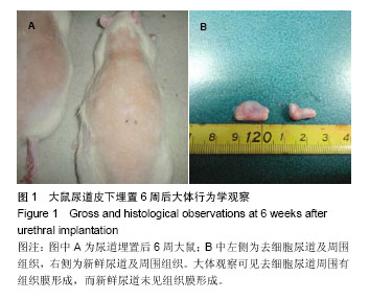
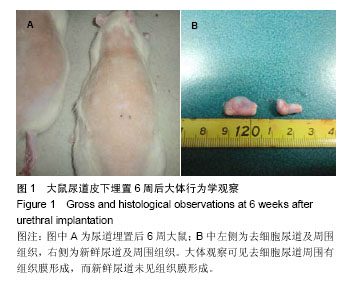
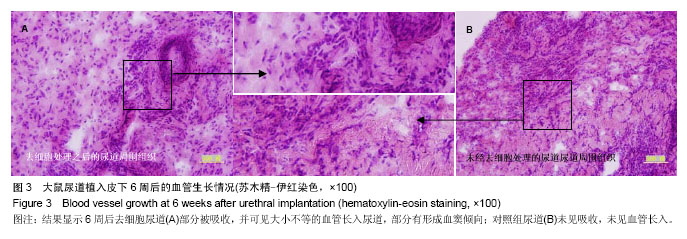
| [1]De Filippo RE,Yoo JJ,Atala A.Urethral replacement using cell seeded tubularized collagen matrices.J Urol. 2002 ;168(4Pt2); 1644-1768.
[2]Figallo E,Flaibani M,Zavan B,et al. Micropatterned biopolymer 3D scaffold for static and dynamic culture of dynamic culture of human fibroblast .Biotechnol Prog. 2007; 23(1):209-212.
[3]Campodonico F,Benelli Michelazzi A,et al.Bladder cell culture on small intestinal submucosa as bioscaffod:experimental study on engineeredurothelial grafts.Eur Urol. 2004;46(4): 531-507.
[4]Wunsch L,Ehlers EM, Russlies M.Matrix testing for urothelial tissue engineering.Eur J Pediatr SurgJT. 2005; 15(3):164-169.
[5]Stack A,Hayward SW,Baskin LS,et al.Mqlecular, cellular and developmental biology of urothelium as a basis of bladder regeneration .Differentiation.2005;73(4):121-103.
[6]Niu YS,Zhang WX,Li HC,et al.Carbon dioxide/propylene oxide coupling reaction catalyzed by chromium salen complexes. Polymer.2009;50(2):441-446.
[7]Wang Jintao,Zhu Quan,Lu Xialian,et al.ZnGA–MMT catalyzed the copolymerization of carbon dioxide with propylene oxide. Eur Polym J.2005; 41(5):1108-1114.
[8]Zhou X, Yang XG, Chen T,et al.Synthesis of Propylene Carbonate from Carbon Dioxide and o-Chloropropanol. Chinese Journal of Catalysis.2009;30(1):7-8.
[9]Wang XL, Li RKY, Cao YX, et al. Essential work of fracture analysis for starch filled poly(propylene carbonate) composites.Materials & Design.2007;28(6):1934-1939.
[10]Bartsch GJ,Atala A.Tissue engineering in urology.Basic principles and application.UrologeA.2003;42(3);255-364.
[11]Lakshmanan Y,Frimberger D,Gearhart JD,et al.Human embryoid body-derived stem cells in co-culture with bladder smooth muscle and urothelium.Urology.2005;65(4):821-826.
[12]Liu CX,Lin YY,LiHL,et al .Application of silk fibroin flim for repairing rabbit urethral defect .Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2007;27(2):182-185
[13]Moradzadeh A, The impact of motor and sensory nerve architecture on nerve regeneration. Exp Neuro.2008;212(2): 370-376.
[14]Atala A,Cima LG,KimWet,et al.Injectable alginate seeded with chondrocytes as apotential treatment for vesicouertal reflux. Urol.2009;150 (3):734-749.
[15]Moradzadeh AL. The impact of motor and sensory nerve architecture on nerve regeneration. Exp Neurol.2008;212(2): 332-334.
[16]Walsh PC, Retik AB ,Vaughan ED,et al.Camp bellps urology. USA:An Imprint of Elsevier science.2002;70(4):243-245.
[17]Henry GD,Wilson SK.UPdates in inflatable penile prostheses.Urol Clin North Am.2007;34(7):534-553.
[18]Simonsen U,Prieto,Hernandez M,et al. Adrenoceptor- mediated regulation of the contractility in horse penile resistance arteries.JVasc Res.2007;34(6):89-111.
[19]Eltahawy EA,VIrasoro P, Schlossber SM.Long2 tem follow up for excision and primary a nastomosis for nteriorurethral stricture.JUrol.2007;177(5):1703-1801.
[20]Bazo A, Rao K. Urethral strictures:once a stricture always a striure.trop Doct. 2003;33(4):68-70.
[21]Saraste A,PulkkiK,Kallajokin M,et al.Apoptosis in human acute myocardial infarction.Circulation. Circulation. 1997; 95(2):320-323.
[22]Yuan H, Pu C, Wei Q,et al.Research progress of extracellular matrix material for tissue engineering.Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi.2012;26(10):1251-1254.
[23]Jiang H, Ma LM, Zhou J,et al.Human foreskin acellular matrix graft: a good scaffold for urethral tissue engineering. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 2009;15(5): 409-412.
[24]Han P, Song C, Yang YR,et al.Urethral acellular matrix graft for repairing urethral defect in rabbits.Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao.2009;29(1):124-127, 132.
[25]Li C, Xu YM, Song LJ,et al. Urethral reconstruction using oral keratinocyte seeded bladder acellular matrix grafts.J Urol. 2008; 180(4):1538-1542.
[26]Fu Q, Deng CL, Liu W, et al.Urethral replacement using epidermal cell-seeded tubular acellular bladder collagen matrix.BJU Int. 2007;99(5):1162-1165.
[27]Bernoulli J,Yatkin E,Talvitie EM,et al.Urodynamic changes in a noble rat model for nonbacterial prostatic inflammation. Prostate.2007;67(8):865-870. |