Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (31): 4998-5003.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.31.014
Previous Articles Next Articles
Percutaneous iliosacral screw versus percutaneous reconstruction plate fixation for Tile C sacral fractures
Yin Shi-yuan, Luo Xue-feng, Shen Ming-quan, Xie Zeng-ru
- Department of Traumatology, Emergency Center, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2014-06-18Online:2014-07-23Published:2014-07-23 -
Contact:Xie Zeng-ru, Master, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Chief physician, Department of Traumatology, Emergency Center, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Yin Shi-yuan, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Traumatology, Emergency Center, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yin Shi-yuan, Luo Xue-feng, Shen Ming-quan, Xie Zeng-ru. Percutaneous iliosacral screw versus percutaneous reconstruction plate fixation for Tile C sacral fractures[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(31): 4998-5003.
share this article
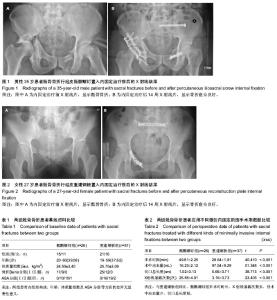
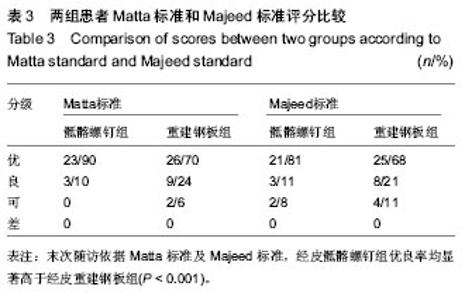
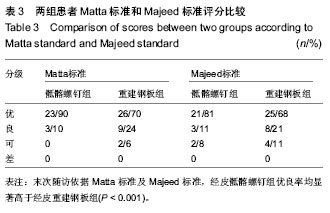
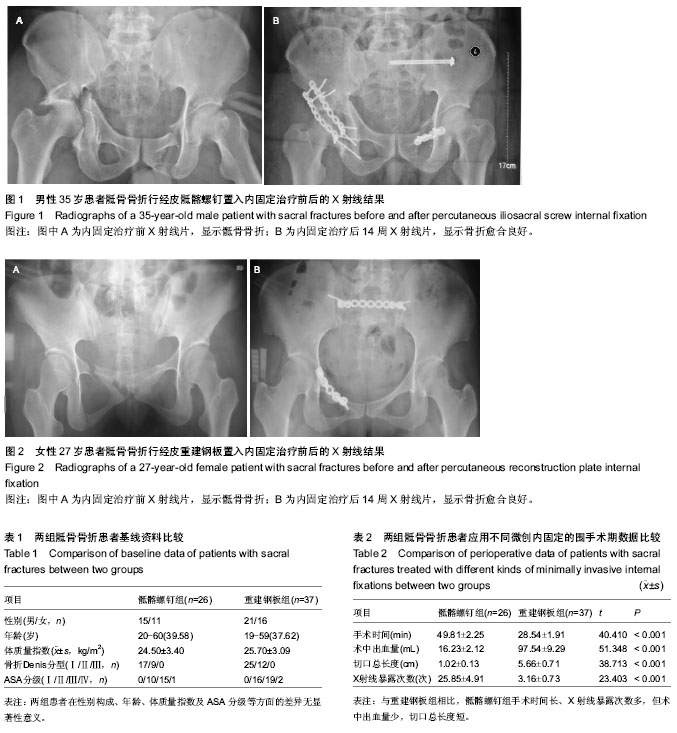
2.1 参与者数量分析 按意向性处理,纳入63例单侧TileC型骶骨骨折患者,经皮骶髂螺钉组26例,经皮重建钢板组37例,均获得完整随访,无脱落。 2.2 基线资料比较 两组患者在性别构成、年龄、体质量指数及ASA分级等方面的差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),具有可比性,见表1。 2.3 围手术期数据比较 骶髂螺钉组与重建钢板组在手术时间、术中出血量、X射线暴露次数和切口总长度的比较中,差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.001)。骶髂螺钉组手术时间长、X射线暴露次数多,但术中出血量少,切口总长度短(表2)。 2.4 随访骨折愈合及并发症情况 两组患者均获得12-36个月随访。骶髂螺钉组平均骨折愈合时间为(14.85±1.74)周,重建钢板组平均骨折愈合时间为(14.11±1.94)个月,组间比较差异无显著性意义(t=1.551,P=0.126)。所有患者均未出现切口感染、内固定物松动、医源性神经损伤等并发症,原存在神经损伤症状的患者未见加重,随访中均有不同程度的恢复。3例患者骶骨残存纵向移位(经皮重建钢板组),13例患者术后1年骶骨骨折处仍有不同程度的慢性疼痛(经皮骶髂螺钉组4例,经皮重建钢板组9例)。 2.5 Matta标准和Majeed标准评价结果 末次随访依据Matta标准,经皮骶髂螺钉组优良率达100%,经皮重建钢板组优良率达95%,且差异有显著性意义(u=3.307,P < 0.001);依据Majeed标准,经皮骶髂螺钉组优良率达92%,经皮重建钢板组优良率达89%,差异同样有显著性意义(u=3.373,P < 0.001,表3)。 2.6 典型病例 病例1:男,35岁,车祸致左侧骶骨DenisⅠ型骨折,合并左侧耻骨上下支及右侧髋臼骨折,体质量指数27.6 kg/m2,ASA分级Ⅲ级,入院后第7天在全身静脉麻醉下先切开复位重建钢板内固定骨盆前环骨折,再经皮置入骶髂螺钉内固定骶骨骨折。术后随访24个月,骨折愈合时间为14周,未出现明显并发症, Matta标准为优,Majeed标准为89分(图1)。 病例2:女,27岁,车祸致左侧骶骨Denis Ⅱ型骨折,合并右侧耻骨上下支骨折,体质量指数25.1 kg/m2,ASA分级Ⅱ级,入院后6 d在全身静脉麻醉下先切开复位重建钢板内固定骨盆前环骨折,再经皮置入重建钢板内固定骶骨骨折。术后随访15个月,骨折愈合时间为15周,腰骶部久坐后常有隐痛,休息后缓解,无其他并发症,Matta标准为优,Majeed标准为86分(图2)。"
| [1] Roy-Camille R, Saillant G, Gagna G, et al. Transverse fracture of the upper sacrum. Suicidal jumper's fracture. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 1985;10(9):838-845. [2] 蔡军辉,王伟良,张力成.骶骨纵形骨折的治疗进展[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2011,13(9):881-884. [3] Mehta S, Auerbach JD, Born CT, et al. Sacral fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2006;14(12):656-665. [4] 陈爱民,李永川, 赵良瑜,等.骨盆后环不稳定伴骶丛损伤的诊断和治疗[J].中华骨科杂志,2012,28(6):516-519. [5] 贾健,胡永成,张铁良,等. 骶骨骨折的诊治现状[J].中华骨科杂志, 2009,29(12):1168-1176. [6] 陈明,谢鸣,勘武生,等. 不稳定型骨盆骨折的手术方式探讨[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2013,15(5):445-447. [7] 蔡军辉,王伟良,张力成.骶骨纵形骨折的治疗进展[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2011,13(9):881-884. [8] Schildhauer TA, Chapman JR, Mayo KA.Multisegmental open sacral fracture due to impalement: a case report. Orthop Trauma. 2005;19(2):134-139. [9] Denis F, Davis S, Comfort T. Sacral fractures:an important problem. Retrospective analysis of 236 cases. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988;(227):67-81. [10] Schmidek HH,Smith DA,Kristiansen TK. Sacral fractures. Neurosurgery. 1984;15(5):735-746. [11] 王雷,柳超,田纪伟.腰骨盆重建术治疗不稳定骶骨骨折[J].中华创伤杂志,2013,29(7):619-623. [12] 胡旭栋,向宁,王光林,等.三角固定技术治疗Tile C型骨盆骨折[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2012,14(5):399-404. [13] 王奇,黄其杉,王向阳,等.骶骨后路钉板固定的解剖学研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2010,30(3):277-281. [14] Tonetti J. Management of recent unstable fractures of the pelvic ring. An update Conference supported by the Club Bassin Cotyle. (Pelvis-Acetabulum Club). Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2013;99(1):S77-86. [15] Park YS, Baek SW, Kim HS, et al. Management of sacral fractures associated with spinal or pelvic ring injury. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012;73(1): 239-242. [16] 赵艳.螺钉与钢板在骨盆骨折置入内固定应用中的生物力学评价[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(48):9070-9073. [17] 肖丹,柯雨洪,王义生.经皮骶髂关节空心螺钉置入联合骨盆外固定架治疗C型骨盆骨折48例:回顾性病例对照[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(43):8560-8563. [18] Matta JM, Tornetta P 3rd. Internal fixation of unstable pelvic ring injuries. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;(329):129-140. [19] Majeed SA. Grading the outcome of pelvic fractures. J Bone Joint Surg. 1989;71(2):304-306. [20] Tan GQ, He JL, Fu BS, et al. Lumbopelvic fixation for multiplanar sacral fractures with spinopelvic instability. Injury. 2012;43(8):1318-1325. [21] Dudda M,Hoffmann M,Schildhauer TA. Sacrum fractures and lumbopelvic instabilities in pelvic ring injuries:Classification and biomechanical aspects. Unfallchirurg. 2013;116(11):972-978. [22] Hoskins J, Lewis PB., Smith S, et al. Diagnosis and Management of Sacral Fractures. Contemp Spine Surg. 2011; 12(9): 1-8. [23] Ge Z, Wang B, Zhang D, et al. Effect of iliolumbar fixation in patients with Tile C pelvic injury and analysis of relative factors. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2012; 26(11):1285-1290. [24] Mendel T,Noser H,Kuervers J,et al. The influence of sacral morphology on the existence of secure S1 and S2 transverse bone corridors for iliosacroiliac screw fixation. Injury. 2013; 44(12):1773-1779. [25] Miller AN, Routt ML.Variations in Sacral Morphology and Implications for Iliosacral Screw Fixation. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2012;20(1):8-16. [26] Osterhoff G,Ossendorf C,Wanner GA,et al. Percutaneous iliosacral screw fixation in S1 and S2 for posterior pelvic ring injuries: technique and perioperative complications. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011;131(6):809-813. [27] Reilly MC,Bono CM,Litkouhi B,et al.The effect of sacral fracture malreduction on the safe placement of iliosacral screws.Orthop Trauma. 2003;17(2):88-94. [28] Bodzay T,Szita J,Mano S,et al. Biomechanical comparison of two stabilization techniques for unstable sacral fractures. J Orthop Sci.2012;17(5):574-579. [29] Padalkar P,Pereira BP,Kathare A,et al. Trans-iliosacral plating for vertically unstable fractures of sacral spine associated with spinopelvic dissociation: A cadaveric study. Indian J Orthop. 2012;46(3):274-278. [30] Suzuki T,Hak DJ,Ziran BH,et al. Outcome and complications of posterior transiliac plating for vertically unstable sacral fractures. Injury. 2009;40(4):405-409. [31] König MA, Seidel U, Heini P,et al. Minimal-invasive Percutaneous Reduction and Transsacral Screw Fixation for U-shaped Fractures. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2013;26(1):48-54. [32] Koenig MA,Jehan S,Boszczyk AA,et al. Surgical management of U-shaped sacral fractures: a systematic review of current treatment strategies. Eur Spine J. 2012;21(5):829-836. [33] König MA, Seidel U, Heini P, et al. Minimal-invasive Percutaneous Reduction and Transsacral Screw Fixation for U-shaped Fractures. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2013;26(1):48-54. [34] 王国栋,周东生.骶骨多平面骨折的治疗现状[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2012,14(7):621-623. [35] Matta JM, Yerasimides JG. Table-skeletal fixation as an adjunct to pelvic ring reduction.Orthop Trauma. 2007; 21(9): 647-656. [36] Ruatti S,Kerschbaumer G,Gay E,et al. Technique for reduction and percutaneous fixation of U- and H-shaped sacral fractures. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res.2013;99(5): 625-629. [37] Schweitzer D,Zylberberg A,Cordova M,et al. Closed reduction and iliosacral percutaneous fixation of unstable pelvic ring fractures. Injury. 2008;39(8):869-874. [38] Chen HW,Liu GD,Ou S,et al. Treatment of unstable sacral fractures with percutaneous reconstruction plate internal fixation. Acta Cir Bras. 2012;27(5):338-342. [39] Coste C,Asloum Y,Marcheix PS,et al. Percutaneous iliosacral screw fixation in unstable pelvic ring lesions: The interest of O-ARM CT-guided navigation. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2013;99(4):S273-278. |
| [1] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [2] | He Li, Tian Wei, Xu Song, Zhao Xiaoyu, Miao Jun, Jia Jian. Factors influencing the efficacy of lumbopelvic internal fixation in the treatment of traumatic spinopelvic dissociation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 884-889. |
| [3] | Fang Yi, Zhao Wenzhi, Pan Deyue, Han Xin, Zhang Lu, He Hongtao, Shi Feng, Tian Tingxiao. Acromioclavicular joint dislocation: how to achieve anatomical reduction, sustained stability and micro-motion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 796-802. |
| [4] | Mu Shuai, Xiao Peng, Zhang Jianliang, Hou Weiguang. Incidence of femoral neck shortening after internal fixation of femoral neck fracture and prognostic factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(21): 3304-3309. |
| [5] | Fu Jiaxin, Xiao Lianping, Wang Shusen, Li Xiaodong, Han Liqiang, Wang Tonghao. Therapeutic effects of paraspinal approach combined with internal fixation through pedicle of fractured vertebra versus traditional AF screw-rod system for thoracolumbar fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1177-1181. |
| [6] | Qiu Zhongpeng, Li Ke, Li Gang, Liu Keyu, Du Xinhui, Meng Defeng, Shi Chenhui, Wang Weishan. Different treatments for two-part and three-part proximal humeral fractures by Neer classification: follow-up results analyzed using clinical economics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1188-1195. |
| [7] | Ke Wei, Li Ke, Wang Sibo, Du Xinhui, Qiu Zhongpeng, Kang Zhilin, Wang Weishan, Li Gang . Open reduction and plate fixation versus closed reduction and external fixation for distal radius fractures: scores and linear regression analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1196-1202. |
| [8] | Fan Zhirong, Peng Jiajie, Zhong Degui, Zhou Lin, Su Haitao, Huang Yongquan, Wu Jianglin, Liang Yihao. Suture anchor combined with open reduction and internal fixation versus open reduction and internal fixation for ankle fracture combined with deltoid ligament injury: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1307-1312. |
| [9] | Li Xianzhou, Wang Qian, Zhang Cunxin . Lumbar spondylolisthesis: status and prospects of implant treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(4): 621-627. |
| [10] | Zhou Yu, Liu Yuehong, Liu Shuping, Chen Xi, Qin Wei, Li Qifeng. Spinal stability of intervertebral grafting reinforced by five or six augmenting screws versus transvertebral grafting reinforced by four augmenting screws for thoracolumbar vertebral fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(4): 505-511. |
| [11] | Yin Hao, Zhou Enchang, Pan Zhengjun, Chen Guang, Jiang Hua. Finite element analysis of the four and three cannulated screws combined with buttress plate fixation for the treatment of Pauwels III femoral neck fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(32): 5133-5137. |
| [12] |
Wang Lei, Li Zilong, Yuan Binbin, Wu Qingwei, Tang Fengming.
Clinical effect of locking plate versus anterograde intramedullary nail in the treatment of adult humeral shaft fractures: a meta-analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(24): 3924-3930.
|
| [13] | Hao Liang, Zhang Zhonglin, Wang Baodong, Bi Zhenggang. Intertrochanteric fracture of the femur: improvement of internal fixation device, surgical changes and related disputes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(18): 2927-2935. |
| [14] | Yao Liquan, Ling Qinjie, Li Jiaying, Zhong Letian, Zhou Xingping, Liu Jintao, He Erxing, Yin Zhixun. Antibiotic artificial bone implantation for treating pyogenic spondylodiscitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(14): 2133-2139. |
| [15] | Gong Zhibing, Wu Zhaoke, Zhang Huantang, Xu Zhiqing, Zhuang Zhikun, Zhang Qianjin. Allogeneic cortical bone plate combined with locking plate for Vancouver type B1 and C osteoporotic periprosthetic femoral fractures after hip arthroplasty in older adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(12): 1812-1817. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||