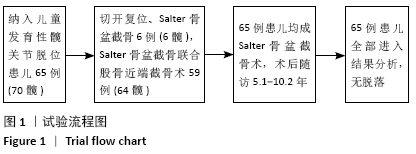
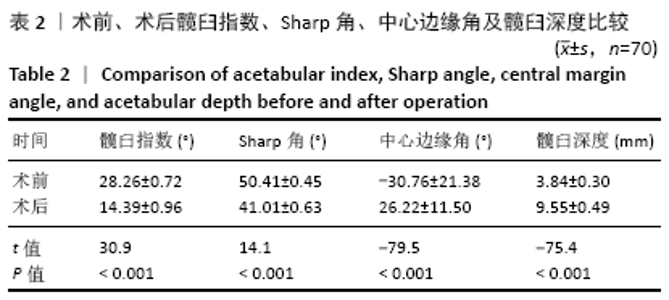
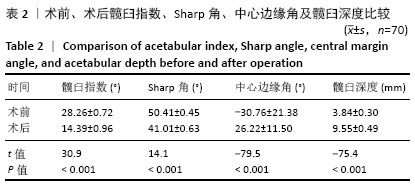
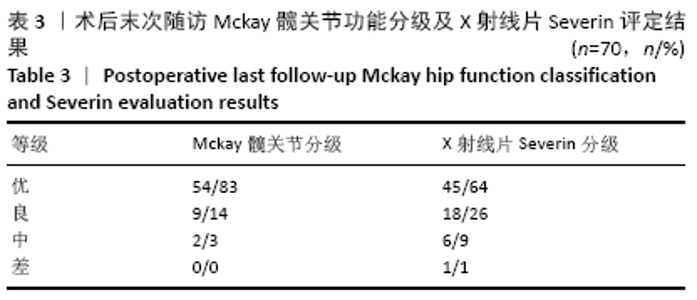
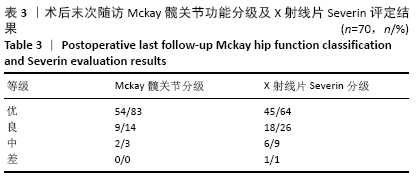
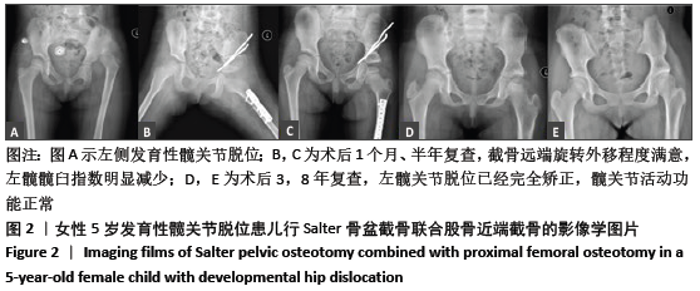
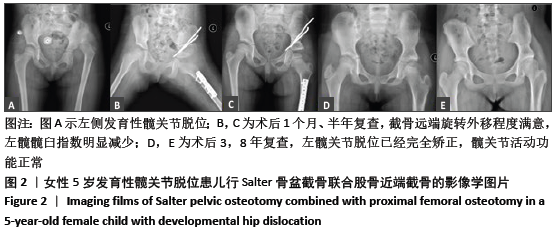
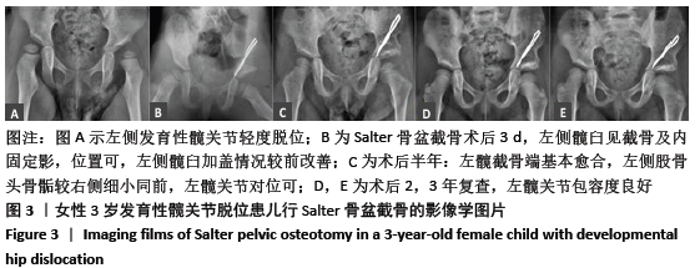
[1] SHARPE P, MULPURI K, CHAN A, et al. Differences in risk factors between early and late diagnosed developmental dysplasia of the hip. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2006;91(3):F158-162.
[2] 高许斌,周建生.髋关节发育不良诊断和治疗进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2010,18(5):401-404.
[3] 徐涛涛,康晓鹏,胡熙.单纯Salter骨盆截骨术与联合股骨近端旋转截骨术在儿童发育性双侧髋关节脱位中的应用[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2020,28(5):23-27.
[4] 赵书一,王恩波,刘天婧,等.前方小切口单纯切开复位治疗婴幼儿发育性髋关节脱位的短期疗效分析[J].中国骨与关节杂志, 2020,9(3):164-169.
[5] 吕学敏,郭源,边臻,等.婴儿发育性髋关节发育不良自然发育过程研究[J].中华小儿外科杂志,2014,35(11):848-852.
[6] 卢红信,陈笑天,肖玉周.儿童发育性髋关节脱位的治疗进展[J].安徽医药,2019,23(4):738-742.
[7] 汪楠,陈文建,孙军.Salter骨盆截骨术对发育性髋关节脱位的效果研究[J].安徽医科大学学报,2019,54(12):1971-1974.
[8] 蔡威,孙宁,魏光辉.小儿外科学[M].5版.北京:人民卫生出版社, 2014:476-485.
[9] Mckay DW. A comparison of the innominate and the pericapsular osteotomy in the treatment of congenital dislocation of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1974;(98):124-132.
[10] Ward WT, Vogt M, Grudziak JS, et al. Severin classification system for evaluation of the results of operative treatment of congenital dislocation of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg. 1997;79A(5):656-663.
[11] 张怀波,胡月光,俞松.雌激素受体在发育性髋关节脱位患儿髋臼软骨中的表达[J]. 中华小儿外科杂志,2009,30(12) :890-892.
[12] 黄济煌,孙客,唐盛平,等.Graf Ⅱ型发育性髋关节脱位409例不同干预后转归的回顾性多中心研究[J].中华小儿外科杂志,2016, 37(12):893-897.
[13] 晏建森,南国新.儿童发育性髋关节发育不良的手术治疗进展[J].临床小儿外科杂志,2018,17(10):731-735.
[14] Salter RB. The classic.Innominate osteotomy in the treatment of congenital dislocationand subluxation of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1978;(137):2-14.
[15] 乔永东,司建炜,刘建波,等.改良及经典Salter截骨术治疗先天性髋关节发育不良的疗效比较[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2010,18(11): 944-946.
[16] 王伟,王晓东.一期Salter截骨联合股骨近端截骨在3-8岁延迟治疗发育性髋关节脱位中的应用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2011,19(9): 718-720.
[17] 丁晓飞,苏柱程,廖世杰,等.切开复位、Salter骨盆截骨术治疗儿童发育性髋关节脱位的近期治疗评价[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2013,21(9): 879-882.
[18] SANKAR WN, TANG EY, MOSLEY CF. Predictors of the need for femoral shortening ostetotomy during open treatment of developmental dislocation of the hip. J Pediar Orthop. 2009;29(8):868-871
[19] GLOVE PA, FLYN JM, GARNER MR, et al. Predicors for for secondary procedures in walking DDH . J Pediar Orthop. 2012;32(3):282.
[20] 郭新军,周大凯,张峰,等.改良Salter骨盆截骨联合股骨旋转、短缩截骨术在小儿发育性髋关节脱位治疗中的应用[J].实用儿科临床杂志,2012,27(9):723-724.
[21] CHAKER M, PICAULT C, KOHLER R. Long term results in treatment of residual hip dysplasia by Salter osteotomy ( study of 31 cases). Acta Orthop Belg. 2001;67(1):6-18.
[22] 倪磊,楼跃,范毓华,等.比基尼切口治疗儿童发育性髋关节脱位[J].实用儿科临床杂志,2010,25(11):823-825.
[23] 王明帅,杨永涛,张廷龙,等.Salter 骨盆截骨治疗小儿发育性髋关节脱位疗效分析[J].中国现代手术学杂志,2016,20(4):287-290.
[24] 刘亚峰.Salter截骨术在发育性髋关节脱位手术治疗中的应用分析[J]河南医学研究,2016,25(5):915-916.
[25] 李广海,肖莉.改良Salter骨盆截骨治疗小儿先天性髋关节脱位[J].中医正骨,2014,26(5):336-338.
[26] GARDNER ROE, BRADLEY CS, HOWARD A, et al. The incidence of avascular necrosis and the radiographic outcome following medial open reduction in children with development dysplasia of the hip: A sytemmatic report. Bone J. 2014; 96-B(2):279-286.
[27] POSSICH R, WENGER J, GANGER R, et al. Does open reduction of the development dist located hip increase the risk of osteonecrosis? Clinic Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470(1):250-260.
[28] DOMZALSKI M, SYNDER M. Avastral necrosisis after surgical treatment for development dysplasia of the hip. Int Orthop. 2004;28(2):65-68.
[29] 唐学阳,蒋欣,王道喜,等.发育性髋脱位切开复位手术失败及术后再脱位的原因分析[J].中华小儿外科杂志,2010,31(3):195-199. |