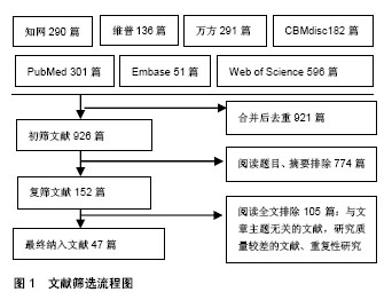
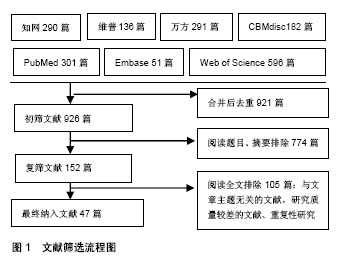
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (35): 5687-5693.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1017
Previous Articles Next Articles
Advances in the application of antibiotics for periprosthetic joint infection after total knee and hip arthroplasties
Hou Senrong1, Lin Jiongtong1, Liu Jun2, Han Yanhong1, Pan Jianke2, Zeng Lingfeng2, Liang Guihong2
- 1the Second School of Clinical Medicine, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; 2Department of Bone and Joint Surgery, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine), Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China
-
Contact:Liu Jun, Chief physician, Professor, Co-doctoral supervisor, Department of Bone and Joint Surgery, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine), Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Hou Senrong, the Second School of Clinical Medicine, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the Chinese Medicine Standardization Project of State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine of China, No. SATCM-2015-BZ115; the “Orthopedic Surgery Robot Application Center” Construction Project of the National Ministry of Industry and Information Technology and National Health and Family Planning Commission of China, No. 2017MHDOSR1008; the Science and Technology Program of Guangdong Province, No. 2012B061700037; the Project of Department of Finance of Guangdong Province, No. [2014]157 and [2018]8; the Medical Science Research Foundation of Guangdong Province, No. A2017215; the Traditional Chinese Medicine Science and Technology Project of Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine, No. YK2013B2N19 and YN2015MS15
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Hou Senrong, Lin Jiongtong, Liu Jun, Han Yanhong, Pan Jianke, Zeng Lingfeng, Liang Guihong. Advances in the application of antibiotics for periprosthetic joint infection after total knee and hip arthroplasties[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(35): 5687-5693.
share this article

2.3 全髋和全膝关节置换后感染的分类 髋、膝关节置换术后感染按时间分型可分为3个时期:早期(Early,术后12周内,未累及骨及假体界面)、延迟(Delayed,即术后2年内)、晚期(Late,术后很长时间内血源性)[6]。根据感染的生物类型可分为细菌性感染、真菌性感染、病毒性感染。目前最广为人所接受的分类方式则是将PJI分为以下3种类型,分别是早期感染(6周内)、迟发性感染(1年内)、晚期感染(1年以上)[7]。同时,根据感染部位的深浅程度还可分为浅部感染和深部感染。其中浅部感染多局限于切口及皮下组织;而深部感染则通常筋膜层和假体周围,且多发于术后1年。 2.4 全髋和全膝关节置换后假体周围感染的诊断标准 关于PJI的诊断目前尚无统一的诊断标准,但目前临床通常采用的是以下3大诊断标准[8]。根据Zimmerli和PRO-IMPLANT提出的PJI诊断标准[9-10]、美国肌肉骨骼系统感染协会共识指南(MSIS)[11]、美国感染协会(IDSA)指南[12]。尽管3种诊断标准内容不尽相同,但基本检查手段包括血液检查、X射线平片、CT、MRI、超声检查、核素扫描、正电子发射计算机扫描,且发生PJI的患者普遍有以下共同点:①存在与相通关节的伤口或窦道;②关节疼痛;④多伴有全身性感染;⑤关节穿刺液浑浊,常为脓性液体;③关节穿刺、术中冷冻切片检查、血沉、C-反应蛋白、假体周围或假体表面组织细菌培养中至少3项结果阳性[13]。但由于不同患者其感染的表现通常也不尽相同,故此PJI的诊断依旧极具挑战性。有研究宣称[14],微流控系统可极大程度上提高临床PJI诊断的高效性和准确性,并对其病原菌进行分离。其主要基于EMA分析方法及PCR技术。目前,膝关节和髋关节假体周围感染在诊断上并未存在明显差异。 此外,临床上在诊断PJI时,还需与无菌性松动、金属过敏、假体周围骨折、聚乙烯材料磨损产生的颗粒等其他干扰因素进行鉴别,这无形中也加剧了PJI诊断的困难程度。 2.5 全髋和全膝关节置换后假体周围感染的发病机制 人工关节置换术后感染通常是致病微生物、假体和人体三者相互作用的结果。导致PJI的病原菌多经由以下3种途径进入人体:①黏附于人工假体上,并于术中进入人体;②患菌血症的患者,细菌经血液循环到达假体;③由邻近的感染中心蔓延至假体[15]。无论是患者自身因素、手术环境,还是手术创伤等医源性因素都与PJI的发生密切相关。此外,围手术期的环境因素控制如全身抗生素的应用、紫外线、血糖水平控制、抗生素骨水泥应用、术后口服抗生素等也影响着感染的发生与否[16-18]。 2.6 全髋和全膝关节置换后假体周围感染中微生物的种类 充分把握全髋和全膝关节置换术后假体感染致病菌是防治PJI的基础。目前PJI中微生物的检查主要还是依赖关节液及组织培养[19-20]。Hindle等[21]发现,超过一半以上的膝关节感染患者在接受正规骨科诊治之前接受过抗生素治疗。故而,在接受关节穿刺获取标本之前,应停用抗生素2-4周,当具体停用时长目前仍未有定论。 有循证医学证据表明,在PJI的病原菌中,最常见的是革兰阳性菌,阳性检出率达60%以上,革兰阴性菌则次之,真菌及其他分支杆菌相对较少见。Chaudhary等[22]认为人工关节置换术后PJI的菌群中,有70%-80%为革兰阳性菌。王东伟等[23]的研究结果显示人工关节置换术后感染中,过半数为以铜绿假单胞菌和表皮葡萄球菌为代表的革兰阴性菌感染。高川渤等[24]发现国内导致关节感染的病原菌中革兰染色阳性菌占比例最高 (62.54%),革兰染色阴性菌次之(32.82%),真菌则占 4.12%,其余致病菌所占比例相对较小为0.52%。有台湾学者研究发现,超过50%的PJI致病菌为金黄色葡萄球菌[25]。Sendi等[26]的研究结果则表明,近年来,革兰阴性杆菌呈增长趋势,其发生所占比例为6%-28%。Zimmerli等[27]发现,在关节置换术后3个月内发生的早发性PJI其病原菌多为金黄色葡萄球菌、阴性杆菌、厌氧菌感染以及混合性感染;关节置换术后3个月到1年内的迟发性PJI其病原菌则多为低毒性的链球菌和肠球菌;此外,关节置换术1年后发病的晚期PJI,其致病菌则通常为金黄色葡萄球菌、β溶血性链球菌、肠杆菌。 细菌性感染一般以革兰阳性菌为主,革兰阴性菌的感染则多见于血源性感染及泌尿道感染,混合性的细菌感染一般见于窦道开放后,由一种或多种细菌造成的重复感染;临床上PJI真菌性感染较为少见,且绝大对数临床上分析的PJI真菌感染者出现于获得性免疫缺陷综合征患者或接受过化疗的患者等免疫力极低的群体中。 2.7 全髋和全膝关节置换后假体周围感染治疗中抗生素的应用方案 全髋和全膝关节置换术后假体周围感染临床上目前主要有非手术治疗和手术治疗这两种治疗方式。其中非手术治疗主要是抗生素治疗和支持治疗;手术治疗则囊括了清创保留假体、一期翻修、二期翻修、关节融合、切除成型、截肢等多种方式,其成功与否在很大程度上则要取决于手术切除生物负荷以及宿主免疫状态的有效性。致病菌及其敏感抗生素的确定能更好更有效地指导PJI治疗方案的选择。PJI治疗期间抗生素使用方案的选择不仅涉及感染类型、致病菌药敏、患者对药物的耐受程度,通常还涉及不同手术治疗方案和不同阶段等诸多因素。 2.7.1 抗生素使用时机 抗生素的使用时机对于细菌培养、药敏结果以及最终PJI的治疗效果都有极大影响,不同的PJI治疗方案,抗生素的使用也不尽相同,详见表1。"


(1)非手术治疗:单独使用抗生素很难治愈PJI,通常只能达到一定的抑制效果。因此,临床上通常在特殊情况下才会采用长期抑制性抗生素治疗方案[28]。如没有合适的手术治疗方案或患者高龄、身体基础情况较差合并其他基础病而无法进行手术或患者拒绝手术治疗时可考虑采用此方案。病毒性感染则一般预后较好,通常采取保守治疗的方式即可到达痊愈。通常情况下保守治疗还需要结合外科手术才能达到较好的治疗效果。 (2)清创并保留假体:早期清创联合抗生素治疗较单纯抗生素治疗效果要好,且早期假体周围感染经清创后治愈率较高[29-31]。研究发现,清创保留假体联用以利福平为基础的抗生素治疗,可显著提高疗效[32-34]。文献表明,其根治率可达90%,而未使用利福平对照组其根治率则为50%-60%。部分文献认为,清创保留假体失败很大程度上是由于未使用利福平,且出现了窦道,清创前症状持续时间超过3周。文献表明,清创前症状持续时间超过3周会增加手术失败率,及早行清创手术可一定程度上提高PJI治疗的成功率。 (3)一期翻修:多数迟发性和晚发PJI感染患者都需要通过手术取出假体,见图2。而一期翻修通常适用于身体条件较好,未见严重并发症的患者。在欧洲较多使用这一方法[35]。术中,多会采用抗生素骨水泥。Zeller等[36]认为一期翻修是治疗髋关节置换术后假体周围感染患者比较有效的手术方法,准确的微生物鉴定和长期的适当静脉注射抗生素治疗是成功治疗的关键因素。"
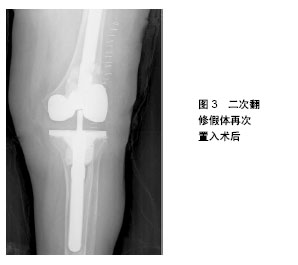
(4)二期翻修:二期翻修中常使用抗生素骨水泥的方法来预防感染。此前,循证医学证据多表明二期翻修成功率高于一期翻修,但由于患者选择以及医疗水平等因素,一期与二期翻修孰优孰劣仍尚未有定论。目前,普遍认为二期翻修对感染的控制率较高,但仍未有高质量的证据表明,在没有系统性抗生素预防的情况下,使用抗生素浸渍的水泥在减少感染方面是有效的。但与此同时,不使用全身抗生素的抗生素浸渍水泥可能不会有效地减少与之相关的疾病[37]。故而,还需根据药敏,配合使用全身抗生素。 (5)假体再置入:国际上有人认为置入时机应该在通过2-4周以上停药观察,每2周复查血沉、C-反应蛋白,且连续2次指标都在正常水平的情况下,见图3。但也有人认为,再置换时血沉、C-反应蛋白升高并不能准确反映PJI的情况。虽然目前没有明确证据表明在停止抗生素治疗后和置入手术之前需要观察期,以此来确保感染的根除,也没有文献有关于2个阶段间的最佳时间间隔的明确证据。但2013年的PJI国际共识仍认为2周到几个月不等的停药时间是有必要的。Osmon等[12]则认为在未见临床感染症状下可直接再置换。 (6)永久性假体取出:PJI国际共识建议假体取出术后抗生素治疗2-6周。 (7)截肢:通常截肢手术仅在感染危及生命或肢体失去活力、组织缺损巨大或伴有血管损伤的患者中进行。当感染的骨与软组织清创彻底,无脓毒血症症状的患者,推荐在截肢后使用敏感抗生素24-48 h。当骨或组织残留存在感染情况时,则需根据药敏来选择合适的抗生素,有学者推荐术后用药周期为4-6周。 2.7.2 抗生素种类的选择 由于全膝和全髋关节置换术后假体周围感染的复杂性,往往单重的抗生素使用并不能起到很好的治疗效果。假体周围感染的发病机制主要是由于病原菌对人工关节假体表面的定植和不可逆的生物膜的形成。细菌特殊的生物膜不仅有利于病原菌的生长而且能最大程度地抵御抗生素。利福平、喳诺酮类药物(环丙沙星、左氧氟沙星)等能通过针对病原菌的生物膜而起作用。Saginur等[38]认为,长期单独使用利福平会加速金黄色葡萄球菌的耐药性。多种抗生素联合使用代替简单地根据药敏结果用药能在一定程度上提高PJI的治愈率[39]。Tornero等[40]对从1999至2013年,对134例早期PJI患者进行了前瞻性的收集和回顾研究。他们发现在革兰阳性感染中,利福平与莱因唑林联合治疗,联合曲莫沙唑或克林霉素联合用药,其失败率较高(27.8%,P=0.026),而在接受利福平与左氧氟沙星、环丙沙星或阿莫西林(8.3%)或联合治疗的患者中,利福平素或联合曲莫沙唑(0%)的患者均有较高的失败率。在革兰阴性菌感染的患者中,使用氟喹诺酮类药物的失败率较低。 对于革兰阳性菌中葡萄球菌感染导致的PJI临床上通常使用青霉素类药物,如萘夫西林、苯唑西林等抗生素,采取2 g每4-6 h静脉滴注的方式治疗或者用头孢唑林采取1.0-2.0 g每8 h脉滴注的方式。此外,有文献表明头孢曲松2 g/d滴注可能同样适用于苯唑西林敏感的PJI患者[41]。对于耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌感染或青霉素过敏的患者则一般采用达托霉素、万古霉素、利奈唑胺或特拉万星。而短期应用莫匹罗星药水则是目前应用最广泛的MASA去定植的方法。据不完全统计,革兰阴性菌感染约占PJI患者的15%,其中多于术后早期发生,且多为老年患者,其以后通常较差。对于氟喹诺酮敏感则可口服环丙沙星500-750 mg,2次/d,铜绿假单胞菌感染患者即便假体移除,依旧难以治愈。Lockhart等[42]推荐以下抗生素使用方案:头孢吡肟2 g 每12 h静脉注射,美罗培南1 g每8 h静脉注射,环丙沙星750 mg,每12 h口服,头孢他啶2 g每8 h静脉注射。Berbari等[43]对895例PJI患者进行回顾性研究。其研究发现,其中有7%的患者关节液培养结果呈菌阴性,而这类患者中有50%有前期抗生素使用史,故而用药时应建议使用万古霉素和环丙沙星或头孢唑林以覆盖革兰阴性和阳性菌。 西班牙感染性疾病和临床微生物学协会最新发表的临床指南(SEIMC指南)则推荐在甲氧西林敏感葡萄球菌感染的初期治疗中予头孢唑啉或邻氯青霉素,或邻氯青霉素联合达托霉素;对于耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌则推荐联合使用达托霉素和邻氯青霉素,或达托霉素及磷霉素联合使用,或单独使用万古霉素;后续治疗中则推荐联合使用利福平和左氧氟沙星。并提出了氟喹诺酮类药物使用的替代方案:即联合应用利福平和复方磺胺甲基异恶唑、利奈唑胺、氯林可霉素、夫西地酸,或者达托霉素。利福平的替代方案则是达托霉素联合邻氯青霉素、磷霉素、利奈唑胺、复方磺胺甲基异恶唑,或左氧氟沙星;或单独使用莫西沙星,或左氧氟沙星、利奈唑胺,或复方磺胺甲基异恶唑,或联合使用2种口服抗生素。对于链球菌感染的则可使用青霉素或头孢曲松。首先可用氨苄青霉素或阿莫西林来治疗粪肠球菌引起的感染。对于革兰阴性菌则推荐初期使用β-内酰胺类抗生素,在后期的治疗则推荐使用氟喹诺酮类药即环丙沙星。 根据2013年PJI的国际共识,在药敏试验结果出来之前,经验性使用抗生素则需要根据当地的致病菌流行病学来选择用药。每个治疗中心需在所在医院的流行病学特点制定相应治疗方案:在耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌高流行的地区,革兰阳性菌建议使用万古霉素,革兰阳性菌则建议使用庆大霉素或第三、四代头孢类抗生素;在耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌低流行地区,在未获得药敏结果的情况下,通常不建议经验性使用万古霉素。 临床上治疗PJI抗生素骨水泥必不可少。加入骨水泥的抗生素多为热稳定性良好、细菌敏感性抗生素。目前骨水泥中加入较多为庆大霉素、万古霉素及妥布霉素。 2.7.3 抗生素的使用时长 目前,医学界对于髋膝关节置换术后PJI需使用多长时间的抗生素仍无定论,但普遍认为抗生素的使用时长应根据与病原菌的种类、给药途径、PJI的严重程度、采取的治疗方式来决定。 Bernard等[44]对144例髋、膝置换术后PJI的病例进行观察。分别予保留假体清创、一期翻修、二期翻修、膝关节融合等治疗,术后随机分为6周、12周抗感染治疗(基础疗程为静脉用药1周),发现进行为期6周的PJI抗感染治疗已足矣,延长其疗程在一定程度上并不一定能提高疗效。对于已经形成窦道的患者也适用。国内研究对于保留假体清创术结合药敏、利福平、环丙沙星联合用药,基于安全性考虑,药物治疗选择6个月[45]。Osmon等[12]认为非葡萄球菌感染应感觉药敏使用敏感抗生素或应用较高生物利用度的口服抗生素4-6周。Keller等[46]在4年时间内对89例PJI患者进行统计研究。Keller等[46]发现口服抗生素治疗3个月可增加PJI治疗的成功率,但延长至6个月,并不增加治疗成功的可能性。此外,他还认为治疗的成功率不仅取决于抗生素的使用时长,还与感染有关的病原菌有直接的联系,其中耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌以及革兰阴性菌的患者在手术后1年内都不太可能取得临床成功。Matthews等[47]研究则是发现,口服抗生素最终效果与使用时长无关,口服抑制抗生素治疗往往只是推迟而非阻止感染的复发。通过一期翻修的非葡萄球菌感染的患者应根据药敏,推荐静脉使用敏感抗生素或生物利用度较高的口服药4-6周。而目前PJI国际共识,尚未就长期抗生素抑制性治疗的时间长度达成共识,但多数专家认为其治疗应个体化,且理想状态下应终身使用。2013年的美国感染协会PJI指南则是认为,在葡萄球菌感染后通过一期翻修的患者,推荐使用敏感抗生素联合利福平至术后2-6周,而后使用利福平配合环丙沙星或左氧氟沙星口服,总疗程应达到至少3个月。对于真菌性PJI目前用于全身治疗的药剂是口服或静脉内给药至少6周的唑类和两性霉素产品。 此外,Tornero等[40]的研究则是发现对于早期PJI患者,与失败有关的唯一因素是口服抗生素的选择,而不是治疗的持续时间。"
| [1] Schwab P, Lavand Homme P, Yombi JC, et al. Lower blood loss after unicompartmental than total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015;23(12):3494-3500.[2] 石林,刘丙根,庞清江.人工关节置换术后关节周围假体真菌感染研究进展[J].中国感染与化疗杂志,2015,15(2):184-187.[3] Pivec R, Johnson AJ, Mears SC, et al. Hip arthroplasty. Lancet. 2012;380(9855):1768-1777. [4] 王俏杰,张先龙.人工髋关节置换术的现状与热点[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2015,9(6):718-724.[5] 李涛,翁习生.抗生素骨水泥在人工关节置换术后感染中应用研究的系统性综述[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2014,22(20):1868-1874.[6] Esposito S, Leone S, Bassetti M, et al. Italian guidelines for the diagnosis and infectious disease management of osteomyelitis and prosthetic joint infections in adults. Infection. 2009;37(6):478-496. [7] 张晓岗,曹力.人工全髋关节置换术后假体周围感染的处理[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2014,8(1):101-104.[8] 王常德,康鹏德,裴福兴,等.全关节置换术后假体周围感染诊断的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24(10):907-910.[9] Corvec S, Portillo ME, Pasticci BM, et al. Epidemiology and new developments in the diagnosis of prosthetic joint infection. Int J Artif Organs. 2018;35(10):923-934. [10] Trampuz A, Perka C, Borens O. Gelenkprotheseninfektion: Neue Entwicklungen in der Diagnostik und Therapie. DMW. 2013; 138(31/32):1571-1573. [11] Parvizi J, Gehrke T, Chen AF. Proceedings of the international consensus on periprosthetic joint infection. Bone Joint J. 2013;95-B(11):1450-1452. [12] Osmon DR, Berbari EF, Berendt AR, et al. Executive summary: diagnosis and management of prosthetic joint infection: clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;56(1):1-10. [13] 赵建宁,曾晓峰,王与荣,等.全髋关节置换术后感染的处理[J].医学研究生学报,2002,15(3):250-251.[14] Chang WH, Wang CH, Yang SY, et al. Rapid isolation and diagnosis of live bacteria from human joint fluids by using an integrated microfluidic system. Lab Chip. 2014;14(17):3376-3384. [15] Trampuz A, Zimmerli W. Prosthetic joint infections: update in diagnosis and treatment Swiss Med Wkly. 2005;135(17-18): 243-251. [16] Maradit KH, Schleck CD, Lewallen EA, et al. Diabetes mellitus and hyperglycemia and the risk of aseptic loosening in total joint arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(9S):S251-S253. [17] Nielen JT, Emans PJ, Dagnelie PC, et al. Severity of diabetes mellitus and total hip or knee replacement: a population-based case-control study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(20):e3739. [18] Meding JB, Reddleman K, Keating ME, et al. Total knee replacement in patients with diabetes mellitus. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;(416):208-216. [19] Burnett RS, Kelly MA, Hanssen AD, et al. Technique and timing of two-stage exchange for infection in TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;464:164-178. [20] 张宁,赵翔,周鑫叠,等.关节液与组织培养在髋膝关节置换术后感染诊断价值的Meta分析[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2014,8(1): 72-76.[21] Hindle P, Davidson E, Biant LC. Septic arthritis of the knee: the use and effect of antibiotics prior to diagnostic aspiration. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2012;94(5):351-355. [22] Chaudhary G, Lee JD. Neurologic complications of infective endocarditis. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2013;13(10):380. [23] 王东伟,郑大伟,翟晓慧,等.人工关节置换术后感染病原菌分布与耐药性分析[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2015,25(19):4415-4417.[24] 高川渤,袁绍辉.人工关节置换术后感染病原菌谱的临床意义[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2015,4(4):319-323.[25] Tsai J, Sheng W, Lo W, et al. Clinical characteristics, microbiology, and outcomes of prosthetic joint infection in Taiwan. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2015;48(2):198-204. [26] Sendi P, Zimmerli W. Challenges in periprosthetic knee-joint infection. Int J Artif Organs. 2011;34(9):947-956. [27] Zimmerli W, Trampuz A, Ochsner PE. Prosthetic-joint infections. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(16):1645-1654. [28] Mahmoud SS, Sukeik M, Alazzawi S, et al. Salvage procedures for management of prosthetic joint infection after hip and knee replacements. Open Orthop J. 2016;10:600-614. [29] 万永鲜,张忠杰,陈歌,等.关节置换术后假体周围感染早期诊断与治疗的临床研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2015,30(10):1117-1118.[30] Wang KH, Yu SW, Iorio R, et al. Long term treatment results for deep infections of total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2015; 30(9):1623-1628. [31] Kim JH, Chun SK, Yoon YC, et al. Efficacy of debridement for early periprosthetic joint infection after hip arthroplasty. Hip Pelvis. 2014;26(4):227-234. [32] Sia IG, Berbari EF, Karchmer AW. Prosthetic joint infections. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2005;19(4):885-914. [33] Vlahakis NE, Temesgen Z, Berbari EF, et al. Osteoarticular infection complicating enterococcal endocarditis. Mayo Clin Proc. 2003;78(5):623-628. [34] Marculescu CE, Berbari EF, Hanssen AD, et al. Outcome of prosthetic joint infections treated with debridement and retention of components. Clin Infect Dis. 2006;42(4):471-478. [35] Zimmerli W, Trampuz A, Ochsner PE. Prosthetic-joint infections. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(16):1645-1654. [36] Zeller V, Lhotellier L, Marmor S, et al. One-stage exchange arthroplasty for chronic periprosthetic hip infection: results of a large prospective cohort study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014; 96(1):e1. [37] Zheng H, Barnett AG, Merollini K, et al. Control strategies to prevent total hip replacement-related infections: a systematic review and mixed treatment comparison. BMJ Open. 2014; 4(3):e3978. [38] Saginur R, Stdenis M, Ferris W, et al. Multiple combination bactericidal testing of staphylococcal biofilms from implant-associated infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006;50(1):55-61. [39] Jacqueline C, Caillon J. Impact of bacterial biofilm on the treatment of prosthetic joint infections. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2014;69 Suppl 1:i37-i40. [40] Tornero E, Morata L, Martinez-Pastor JC, et al. Importance of selection and duration of antibiotic regimen in prosthetic joint infections treated with debridement and implant retention. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2016;71(5):1395-1401. [41] Bejon P, Berendt A, Atkins BL, et al. Two-stage revision for prosthetic joint infection: predictors of outcome and the role of reimplantation microbiology. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2010; 65(3):569-575. [42] Lockhart PB, Garvin KL, Osmon DR, et al. The antibiotic prophylaxis guideline for prosthetic joints: trying to do the right thing. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2013;21(3):193-194. [43] Berbari EF, Marculescu C, Sia I, et al. Culture-negative prosthetic joint infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;45(9):1113-1119. [44] Bernard L, Legout L, Zurcher-Pfund L, et al. Six weeks of antibiotic treatment is sufficient following surgery for septic arthroplasty. J Infect. 2010;61(2):125-132. [45] 唐淼,汤瑞新,周烨,等.利福平联合用药结合保留假体清创术治疗人工关节初期感染[J].实用骨科杂志,2017,23(7):593-596.[46] Keller SC, Cosgrove SE, Higgins Y, et al. Role of suppressive oral antibiotics in orthopedic hardware infections for those not undergoing two-stage replacement surgery. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2016;3(4):w176. [47] Matthews PC, Berendt AR, Mcnally MA, et al. Diagnosis and management of prosthetic joint infection. BMJ. 2009;338:b1773. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [3] | Li Dadi, Zhu Liang, Zheng Li, Zhao Fengchao. Correlation of total knee arthroplasty efficacy with satisfaction and personality characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1346-1350. |
| [4] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [5] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [6] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [7] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [8] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [9] | Yuan Jiawei, Zhang Haitao, Jie Ke, Cao Houran, Zeng Yirong. Underlying targets and mechanism of Taohong Siwu Decoction in prosthetic joint infection on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1428-1433. |
| [10] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [11] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [12] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [13] | Zhong Hehe, Sun Pengpeng, Sang Peng, Wu Shuhong, Liu Yi. Evaluation of knee stability after simulated reconstruction of the core ligament of the posterolateral complex [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 821-825. |
| [14] | Zhao Zhongyi, Li Yongzhen, Chen Feng, Ji Aiyu. Comparison of total knee arthroplasty and unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in treatment of traumatic osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 854-859. |
| [15] | Liu Shaohua, Zhou Guanming, Chen Xicong, Xiao Keming, Cai Jian, Liu Xiaofang. Influence of anterior cruciate ligament defect on the mid-term outcome of fixed-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 860-865. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||