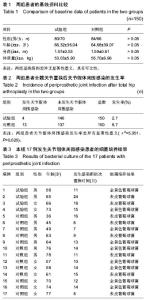
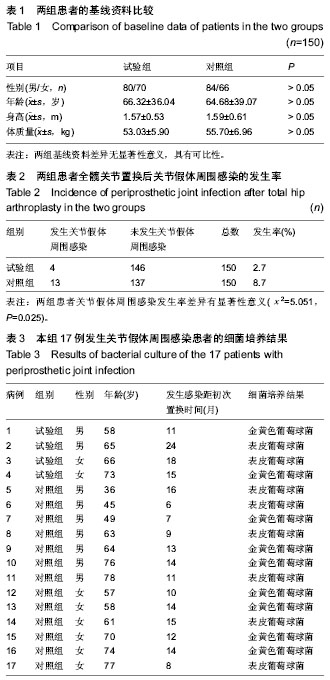
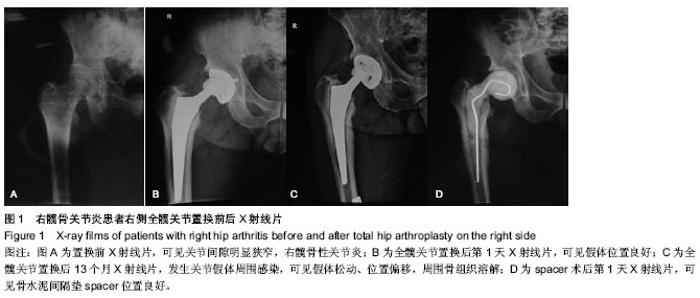
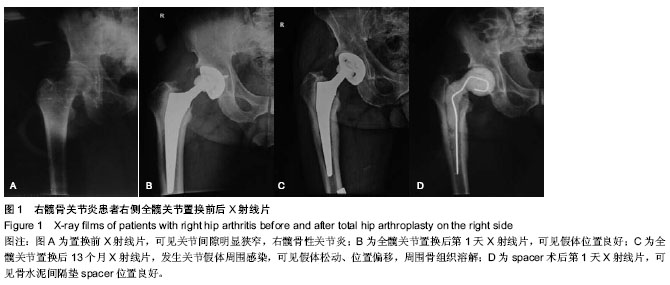
| [1] Beswick AD, Elvers KT, Smith AJ, et al. What is the evidence base to guide surgical treatment of infected hip prostheses? systematic review of longitudinal studies in unselected patients. BMC Med. 2012;10:18.
[2] Kurtz S, Ong K, Lau E, et al. Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(4):780-785.
[3] Levent T, Vandevelde D, Delobelle JM, et al. Infection risk prevention following total knee arthroplasty. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2010;96(1):49-56.
[4] Jørgensen PH, Gromov K, Søballe K. Prevention of prosthesis infections. Ugeskr Laeger. 2007;169(48): 4159-4163.
[5] Gallo J, Landor I, Vavrík P. Current strategies for prevention of prosthetic joint infection. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2006;73(4):229-236.
[6] 吴秋季,李强,张绍,等.手术室环境预防人工关节置换后感染的有效性[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(39):6902-6907.
[7] Jahoda D, Nyc O, Pokorný D, et al. Antibiotic treatment for prevention of infectious complications in joint replacement. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2006;73(2):108-114.
[8] Lewis G. Properties of antibiotic-loaded acrylic bone cements for use in cemented arthroplasties: a state-of-the-art review. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2009;89(2):558-574.
[9] Winkler H. Rationale for one stage exchange of infected hip replacement using uncemented implants and antibiotic impregnated bone graft. Int J Med Sci. 2009;6(5):247-252.
[10] van Kasteren ME, Manniën J, Ott A, et al. Antibiotic prophylaxis and the risk of surgical site infections following total hip arthroplasty: timely administration is the most important factor. KClin Infect Dis. 2007;44(7):921-927.
[11] 陈哲峰,范卫民,李翔,等.国内人工关节术后假体周围感染的细菌学分析[J].南京医科大学学报,2009,29(5):721-725.
[12] Zimmerli W, Trampuz A, Ochsner PE. Prosthetic-joint infections. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(16):1645-1654.
[13] Nuryastuti T, Krom BP, Aman AT, et al. Ica-expression and gentamicin susceptibility of Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm on orthopedic implant biomaterials. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2011;96(2):365-371.
[14] 黄良库,徐涛,唐进,等.夫西地酸钠联合利福平对表皮葡萄球菌体外培养生物膜的作用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011, 15(21): 3891-3894.
[15] Guillaume M, Garraffo R, Bensalem M, et al. Pharmacokinetic and dynamic study of levofloxacin and rifampicin in bone and joint infections. Med Mal Infect. 2012;42(9):414-420.
[16] Soriano A, García S, Bori G, et al. Treatment of acute post-surgical infection of joint arthroplasty. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2006;12(9):930-933.
[17] Barberán J, Aguilar L, Carroquino G, et al. Conservative treatment of staphylococcal prosthetic joint infections in elderly patients. Am J Med. 2006;119(11):993.
[18] Bergin PF, Doppelt JD, Hamilton WG, et al. Detection of periprosthetic infections with use of ribosomal RNA-based polymerase chain reaction. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(3): 654-663.
[19] Della Valle CJ, Zuckerman JD, Di Cesare PE. Periprosthetic sepsis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;(420):26-31.
[20] Cataldo MA, Petrosillo N, Cipriani M, et al. Prosthetic joint infection: recent developments in diagnosis and management. J Infect. 2010;61(6):443-448.
[21] Lauderdale KJ, Malone CL, Boles BR, et al. Biofilm dispersal of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus on orthopedic implant material. J Orthop Res. 2010; 28(1):55-61.
[22] Gristina AG, Costerton JW. Bacterial adherence to biomaterials and tissue. The significance of its role in clinical sepsis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1985;67(2):264-273.
[23] Monzón M, Oteiza C, Leiva J, et al. Biofilm testing of Staphylococcus epidermidis clinical isolates: low performance of vancomycin in relation to other antibiotics. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2002;44(4):319-324.
[24] Bernthal NM, Stavrakis AI, Billi F, et al. A mouse model of post-arthroplasty Staphylococcus aureus joint infection to evaluate in vivo the efficacy of antimicrobial implant coatings. PLoS One. 2010;5(9):e12580.
[25] Darouiche RO, Dhir A, Miller AJ, et al. Vancomycin penetration into biofilm covering infected prostheses and effect on bacteria. J Infect Dis. 1994;170(3):720-723.
[26] Stahl JP, Guery B, Bru JP,et al. Recommendations for clinical practice. Osteo-articular infection therapy according to materials used (prosthesis, implants, osteosynthesis). Med Mal Infect. 2009;39(10):745-774.
[27] Rimmelé T, Boselli E, Breilh D, et al. Diffusion of levofloxacin into bone and synovial tissues. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2004; 53(3):533-535.
[28] Zimmerli W, Widmer AF, Blatter M, et al. Role of rifampin for treatment of orthopedic implant-related staphylococcal infections: a randomized controlled trial. Foreign-Body Infection (FBI) Study Group. JAMA. 1998;279(19):1537-1541.
[29] Drancourt M, Stein A, Argenson JN, et al. Oral rifampin plus ofloxacin for treatment of Staphylococcus-infected orthopedic implants. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993;37(6): 1214-1218.
[30] Fish DN, Chow AT. The clinical pharmacokinetics of levofloxacin. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1997;32(2):101-109.
[31] Woo YK, Kim KW, Chung JW, et al. Average 10.1-year follow-up of cementless total knee arthroplasty in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Can J Surg. 2011;54(3):179-184.
[32] Pulido L, Ghanem E, Joshi A, et al. Periprosthetic joint infection: the incidence, timing, and predisposing factors. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(7):1710-1715.
[33] Min BW, Song KS, Cho CH, et al. Femoral osteolysis around the unrevised stem during isolated acetabular revision. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467(6):1501-1506. |