Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (37): 5923-5928.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.37.004
Previous Articles Next Articles
Isolation and identification of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from transgenic rats with green fluorescent protein gene
Wang Yang, Cao Zhi-qiang
- Department of Urinary Surgery, General Hospital of Shenyang Military Region, Shenyang 110840, Liaoning Province, China
-
Revised:2014-08-24Online:2014-09-03Published:2014-09-03 -
Contact:Cao Zhi-qiang, M.D., Associate chief physician, Department of Urinary Surgery, General Hospital of Shenyang Military Region, Shenyang 110840, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Wang Yang, Master, Department of Urinary Surgery, General Hospital of Shenyang Military Region, Shenyang 110840, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province, No. 2013020199
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Yang, Cao Zhi-qiang. Isolation and identification of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from transgenic rats with green fluorescent protein gene[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(37): 5923-5928.
share this article
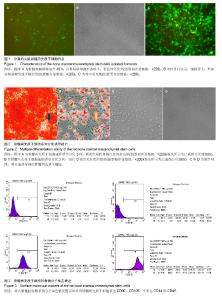
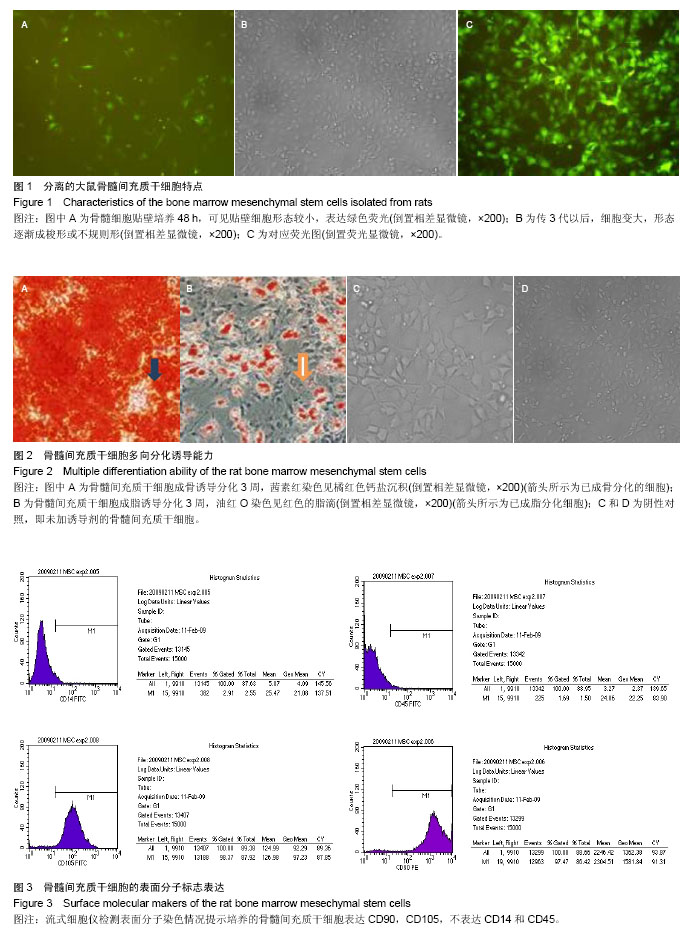
2.1 细胞形态及绿色荧光蛋白表达 倒置显微镜观察幼年大鼠骨髓冲洗液可冲出大量浑浊物,早期贴壁不明显,一般静止48 h后贴壁良好。分离后的浑浊液在培养瓶中接种 2 d后可见多个贴壁细胞,呈梭形或长条形,呈单个或几个细胞克隆性聚集表现,第3-5天细胞生长明显加快,细胞逐渐成不规则形变化。融合约80%以上进行传代后细胞生长迅速。5代以后细胞纯度好并100%显示绿色荧光(图1)。 2.2 骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化能力检测 骨髓间充质干细胞经成骨诱导剂共培养后3周,细胞呈聚集生长,茜素红染色见橘红色钙盐沉积,证实骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化(图2A)。 2.3 骨髓间充质干细胞成脂分化能力检测 骨髓间充质干细胞成脂诱导后3周,细胞融合,油红O染色见红色的脂滴,提示骨髓间充质干细胞成脂分化(图2B)。 2.4 骨髓间充质干细胞生长特性 第1代及第2代细胞生长缓慢,未测生长曲线,第3代以后每代细胞测定生长曲线,细胞经传代后一般第3天进入对数生长期,第5天以后逐渐进入平台期。第5代时连续测定10 d细胞数,根据公式计算群体倍增时间为42 h,与文献报道的野生型骨髓间充质干细胞相似[25]。 2.5 细胞表型 流式细胞仪检测细胞表面分子提示细胞表达CD90,CD105,达到99%以上,不表达或弱表达CD14和CD45,表达量不足10%(图3)。"
| [1] 刘寿生,周敦华.间充质干细胞与移植物抗宿主病及移植物抗白血病的关系[J].中国实用儿科杂志,2012,27(1):69-72. [2] 王佃亮,张艳梅,杜娟.间充质干细胞过滤分离器制备人羊膜间充质干细胞的研究[J].中国生物工程杂志,2012,32(10):63-66. [3] 李敏敏,邹亚伟,陈福雄.骨髓间充质干细胞与肿瘤耐药[J].中国实用儿科杂志, 2011,26(10):792-794. [4] 孙源,吴子征,林红,等.骨髓间充质干细胞诱导内皮细胞与自体骨髓间充质干细胞共培养后的成骨特性[J].中国临床康复,2006, 10(33):68-71. [5] Moon HH, Joo MK, Mok H,et al.MSC-based VEGF gene therapy in rat myocardial infarction model using facial amphipathic bile acid-conjugated polyethyleneimine. Biomaterials. 2014;35(5):1744-1754. [6] Oliveira-Sales EB, Maquigussa E, Semedo P,et al. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) prevented the progression of renovascular hypertension, improved renal function and architecture.PLoS One. 2013;8(11):e78464. [7] 奉婷,朱卫民,余泽波,等.间充质干细胞对急性肝衰竭的治疗及移植途径的优化[J].中国生物制品学杂志,2013,26(9):1290-1294. [8] Mendicino M, Bailey AM, Wonnacott K,et al.MSC-based product characterization for clinical trials: an FDA perspective. Cell Stem Cell. 2014;14(2):141-145. [9] Chiu LH, Lai WF, Chang SF,et al.The effect of type II collagen on MSC osteogenic differentiation and bone defect repair. Biomaterials. 2014;35(9):2680-2691. [10] 陈骅,施佳,罗良生,等.生物发光示踪技术在胶质瘤研究中的进展[J].实用肿瘤杂志, 2014,29(2):107-110. [11] Guo Y, Su L, Wu J,et al.Assessment of the green florescence protein labeling method for tracking implanted mesenchymal stem cells.Cytotechnology. 2012;64(4):391-401. [12] Li N, Yang Y, Ding M,et al.GFP Stable Transfection Facilitated the Characterization of Lung Cancer Stem Cells.Mol Biotechnol. 2014. [Epub ahead of print] [13] Noisa P, Urrutikoetxea-Uriguen A, Li M,et al.Generation of human embryonic stem cell reporter lines expressing GFP specifically in neural progenitors.Stem Cell Rev. 2010;6(3): 438-449. [14] Lippincott-Schwartz J, Patterson GH.Development and use of fluorescent protein markers in living cells.Science. 2003;300 (5616):87-91. [15] Liu Z, Vong QP, Zheng Y.Using ES cells labeled with GFP for analyzing cell behavior during differentiation.Curr Protoc Stem Cell Biol. 2012;Chapter 1:Unit1D.8. [16] 崔向荣,朱静,田杰,等.STAT3 过度表达和激活对骨髓间充质干细胞瘤样转化的作用[J].中国生物制品学杂志,2013,26(3):328-331. [17] 王力,徐小红,张宁坤,等.携带标记基因的慢病毒载体转染人脐带华通胶间充质干细胞的实验研究[J].天津医药, 2013,41(10): 985-988,1044. [18] 朱磊,李鲲鹏,马捷.VEGF基因转染间充质干细胞移植与单纯间充质干细胞移植对大鼠心肌梗死的疗效对比[J].中国当代医药, 2014,21(9):9-11. [19] 管小俊,宋琳,郭雪君,等.携带绿色荧光蛋白基因慢病毒转染的大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的干细胞特性检测[J].诊断学理论与实践,2011,10(6):527-530. [20] 刘曦明,许建中.间充质干细胞修复骨缺损的研究进展[J].华南国防医学杂志,2008,22(1):43-46. [21] 赵君,蒋欣泉,张志愿.骨组织工程中基因修饰的种子细胞的研究进展[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2007,5(2):147-150. [22] 穆传杰, 周继文.报告基因显像监测基因治疗研究进展[J].国外医学:放射医学核医学分册, 2003,27(1):4-8. [23] 王贵利,白琳,陈炜,等.绿色荧光转基因大鼠模型的建立[J].中国比较医学杂志,2013,23(1):5-9. [24] 沈云东,徐建光,徐文东,等.绿色荧光蛋白转基因大鼠神经干细胞体外分化与体内移植的实验研究[J].中华手外科杂志,2007, 23(4): 196-199. [25] 白金萍,李秀英,李雪,等.胎盘间充质干细胞传代后的增殖能力[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(10):1591-1596. [26] James AW.Review of Signaling Pathways Governing MSC Osteogenic and Adipogenic Differentiation.Scientifica (Cairo). 2013;2013:684736. [27] 李佳成,郭燕珊,屠美,等.胚胎干细胞条件培养基对人脂肪干细胞增殖及分化能力的影响[J].中山大学学报:医学科学版,2014, 35(2):169-176. [28] 金颖,任晓慧,刘晓帆.胚胎干细胞或诱导性全能干细胞自我更新和分化机制研究进展[J].上海交通大学学报:医学版, 2012,32(9): 1166-1170. [29] 李宏.基因组稳定性与iPS细胞重编程的分子机制[J].生物技术通报,2013,(12):36-42. [30] 顾卫娟,李小荣,张凤祥,等. iPS细胞移植对猪心肌梗死后梗死区心肌超微结构的影响[J].中华全科医学,2013,11(12):1829-1830, 1889. [31] Yi T, Song SU.Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells and their therapeutic applications.Arch Pharm Res. 2012;35(2):213-221. [32] 刘广龙,刘忠龙,张志愿,等.外源性TGF-β1诱导大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞向肌成纤维细胞分化的实验研究[J].口腔医学,2014, 34(1): 1-4. [33] 白耀邦,李博,陈庆良,等.大鼠脂肪间充质干细胞的分化潜能鉴定及XIAP基因修饰[J].天津医药,2013,41(8):799-801. [34] 古再丽努尔•艾麦提,秦小惠,邵伟,等.移植骨髓间充质干细胞对雌性大鼠生长及生殖器官发育水平的影响[J].新疆农业科学, 2013,50(7):1360-1364. [35] 王一茹,白静,陈杰,等.人羊水间充质干细胞冻存后生物学特性研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2012,26( 2):13-17. [36] 牧仁,边艳超,浦亚斌,等.北京油鸡胚胎肝脏间充质干细胞的生物学特性[J].华中农业大学学报, 2013,32(6):99-105. [37] 黄郁凯,李晓红,潘宇,等.成年大鼠骨骼肌干细胞的制备与新型培养方法[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2013,29(1):183-187. [38] Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I,et al.Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317. [39] Eggenhofer E, Benseler V, Kroemer A,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells are short-lived and do not migrate beyond the lungs after intravenous infusion.Front Immunol. 2012;3:297. [40] Wood JA, Chung DJ, Park SA,et al.Periocular and intra-articular injection of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells: an in vivo imaging and migration study.J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2012;28(3):307-317. [41] Tanimura A, Nezu A, Morita T.Light microscopy techniques for live cell and animal imaging using fluorescent proteins.Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2013;141(5):262-267. [42] Englund U, Fricker-Gates RA, Lundberg C,et al. Transplantation of human neural progenitor cells into the neonatal rat brain: extensive migration and differentiation with long-distance axonal projections.Exp Neurol. 2002;173(1): 1-21. [43] 马群兴,李彤,赵越,等. 脐带间充质干细胞与脐血CD34+细胞联合移植治疗心肌梗死[J].中华胸心血管外科杂志,2014,30(2): 82-85,89. [44] 邹松平,王宇,李春雨,等.骨髓间充质干细胞旁分泌对急性心肌梗死心肌的保护作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(23): 3653-3659. [45] 樊艳,王建军,魏峰,等.脂肪间充质干细胞移植对心肌梗死后炎症反应及心室重构的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(6): 900-905. [46] 高延明,张路.骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗糖尿病足过程中血管内皮生长因子的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(40): 7169-7174. [47] 郭剑,李晓燕,李辉,等.人脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗糖尿病足的临床研究[J].陕西医学杂志,2013,42(2):191-192. [48] 万江波,蔡黔,刘毅. 骨髓间充质干细胞不同移植方式治疗大鼠糖尿病足溃疡的疗效观察[J].中南大学学报:医学版,2013,38(4): 347-355. [49] 陆英,张祥忠,刘相富,等.间充质干细胞输注对移植物抗宿主病中不同受损器官的治疗效果[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(23): 3676-3681. [50] 王黎明,周建军,白雯,等.脐带间充质干细胞治疗17 例类风湿性关节炎患者的临床疗效观察[J].中国免疫学杂志,2010,26(7): 659-662. [51] 徐如霞,李静,葛向红,等.BMSCs与曲安奈德治疗兔实验性自身免疫性葡萄膜炎的疗效比较[J].中华实验眼科杂志,2014, 32(7): 600-606. [52] 杨华强,李红,胡明均,等. 脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗系统性红斑狼疮五例并文献复习[J].中华临床医师杂志:电子版,2013, 7(14):6735-6737. [53] 季兴,李波,李婛,等.脐带间充质干细胞联合利妥昔单抗治疗多发性硬化症30例临床观察[J].现代生物医学进展,2013,13(17): 3307-3310. [54] 顾菲,张华勇,王红,等.间充质干细胞移植治疗多发性硬化一例[J].中华医学杂志,2009,89(17):1224. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [4] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [5] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [6] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [7] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [8] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [9] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [10] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [11] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [12] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [13] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [14] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [15] | Chen Junyi, Wang Ning, Peng Chengfei, Zhu Lunjing, Duan Jiangtao, Wang Ye, Bei Chaoyong. Decalcified bone matrix and lentivirus-mediated silencing of P75 neurotrophin receptor transfected bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct tissue-engineered bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 510-515. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||