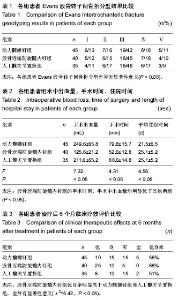
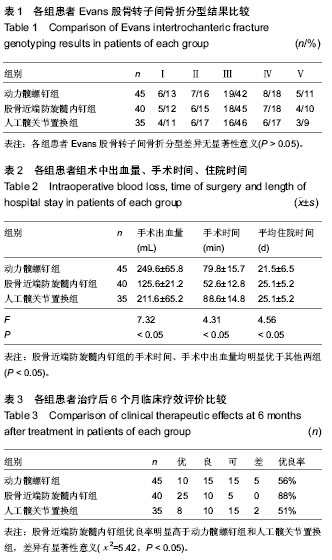
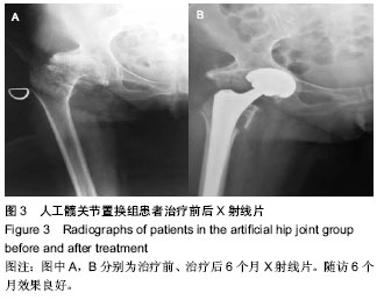
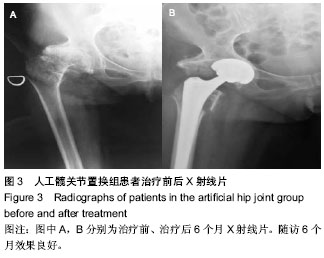
| [1] Hwang JH, Oh JK, Han SH, et al.Clinical effect of DHS, PFNA and artificial joints replacement in the treatment of senile patients with intertrochanteric fractures.Hainan Med J. 2013; 24(20):3001-3003.
[2] 李康养,马楚平,梁江山,等.DHS、PFNA 及人工关节治疗老年股骨粗隆间骨折临床疗效分析[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2011, 19(7): 25-27.
[3] 刘丙东.FNA治疗老年股骨粗隆间骨折31例疗效分析[J].海南医学,2010,21(5):81-83.
[4] Shen J, Luo F, Sun D, et al. Mid-term results after treatment of intertrochanteric femoral fractures with percutaneous compression plate (PCCP). Injury. 2014. pii: S0020-1383(14) 00200-9.
[5] 胡福云.老年股骨粗隆间骨折股骨近端防旋髓内钉的治疗效果及其对生活质量的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2012,32(9): 1926-1927.
[6] 曾超,王一任,魏捷,等.股骨近端防旋髓内钉与动力髋螺钉固定治疗股骨转子间骨折的Meta分析[J].中南大学学报,2012,37(6): 606-615.
[7] Kouzelis A, Kravvas A, Mylonas S, et al. Double axis cephalocondylic fixation of stable and unstable intertrochanteric fractures: early results in 60 cases with the veronail system. Open Orthop J. 2014;8:60-68.
[8] Daruwalla ZJ, Wong KL, Pillay KR, et al. Does ageing Singapore need an electronic database of hip fracture patients? The value and role of a National Joint Registry and an electronic database of intertrochanteric and femoral neck fractures . Singapore Med J. 2014;55(5):287-288.
[9] 钱忠来,徐耀增,王现彬,等.动力髋螺钉、股骨近端防旋髓内钉和第3代Gamma钉置入内固定后生物力学性能与临床效果的比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,14(48):8974-8978.
[10] 马健,杨明贵,段政,等.股骨近端锁定钢板、PFNA 和人工髋关节置换术治疗老年股骨粗隆间骨折的疗效比较[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2013,28(8):762-763.
[11] 魏宁波.股骨近端防旋髓内钉(PFNA)与动力髋螺钉(DHS)治疗老年不稳定型股骨粗隆间骨折的系统评价[D].新疆医科大学, 2013.
[12] 赵存跃.股骨近端防旋髓内钉(PFNA)治疗股骨粗隆间骨折的临床疗效观察[D].山东中医药大学,2013.
[13] 雷光华,曾超,魏捷,等.股骨近端防旋髓内钉与常用髓内固定治疗成人股骨转子间骨折的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012, 16(48):9002-9009.
[14] 王亚平,路通.人工髋关节置换与股骨近端髓内钉治疗股骨转子间骨折的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(52):8961-8966.
[15] 张明勇,郭卫春,胡锐,等.人工半髋置换和PFNA治疗高龄股骨转子间骨折[J].实用骨科杂志,2013,17(5):453-455.
[16] 周凯华,刘丰,潘福根.股骨近端防旋髓内钉-Ⅱ在股骨粗隆间骨折中的应用[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2011,5(2): 232-235.
[17] Borges A, Torres J, São Simão R, et al. Impact of preoperative analytical values on post-operative mortality rate of intertrochanteric fractures. Acta Med Port. 2014;27(2): 218-222.
[18] 张进要,蔡宗新.髋关节置换治疗老年性股骨颈骨折60例[J].按摩与康复医学,2012,3(1):208-209.
[19] 张丛笑,杨明连,刘新房,等.老年粗隆部骨折多种内固定方式的选择[J].现代生物医学进展,2012,12(25):4937-4939.
[20] 王臣.PFNA和人工髓关节置换治疗老年股骨粗隆间骨折的疗效分析[J].中国医药指南,2012,10(29):567-569.
[21] Meredddy P,Kamath S,Ramakrishnan M,et al. The AO/ASIF Proximal femoral nail antirota- tion(PFNA):a new design for the treatment of unstable proximal femoral fractures. Injury. 2009;40(4):428-432.
[22] Waddell JP, Morton J, Schemitsch EH.The role of total hip replacement in intertrochanteric fractures of the femur. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;12(429):49-53.
[23] Brunner A, JSckel JA, Babst R. The PFNA proximal femur nail in treatment of unstable proximal femur fractures 3 cases of postop-erative perforation of the helical blade into the hip joint. J Orthop Trauma. 2008;22(10):731-736.
[24] Liu Y, Tao R, Liu F, et al. Mid-term outcomes after intramed- ullary fixation of peritrochanteric femoral fractures using the new proximal femoral nail antirotation(PFNA). Injury.2010; 41(8):810-817.
[25] 王明辉. DHS和PFNA治疗老年股骨转子间骨折疗效比较[J]. 陕西医学杂志,2014,3(42):344-345.
[26] 黄诚,付聪聪,黄相杰,等. DHS和PFNA治疗老年骨质疏松性转子间骨折的临床疗效对比[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(6): 568-570.
[27] 丁华,章洪喜,袁即山,等. 股骨近端髓内钉-螺旋刀片内固定与人工股骨头置换术治疗老年股骨转子间不稳定型骨折的疗效比较[J]. 生物医学工程与临床,2013,17(5):450-454.
[28] 张明勇,郭卫春,胡锐,等.人工半髋置换和PFNA治疗高龄股骨转子间骨折[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2013,19(5):453-455. |