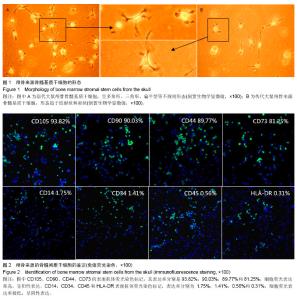
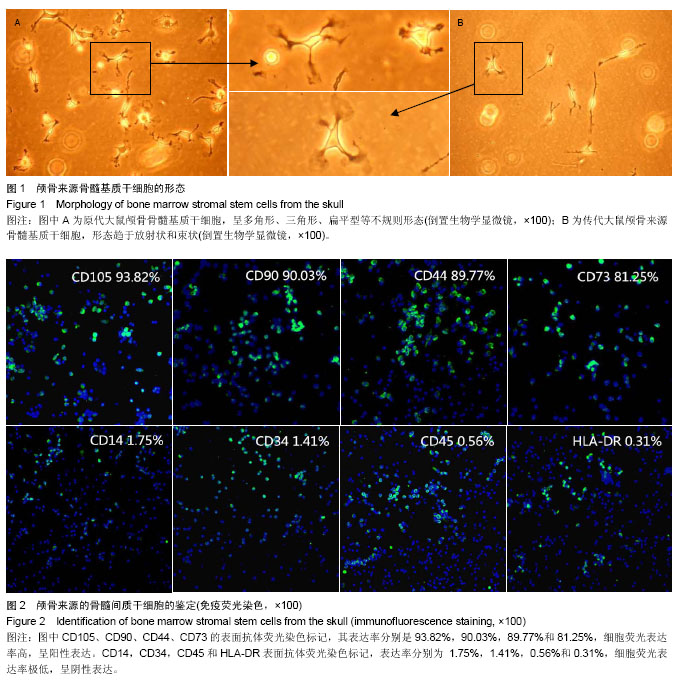
|
[1] 杨红旗.胚胎干细胞移植治疗帕金森病研究进展[J].河南医学研究,2003,12(4):377-380.
[2] Kawasaki H, Suemori H, Mizuseki K,et al. Generation of dopaminergic neurons and pigmented epithelia from primate ES cells by stromal cell-derived inducing activity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(3):1580-1585.
[3] Kawasaki H, Mizuseki K, Nishikawa S,et al. Induction of midbrain dopaminergic neurons from ES cells by stromal cell-derived inducing activity.Neuron. 2000;28(1):31- 40.
[4] Mizuseki K, Sakamoto T, Watanabe K,et al. Generation of neural crest-derived peripheral neurons and floor plate cells from mouse and primate embryonic stem cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(10):5828-5833.
[5] Yamazoe H, Murakami Y, Mizuseki K,et al. Collection of neural inducing factors from PA6 cells using heparin solution and their immobilization on plastic culture dishes for the induction of neurons from embryonic stem cells. Biomaterials. 2005;26(28):5746-5754.
[6] Ishii S, Okada Y, Kadoya T,et al. Stromal cell-secreted factors promote the survival of embryonic stem cell-derived early neural stem/progenitor cells via the activation of MAPK and PI3K-Akt pathways. J Neurosci Res. 2010;88(4):722-734.
[7] Vazin T, Becker KG, Chen J,et al. A novel combination of factors, termed SPIE, which promotes dopaminergic neuron differentiation from human embryonic stem cells .PLoS One. 2009;4(8):e6606.
[8] Torres J, Prieto J, Durupt FC,et al. Efficient differentiation of embryonic stem cells into mesodermal precursors by BMP, retinoic acid and Notch signalling. PLoS One. 2012;7(4): e36405.
[9] Belinsky GS, Sirois CL, Rich MT,et al. Dopamine receptors in human embryonic stem cell neurodifferentiation.Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(10):1522-1540.
[10] Wang Y, Zhang J.Thermal stabilities of drops of burning thermoplastics under the UL 94 vertical test conditions. J Hazard Mater. 2013;246-247.
[11] Yang T, Liu LY, Ma YY,et al. Notch signaling-mediated neural lineage selection facilitates intrastriatal transplantation therapy for ischemic stroke by promoting endogenous regeneration in the hippocampus.Cell Transplant. 2014;23(2): 221-238.
[12] Pereira A, Hernández P, Martinez J,et al. Surface topographic characterization for polyamide composite injection molds made of aluminum and copper alloys.Scanning. 2014;36(1): 39-52.
[13] Khadka A, Li J, Li Y,et al. Evaluation of hybrid porous biomimetic nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide 6 and bone marrow-derived stem cell construct in repair of calvarial critical size defect.J Craniofac Surg. 2011;22(5):1852-1858.
[14] Qu D, Li J, Li Y,et al. Ectopic osteochondral formation of biomimetic porous PVA-n-HA/PA6 bilayered scaffold and BMSCs construct in rabbit.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2011;96(1):9-15.
[15] Yoshida S, Yasuda M, Miyashita H,et al. Generation of stratified squamous epithelial progenitor cells from mouse induced pluripotent stem cells. PLoS One. 2011;6(12): e28856.
[16] Cheng HK, Sahoo NG, Khin TH,et al. The role of functionalized carbon nanotubes in a PA6/LCP blend.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2010;10(8):5242-5251.
[17] Huang S, Peng H, Tjiu WW,et al. Assembling exfoliated layered double hydroxide (LDH) nanosheet/carbon nanotube (CNT) hybrids via electrostatic force and fabricating nylon nanocomposites.J Phys Chem B. 2010;114(50):16766-16772.
[18] Löhle M, Hermann A, Glass H,et al.Differentiation efficiency of induced pluripotent stem cells depends on the number of reprogramming factors.Stem Cells. 2012;30(3):570-579.
[19] Torres J, Prieto J, Durupt FC,et al. Efficient differentiation of embryonic stem cells into mesodermal precursors by BMP, retinoic acid and Notch signalling. PLoS One. 2012;7(4): e36405.
[20] Calderón-Martínez D, Garavito Z, Spinel C,et al. Schwann cell-enriched cultures from adult human peripheral nerve: a technique combining short enzymatic dissociation and treatment with cytosine arabinoside (Ara-C).J Neurosci Methods. 2002;114(1):1-8.
[21] 李皓恒,彭昊,刘世清,等.冷洗涤法纯化培养Schwann细胞的研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2007,24(12):1604-1608.
[22] 黄明,罗卓荆,肖伟,等.免疫磁珠法分离和提纯雪旺细胞的实验研究[J].中华矫形外科杂志,2008,16(8):599-601.
[23] Morrissey TK, Kleitman N, Bunge RP. Isolation and functional characterization of Schwann cells derived from adult peripheral nerve. J Neurosci. 1991;11(8):2433-2442.
[24] 梅玉峰,汪静,闫玉华,等.冷酶消化法在分离和培养新生大鼠Schwann细胞的应用[J].神经解剖学杂志,2007,23(2):205-208.
[25] 连小峰,候铁胜,傅强,等.植块法与酶消化法结合培养原代大鼠雪旺细胞[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2008,18(9):703-706.
[26] 中华人民共和国科学技术部. 关于善待实验动物的指导意见. 2006-09-30.
[27] 王艳,胡翰青,邢红艳,等.小鼠骨髓干细胞的分离培养鉴定及诱导分化的研究[J].西南国防医药,2013,1(1):8-11.
[28] 王美华,胡锴勋,邱泽武,等.改良小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞培养方法及长效荧光标记的可行性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2009,13(45):8929-8934.
[29] 赵富生,武庚,武杨,等.不同年龄段大鼠骨髓基质干细胞生物学特性的比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(49): 9147-9150.
[30] 宫晓洁,孙莉,黎靖宇,等.小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的分离培养及形态学观察[J].解剖学研究,2008,30(1):54-56.
[31] Kretlow JD, Jin YQ, Liu W,et al. Donor age and cell passage affects differentiation potential of murine bone marrow-derived stem cells. BMC Cell Biol. 2008;9:60.
[32] Sung JH, Yang HM, Park JB,et al. Isolation and characterization of mouse mesenchymal stem cells. Transplant Proc. 2008;40(8):2649-2654.
[33] 刘志新,张晓莉,武庚,等.利用贴壁特点提取和纯化乳鼠雪旺细胞[J].解剖科学进展,2010,16(1):21-23.
[34] Barry F, Boynton R, Murphy M,et al.The SH-3 and SH-4 antibodies recognize distinct epitopes on CD73 from human mesenchymal stem cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;289(2):519-524.
[35] Hung SC, Chen NJ, Hsieh SL,et al. Isolation and characterization of size-sieved stem cells from human bone marrow.Stem Cells. 2002;20(3):249-258.
[36] 赵文静,陈亚洁,刘薇.人骨髓间充质干细胞分离培养及生物学特性研究[J].中国现代医学杂志,2006,16(18):2744-2747.
[37] Sotiropoulou PA, Perez SA, Salagianni M,et al. Characterization of the optimal culture conditions for clinical scale production of human mesenchymal stem cells.Stem Cells. 2006;24(2):462-471. .
[38] Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC,et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells.Science. 1999;284(5411):143-147.
|