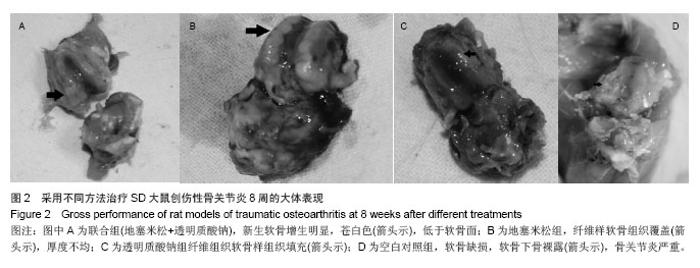
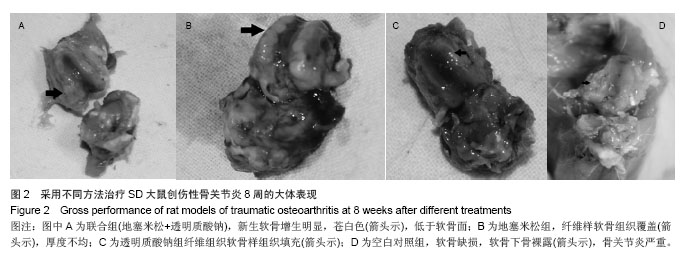
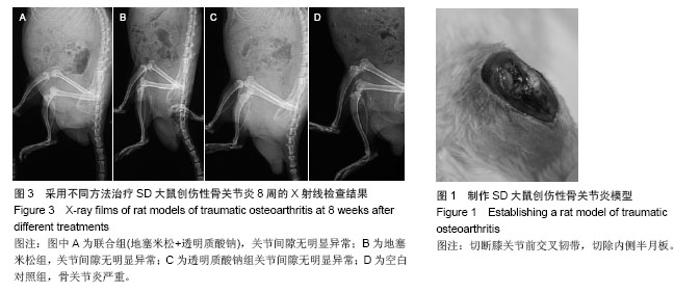
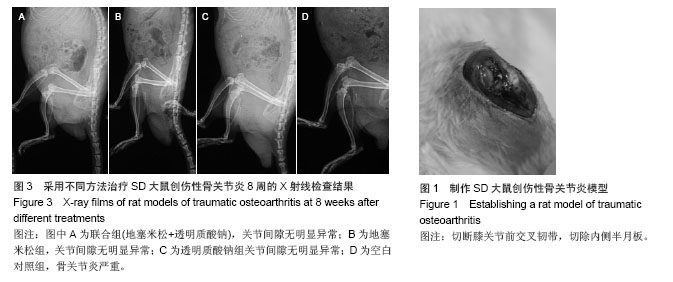
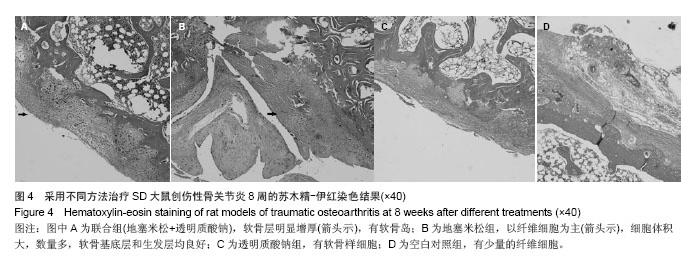
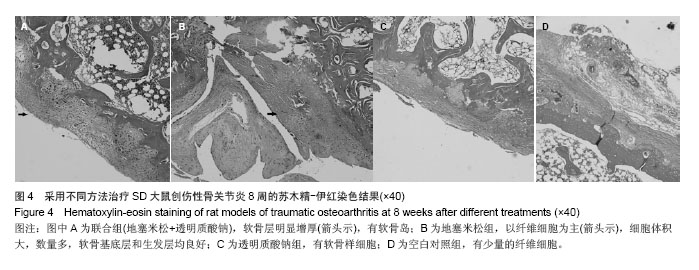
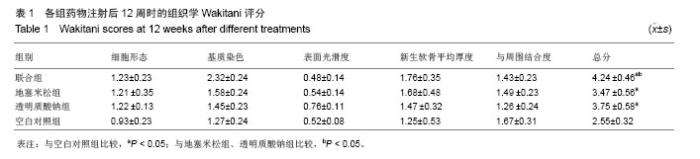
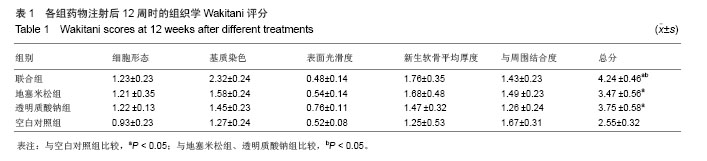
| [1]Bijisma JW,Berenbaum F,Lafeber FP.Osteoarthritis:an update with relevance for clinical practice. Lancet. 2011;377 (9783):2115-2126.
[2]Goldring MB.The role of the chondrocyte in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43(9):1916-1926.
[3]Mathieu P,Conrozier T,Vignon E,et al.Rheologic behavior of osteoarthritic synovial fluid after addition of hyaluronic acid: a pilot study.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2009;467(11):3002-3029.
[4]Lee YT,Shao HJ,Wang JH,et al.Hyaluronic acid modulates gene expression of connective tissue growth factor (CTGF), transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in human fibroblast-like synovial cells from advanced-stage osteoarthritis in vitro.J Orthop Res. 2010;28(4):492-496.
[5]Zhou JL,Liu SQ,Qiu B,et al.Effects of hyaluronan on vascular endothelial growth factor and receptor-2 expression in a rabbit osteoarthritis model.J Orthop Sci. 2009;14(3):313-319.
[6]Gigante A,Callegari L.The role of intra-articular hyaluronan (Sinovial) in the treatment of osteoarthritis.Rheumatol Int. 2011; 31(4):427-444.
[7]张燕.60例玻璃酸钠、地塞米松联合用药对退行性膝关节炎的疗效观察[J].中国卫生产业,2014,12(10):84-85.
[8]Randau TM,Schildberg FA,Alini M,et al.The effect of dexamethasone and triiodothyronine on terminal differentiation of primary bovine chondrocytes and chondrogenically differentiated mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS One.2013;8(8): e72973.
[9]Chrysis D,Zaman F,Chagin AS,et al.Dexamethasone induces apoptosis in proliferative chondrocytes through activation of caspases and suppression of the Akt-phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase signaling pathway. Endocrinology. 2005;146(3): 1391-1397.
[10]Naves MA,Pereira RM,Comodo AN,et al.Effect of dexamethasone on human osteoblasts in culture: involvement of β1 integrin and integrin-linked kinase.Cell Biol Int. 2011;35 (11):1147-1151.
[11]Kataoka Y,Ariyoshi W,Okinaga T,et al.Mechanisms involved in suppression of ADAMTS4 expression in synoviocytes by high molecular weight hyaluronic acid.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;432(4):580-585.
[12]王云峰,白人晓,张扬,等.改良Hulth模型复制膝不同时期骨关节炎的实验研究[J].天津医科大学学报,2009,15(3):401-404.
[13]王斌.骨性关节炎的动物模型研究进展[J].中医临床研究, 2013, 5(10):120-122.
[14]Westacott CI, Barakat AF, Wood L,et al.Tumor necrosis factor alpha can contribute to focal loss of cartilage in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2000;8(3):213-221.
[15]Herrero-Beaumont G,Ivorra JA,Del Carmen Trabado M,et al.Glucosamine sulfate in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis symptoms: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study using acetaminophen as a side comparator.Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56(2):555-567.
[16]Lin PM,Chen CT,Torzilli PA.Incrresed stomelysin-1(MMP-3), protepglycan degradation(3B3- and 7 D4) and collagen damange in cyclincally laod-injured articular catialge. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2004;12(6):485.
[17]Stannus O,Jones G,Cicuttini F,et al.Circulating levels of IL-6 and TNF-α are associated with knee radiographic osteoarthritis and knee cartilage loss in older adults. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010;18(11):1441-1447.
[18]Intekhab-Alam NY,White OB,Getting SJ,et al.Urocortin protects chondrocytes from NO-induced apoptosis: a future therapy for osteoarthritis?Cell Death Dis. 2013;4:e717.
[19]张银网,苑建新,汤杰,等.关节镜微创清理术治疗膝关节骨性关节炎[J].中国内镜杂志,2006,12(2):142-145,
[20]Joos H,Wildner A,Hogrefe C,et al.Interleukin-1 beta and tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibit migration activity of chondrogenic progenitor cells from non-fibrillated osteoarthritic cartilage.Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15(5):R119.
[21]孙昌荣,管兴发,石新.透明质酸与膝骨关节炎的研究进展[J].中国实用医药,2010,9(27):251-252.
[22]Wen DY.Intra-articular hyaluronic acid injections for knee osteoarthritis.Am Fam Physician.2006;62(3):565-570.
[23]Tasciotalglu F,Oner C.Efficacy of intra-articular sodium hyaluronme in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis.Clin Rheumatoumatol.2006;22:112-117.
[24]Kaneva MK,Kerrigan MJ,Grieco P,et al.Chondroprotective and anti-inflammatory role of melanocortin peptides in TNF-a activated human C-20/A4 chondrocytes. Br J Pharmacol. 2012;167:67-79.
[25]Kim J, Xu M, Xo R,et al.Mitochondrial DNA damage is involved in apoptosis caused by pro-inflammatory cytokines in Human OA chondrocytes.Osteoarthr Cartil.2010;18:424-432.
[26]Horton WE Jr,Bennion P,Yang L.Cellular, molecular, and matrix changes in cartilage during aging and osteoarthritis.J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2006;6(4):379-381. |