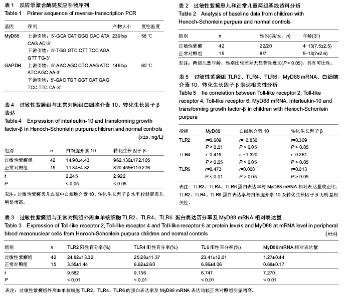
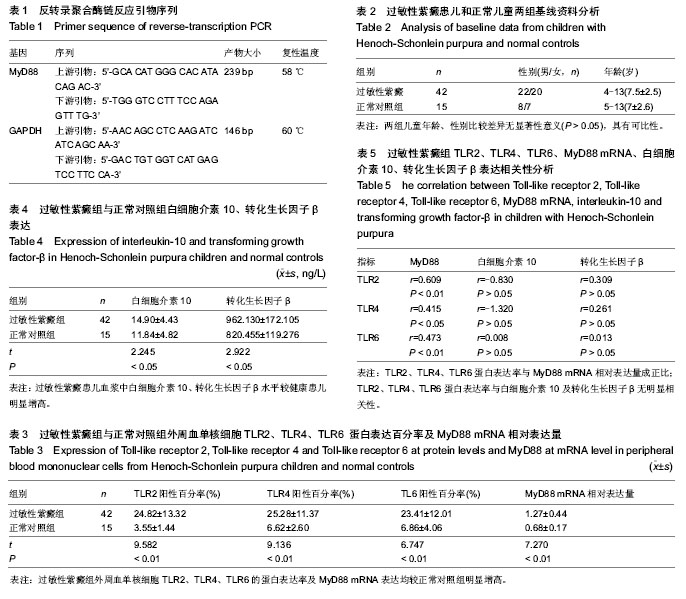
| [1] Saulsbury FT.Henoch-Schonlein purpura in children. Report of 100 patients and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore).1999;78(6):395-409.
[2] 陈洪敏,链球菌感染与过敏性紫癜及肾损害的关系[J].江苏医药, 2011,37(8): 978-979.
[3] 马莲美,贾秀红,王宝宏,等.过敏性紫癜并支原体感染患儿细胞免疫功能的研究[J].中华临床医师杂志:电子版,2011,5(11): 3179-3184.
[4] 仝桃玲.过敏性紫癜复发与幽门螺杆菌感染的关系[J].医药论坛杂志,2011,32(7):85-86.
[5] 路娟.呼吸道病毒感染与过敏性紫癜肾损伤的相关性分析[D]. 石家庄市:河北医科大学,2013.
[6] 张建江.儿童过敏性紫癜外周血IL-17、TGF-β1的变化及意义[C]. 郑州:中华医学会第十七次全国儿科学术大会,2012.
[7] 陈小红,何芳,柳青,等.肾型过敏性紫癜患者血清IL-5、IL-10、CD_4~+ CD_(25)~+调节性T细胞测定及意义[J]. 疑难病杂志, 2013,12(2):140-141.
[8] 孙晓,秦桂秀.Toll 样受体在新生儿感染性疾病中的研究进展[J]. 中国新生儿科杂志, 2014,29(3): 206-208.
[9] 张金萍,陈超.Toll样受体与感染性疾病的关系[J]. 国外医学:儿科学分册,2005,32(6):30-32.
[10] 常红,张秋业,程娜,等.过敏性紫癜患儿外周血单个核细胞 TLR2、TLR4表达及其与Th1和Th2型免疫应答相关性观察[J]. 中华微生物学和免疫学杂志,2013,(11):839-844.
[11] 李媛媛,李成荣,王国兵,等.Toll样受体信号途径异常活化在过敏性紫癜免疫发病机制中的作用初探[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2010. 14(8):538-542.
[12] Ozen S, Ruperto N, Dillon MJ,et al.EULAR/PReS endorsed consensus criteria for the classification of childhood vasculitides. Ann Rheum Dis.2006;65(7):936-941.
[13] Yang YH, Hung CF, Hsu CR, et al.A nationwide survey on epidemiological characteristics of childhood Henoch- Schonlein purpura in Taiwan. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005; 44(5):618-22.
[14] 黄彬,陈茶,姜傥.免疫调节性T细胞和自身免疫性疾病[J].国际检验医学杂志, 2006,(3):240-242.
[15] 孙丽萍,孙春荣,崔小岱,等.自身免疫性疾病患儿CD4+CD25+调节性T细胞的变化[J].实用儿科临床杂志,2009,24(9):664.
[16] Gu Y, Yang J, Ouyang X, et al.Interleukin 10 suppresses Th17 cytokines secreted by macrophages and T cells. Eur J Immunol. 2008;38(7):1807-1813.
[17] 刘磊,江捍平,王兵.IL-10在过敏性紫癜血管内皮损伤中的作用机制研究[J].小儿急救医学, 2004,11(4): 225-227.
[18] 姜晶,陆彪.过敏性紫癜患儿急性期血清IL-10、IL-13、IL-15水平的变化及意义[J].宁夏医科大学学报, 2012,34(3): 225-228.
[19] 王兰英,张慧玉,岳爱红.过敏性紫癜患儿血、尿TGF-β_1检测及临床意义[J].现代预防医学, 2010,37(7):1257-1259.
[20] Ishida H.[Henoch-Schonlein purpura accompanied with myeloperoxidase-antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (MPO-ANCA) associated vasculitis with elevated serum interleukin-10]. Nihon Naika Gakkai Zasshi.2005;94(8): 1615-1617.
[21] Yang YH, Lai HJ, Kao CK, et al.The association between transforming growth factor-beta gene promoter C-509T polymorphism and Chinese children with Henoch-Schonlein purpura. Pediatr Nephrol.2004;19(9): 972-975.
[22] 吴容,王强,董巍,过敏性紫癜患儿血浆IL-2、IFN-γ、IL-4与TGF-β1的变化及其意义.实用医院临床杂志, 2014(01): p.144-146.
[23] 唐雪梅,过敏性紫癜病因及免疫发病机制.实用儿科临床杂志, 2012(21): p.1634-1636.
[24] Yang YH, Lai HJ, Kao CK, et al.The immunobiology of Henoch-Schonlein purpura. Autoimmun Rev.2008;7(3): 179-184.
[25] 赵梅青,赵洪国.过敏性紫癜病人血清TGF-β_1和HGF水平的变化[J].齐鲁医学杂志, 2011,26(6):513-514.
[26] Liu B, Yang Y, Dai J, et al.TLR4 up-regulation at protein or gene level is pathogenic for lupus-like autoimmune disease. J Immunol.2006;177(10): 6880-6888.
[27] Radstake TR, Roelofs MF, Jenniskens YM, et al.Expression of toll-like receptors 2 and 4 in rheumatoid synovial tissue and regulation by proinflammatory cytokines interleukin-12 and interleukin-18 via interferon-gamma. Arthritis Rheum.2004; 50(12):3856-3865.
[28] Tamaki Y, Takakubo Y, Hirayama T, et al. Expression of Toll-like receptors and their signaling pathways in rheumatoid synovitis.J Rheumatol.2011;38(5):810-820.
[29] Abdollahi-Roodsaz S, Joosten LA, Koenders MI, et al. Stimulation of TLR2 and TLR4 differentially skews the balance of T cells in a mouse model of arthritis. J Clin Invest; 2008; 118(1):205-216.
[30] Spachidou MP, Bourazopoulou E, et al,Expression of functional Toll-like receptors by salivary gland epithelial cells: increased mRNA expression in cells derived from patients with primary Sjögren's syndrome..Clin Exp Immunol. 2007; 147(3):497-503.
[31] Kawakami A, Nakashima K, et al, Toll-like receptor in salivary glands from patients with Sjögren's syndrome: functional analysis by human salivary gland cell line.J Rheumatol. 2007; 34(5):1019-1026. |