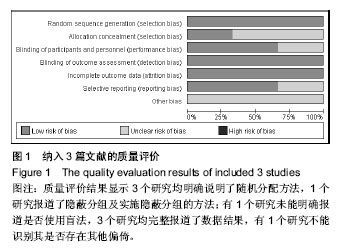
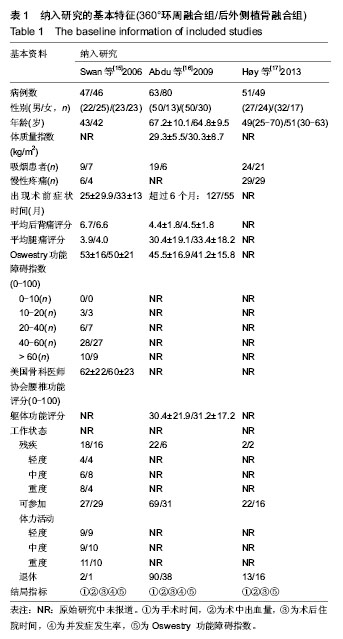
2.1 纳入文献的基本特征 2.1.1 文献筛选结果 经检索数据库,共查找到相关文献233篇,Endnote X6去重95篇。由2名研究员严格按照纳入排除标准独立阅读问题和摘要进行初步筛选,排除文献131篇,其中包括综述32篇,回顾性研究43篇,病例对照16篇,无关文献23篇,重复发表17篇,初步纳入7篇文献。经获取并阅读全文后排除非随机对照试验2篇,Meta分析1篇,无可用数据1篇,最终纳入3个随机对照试验进行定量分析。 2.1.2 纳入文献的基本特征 最终纳入3个随机对照试验[15-17],共336例患者,其中后外侧植骨融合组175例,360°环周融合组161例;男204例,女132例;年龄42-67岁,随访时间最长为4年。纳入研究的基本特征见表1。"
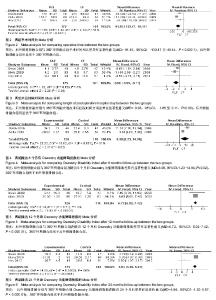
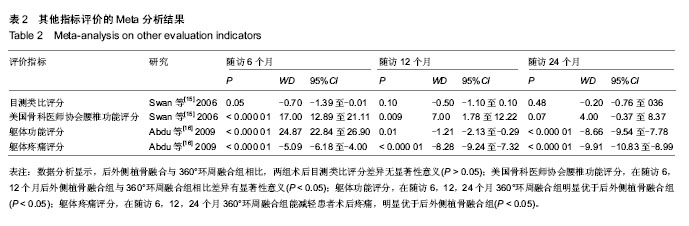
2.3 手术时间比较的Meta分析 纳入的3个随机对照试验均报道了两组手术方式的手术时间(min)[15-17],各研究间存在统计学异质性(I2=51%,P=0.13),采用随机效应模型进行Meta分析,结果显示,后外侧植骨融合组与360°环周融合组相比手术时间差异有显著性意义(MD=-91.15, 95%CI:-133.17至-49.14,P < 0.000 1),后外侧植骨融合组明显优于360°环周融合组。两组手术时间Meta分析结果见图2。 2.4 术中出血量比较的Meta分析 纳入的3个随机对照试验均报道了两组手术出血量(mL)[15-17],各研究间存在统计学异质性(I2=89%,P=0.000 2),采用随机效应模型进行Meta分析,结果显示,后外侧植骨融合组与360°环周融合组术中出血量差异无显著性意义(MD=-165.51,95%CI:-375.89至44.86,P=0.12)。 2.5 术后住院时间比较的Meta分析 纳入的3个随机对照试验均报道了术后住院时间(d)[15-17],各研究间无统计学异质性(I2=0%,P=0.60),采用固定模型进行Meta分析,结果显示,后外侧植骨融合组与360°环周融合组在术后住院时间方面差异有显著性意义(MD=-0.98,95%CI:-1.85至-0.11,P=0.03),后外侧植骨融合组明显优于360°环周融合组。两组术后住院时间的比较见图3。 2.6 术后并发症比较的Meta分析 纳入的研究中有2个随机对照试验,报道了术后并发症的发生例数(例)[15-16],各研究间无统计学异质性(I2=0%,P=0.92),采用固定模型进行Meta分析,结果显示,后外侧植骨融合组与360°环周融合组在并发症发生率方面差异无显著性意义(OR=1.16,95%CI:0.51至2.62,P=0.72)。 2.7 Oswestry功能障碍指数比较的Meta分析 纳入的3个随机对照试验分别报道了两组Oswestry功能障碍指数随访6,12及24个月的结果[15-17]。Meta分析结果显示,2个研究报道了随访6个月后的Oswestry功能障碍指 数[15-16],各研究间存在统计学异质性(I2=91%,P=0.001),采用随机效应模型进行Meta分析,结果显示,后外侧植骨融合组与360°环周融合组Oswestry功能障碍指数差异有显著性意义(MD=8.08,95%CI:1.23-14.94, P=0.02),360°环周融合组优于后外侧植骨融合组。有2个研究报道了随访12个月后的Oswestry功能障碍指数[15-16],各研究间无统计学异质性(I2=0%,P=0.71),采用固定效应模型进行Meta分析,结果显示,后外侧植骨融合组与360°环周融合组Oswestry功能障碍指数差异有显著性意义(MD= 6.72,95%CI:6.02-7.42,P < 0.000 01),360°环周融合组优于后外侧植骨融合组。3个研究报道了随访24个月后的Oswestry功能障碍指数[15-17],各研究间存在统计学异质性(I2=86%,P=0.000 9),采用随机效应模型进行Meta分析,结果显示,后外侧植骨融合组与360°环周融合组Oswestry功能障碍指数差异有显著性意义(MD=4.94,95%CI:4.30-5.57,P < 0.000 01),360°环周融合组优于后外侧植骨融合组。随访6,12,24个月Oswestry功能障碍指数的比较见图4-6。 2.8 其他指标的Meta分析 纳入的研究中,仅有1个研究报道了随访6,12,24个月后患者目测类比评分[15],数据分析显示,后外侧植骨融合与360°环周融合组相比,两组术后目测类比评分差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。Swan等[15]报道了两组患者术后美国骨科医师协会腰椎功能评分,数据分析结果显示,在随访6个月(MD=17.00,95%CI:12.89-21.11,P < 0.000 01)、12个月(MD=7.00,95%CI:1.78至12.22,P=0.009),后外侧植骨融合组与360°环周融合组相比差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);而在随访24个月(MD=4.00,95%CI:-0.37至8.37,P=0.07)后差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。Abdu等[16]报道了躯体功能评分指标,数据分析结果显示,在随访6个月(MD=24.87,95%CI: 22.84-26.90,P < 0.000 01)、12个月(MD=-1.21, 95%CI:-2.13至-0.29,P=0.01)、24个月(MD=-8.66,95%CI:-9.54至-7.78,P < 0.000 01)后,两组患者躯体功能评分差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),表明360°环周融合组明显优于后外侧植骨融合组。Abdu等[16]同时也报道了两组躯体疼痛评分指标,数据分析结果显示,在随访6个月(MD=-5.09,95%CI:-6.18至-4.00,P < 0.000 01)、12个月(MD=-8.28,95%CI:-9.24至-7.32,P < 0.000 01)、24个月(MD=-9.91,95%CI: -10.83至-8.99, P < 0.000 01)后,两组患者躯体疼痛评分差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),表明360°环周融合组能减轻患者术后疼痛,明显优于后外侧植骨融合组。各评价指标数据分析结果见表2。"

| [1] 黄善武,欧阳永生.腰椎滑脱症外科手术治疗进展[J].吉林医学, 2014, 35(7):1490-1493. [2] Jacobsen S, Sonne-Holm S, Rovsing H, et al. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: an epidemiological perspective: the Copenhagen Osteoarthritis Study. Spine. 2007;32(1): 120-125. [3] Kalichman L, Hunter DJ. Diagnosis and conservative management of degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J. 2008; 17(3): 327-335. [4] 李家速,陈守剑,肖红兴,等.退行性腰椎滑脱治疗的循证医学进展[J].颈腰痛杂志,2014,35(3): 224-226. [5] Ha KY, Na KH, Shin JH, et al. Comparison of posterolateral fusion with and without additional posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2008;21(4): 229-234. [6] Kimball J,Yew A, Getachew R, et al. Minimally invasive tubular surgery for transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. Neurosurg Focus. 2013;35:19. [7] Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Bullis D, et al. Results of in situ fusion for isthmic spondylolisthesis. J Spinal Disord Tech.1992;5(4): 433-442. [8] Resnick DK, Choudhri TF, Dailey AT, et al. Guidelines for the performance of fusion procedures for degenerative disease of the lumbar spine. Part 9: fusion in patients with stenosis and spondylolisthesis. J Neurosurg. 2005; 2(6): 679-685. [9] Kim JS, Kim DH, Lee SH, et al. Comparison study of the instrumented circumferential fusion with instrumented anterior lumbar interbody fusion as a surgical procedure for adult low-grade isthmic spondylolisthesis. World Neurosurg. 2010; 73(5): 565-571. [10] Zhou ZJ, Zhao FD, Fang XQ, et al. Meta-analysis of instrumented posterior interbody fusion versus instrumented posterolateral fusion in the lumbar spine: A review. J Neurosurg. 2011;15(3): 295-310. [11] 买尔旦,买买提,盛伟斌,等.椎间融合器融合和自体骨融合治疗腰椎滑脱效果的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013, 17(52): 9041-9048. [12] 王旭.后外侧植骨融合与后路椎间融合手术治疗轻度峡部裂性腰椎滑脱症疗效Meta分析[D].吉林大学, 2013. [13] 刘绮,马超,伍少玲,等. Oswestry功能障碍指数评定慢性腰痛患者的效度分析[J].中国康复医学杂志, 2010,25(3): 228-231. [14] Higgins JPT, Green S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Version 5.1.0. The Cochrane Collaboration; 2011. 2011-03-01. [15] Swan J, Hurwitz E, Malek F, et al. Surgical treatment for unstable low-grade isthmic spondylolisthesis in adults: a prospective controlled study of posterior instrumented fusion compared with combined anterior-posterior fusion. Spine J. 2006;6(6): 606-614. [16] Abdu WA, Lurie JD, Spratt KF, et al. Degenerative spondylolisthesis: does fusion method influence outcome? Four-year results of the spine patient outcomes research trial (SPORT). Spine. 2009;34(21): 2351. [17] Høy K, Bünger C, Niederman B, et al. Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) versus posterolateral instrumented fusion (PLF) in degenerative lumbar disorders: a randomized clinical trial with 2-year follow-up. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(9): 2022-2029. [18] 张盛强,朱干,陈东军.腰椎滑脱症诊疗指南编写报告[J].世界中医骨科杂志, 2012,12(1): 24-25. [19] Weinstein JN, Lurie JD, Tosteson TD, et al. Surgical versus nonsurgical treatment for lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis. New Eng J Med. 2007;356(22): 2257-2270. [20] Rampersaud YR, Wai EK, Fisher CG, et al. Postoperative improvement in health-related quality of life: a national comparison of surgical treatment for focal (one-to two-level) lumbar spinal stenosis compared with total joint arthroplasty for osteoarthritis Spine J. 2011, 11(11): 1033-1041. [21] Gelalis ID, Arnaoutoglou C, Christoforou G, et al. Prospective analysis of surgical outcomes in patients undergoing decompressive laminectomy and posterior instrumentation for degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. Acta Orthopaedica Et Traumatologica Turcica.2010;44(3): 235-240. [22] Kornblum MB, Fischgrund JS, Herkowitz HN, et al. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis: a prospective long-term study comparing fusion and pseudarthrosis. Spine. 2004; 29(7): 726-733. [23] Fernández-Fairen M, Sala P, Ramírez H, et al. A prospective randomized study of unilateral versus bilateral instrumented posterolateral lumbar fusion in degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine. 2007;32(4): 395-401. [24] Wu RH, Fraser JF, Härtl R. Minimal access versus open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: meta-analysis of fusion rates. Spine. 2010;35(26): 2273-2281. [25] Kim JS, Kim DH, Lee SH, et al. Comparison study of the instrumented circumferential fusion with instrumented anterior lumbar interbody fusion as a surgical procedure for adult low-grade isthmic spondylolisthesis. World Neurosurg. 2010; 73(5): 565-571. [26] 张为,丁文元,申勇,等. 360度环状融合内固定术治疗腰椎滑脱[J]. 河北医科大学学报,2005,26(2): 102-104. [27] 王波,刘海鹰,王会民,等.后路环周融合治疗老年人重度腰椎管狭窄症[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2006,14(15): 1121-1123. [28] 张海波,王义生,贾思明,等.后路环状融合术在腰椎滑脱症外科手术中的应用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2008,16(9): 657-659. [29] Liu X, Wang Y, Qiu G, et al. A systematic review with meta-analysis of posterior interbody fusion versus posterolateral fusion in lumbar spondylolisthesis. Europ Spine J. 2014;23(1): 43-56. [30] 曾水平,黄冬莲,郭建中,等. 360°环形融合术(后路椎间融合+ 后外侧植骨融合)在成人腰椎滑脱中的临床研究[J].中国现代医生, 2013, 51(28): 145-146. [31] 黎庆初,金大地,胡辉林.三种融合方式治疗腰椎滑脱症的疗效比较[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2010, 18(7): 608-609. [32] Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Bullis D, et al. Results of in situ fusion for isthmic spondylolisthesis. J Spinal Disord Tech. 1992; 5(4): 433-442. [33] Butt MF, Dhar SA, Hakeem I, et al. In situ instrumented posterolateral fusion without decompression in symptomatic low-grade isthmic spondylolisthesis in adults. Int Orthop. 2008; 32(5): 663-669. [34] Girardo M, Bettini N, Dema E, et al. Uninstrumented posterolateral spinal arthrodesis: is it the gold standard technique for I° and II° grade spondylolisthesis in adolescence? Europ Spine J. 2009; 18(1): 126-132. [35] Carragee EJ. Single-Level Posterolateral Arthrodesis, with or without Posterior Decompression, for the Treatment of Isthmic Spondylolisthesis in Adults. A Prospective, Randomized Study. J Bone Joint Surg. 1997; 79(8): 1175-1180. [36] de Loubresse CG, Bon T, Deburge A, et al. Posterolateral fusion for radicular pain in isthmic spondylolisthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996; 323: 194-201. [37] Sherman FC, Rosenthal RK, Hall JE. Spine fusion for spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis in children. Spine. 1979; 4(1): 59-67. [38] Muschik M, Zippel H, Perka C. Surgical management of severe spondylolisthesis in children and adolescents: anterior fusion in situ versus anterior spondylodesis with posterior transpedicular instrumentation and reduction. Spine.1997; 22(17): 2036-2042. [39] Johnson LP, Nasca RJ, Dunham WK. Surgical management of isthmic spondylolisthesis. Spine.1988; 13(1): 93-97. [40] Wiltse LL, Jackson DW. Treatment of spondylolisthesis and spondylolysis in children. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1976; 117: 92-100. [41] Adam FF. Surgical management of isthmic spondylolisthesis with radicular pain. Int Orthop. 2003; 27(5): 311-314. [42] Moher D, Hopewell S, Schulz KF, et al. CONSORT 2010说明与详述:报告平行对照随机临床试验指南的更新[J].中西医结合学报, 2010, 8(8):701-741. |
| [1] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [2] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [3] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [4] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [5] | Wang Yongsheng, Wu Yang, Li Yanchun. Effect of acute high-intensity exercise on appetite hormones in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1305-1312. |
| [6] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [7] | Hou Guangyuan, Zhang Jixue, Zhang Zhijun, Meng Xianghui, Duan Wen, Gao Weilu. Bone cement pedicle screw fixation and fusion in the treatment of degenerative spinal disease with osteoporosis: one-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 878-883. |
| [8] | Song Chengjie, Chang Hengrui, Shi Mingxin, Meng Xianzhong. Research progress in biomechanical stability of lateral lumbar interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 923-928. |
| [9] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Intravenous, topical tranexamic acid alone or their combination in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 948-956. |
| [10] | Li Yan, Wang Pei, Deng Donghuan, Yan Wei, Li Lei, Jiang Hongjiang. Electroacupuncture for pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 957-963. |
| [11] | He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan. Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [12] | Hua Haotian, Zhao Wenyu, Zhang Lei, Bai Wenbo, Wang Xinwei. Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of antibiotic artificial bone in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 970-976. |
| [13] | Zhan Fangbiao, Cheng Jun, Zou Xinsen, Long Jie, Xie Lizhong, Deng Qianrong. Intraoperative intravenous application of tranexamic acid reduces perioperative bleeding in multilevel posterior spinal surgery: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 977-984. |
| [14] | Zhong Yuanming, Wan Tong, Zhong Xifeng, Wu Zhuotan, He Bingkun, Wu Sixian. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of percutaneous curved vertebroplasty and unilateral pedicle approach percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 456-462. |
| [15] | Li Yang, Zhang Mingyong. Meta-analysis of the effect of double Endobutton and clavicular hook plate on the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 463-470. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||