Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (28): 4563-4567.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.28.022
Previous Articles Next Articles
Human cytomegalovirus detection in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: value of fluorescence quantitative PCR in the early diagnosis
Liu Chuan1, Zou Ye-qing1, Shi Qing-zhi2
- 1 Laboratory of Molecular Medicine, 2 Department of Hematology, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China
-
Online:2014-07-02Published:2014-07-02 -
Contact:Liu Chuan, Master, Associate chief technician, Laboratory of Molecular Medicine, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China -
About author:Liu Chuan, Master, Associate chief technician, Laboratory of Molecular Medicine, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Chuan, Zou Ye-qing, Shi Qing-zhi. Human cytomegalovirus detection in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: value of fluorescence quantitative PCR in the early diagnosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(28): 4563-4567.
share this article
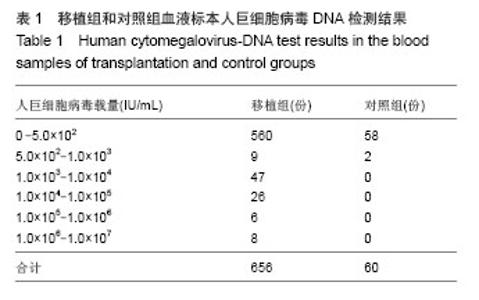
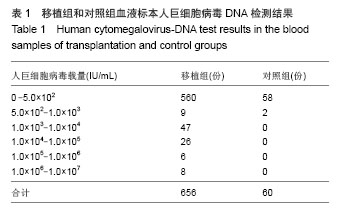
2.1 造血重建及植入情况 41例患者均获造血重建。中性粒细胞植活的中位时间为+11(+10至+16) d,血小板植活的中位时间为+17(+15至+24)d。所有患者均于移植后+30 d行骨髓穿刺检查,骨髓象为增生活跃或明显活跃,STR检测结果为完全供者嵌合。不同血型适时转变为供者血型。移植后+30 d,41例达完全缓解标准,+365 d 32例均达到完全缓解标准。2.2 实时荧光定量PCR检测结果 Real-time PCR共检测41例造血干细胞移植患者656份血标本,其中12例共96份标本阳性,人巨细胞病毒载量介于5.0×102-1.0×107 IU/mL之间。对照组2份标本阳性,人巨细胞病毒载量介于5.0×102- 1.0×103 IU/mL之间。移植组平均为(4.69±1.54)×105 IU/mL, 对照组平均为(11.6±2.21)×102 IU/mL。移植组与对照组均值比较采用t 检验,P < 0.01(t=2.087),差异有显著性意义(表1)。"
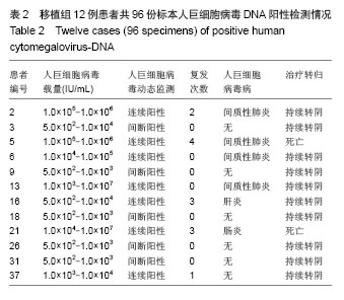
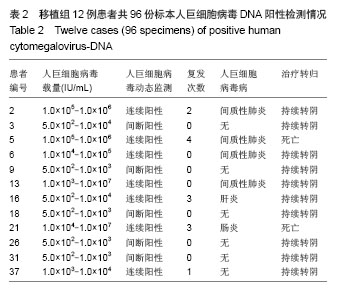
2.3 人巨细胞病毒DNA检测与人巨细胞病毒感染的治疗 Real-time PCR共检出12例患者阳性,人巨细胞病毒载量在5.0×102-1.0×107 IU/mL之间,其中7例患者表现为连续PCR阳性,伴DNA拷贝数逐渐升高,给予更昔洛韦治疗,患者均在一两周后DNA转阴,但仍有5例患者停药两三周后复发。其中5号患者共复发4次,第4次复发时表现为对更昔洛韦耐药,DNA不能转阴,很快死亡;16号患者第3次复发改为磷甲酸钠后DNA转阴,3,9,18,26,31号患者表现为非连续人巨细胞病毒DNA阳性,人巨细胞病毒载量未超过1.0×104 IU/mL,给予阿昔洛韦预防治疗,5例患者均未发展为人巨细胞病毒疾病(表2)。"
| [1]Griffiths PD, Emery VC, Milne RC. Cytomegalovirus[A]// Douglas D,Richmand, Whitley RJ, ed. Clinical virology[M]. 3rd ed. ASM Press,2009: 475-506. [2]周文强,石炳毅,蔡明,等.器官移植受者术后巨细胞病毒感染的监测[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(18):3479-3481. [3]Ichihara H, Nakamae H, Hirose A,et al. Immunoglobulin prophylaxis against cytomegalovirus infection in patients at high risk of infection following allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation.Transplant Proc. 2011;43(10):3927-3932. [4]Cantoni N, Hirsch HH, Khanna N,et al.Evidence for a bidirectional relationship between cytomegalovirus replication and acute graft-versus-host disease.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2010;16(9):1309-1314. [5]Borchers S, Luther S, Lips U,et al.Tetramer monitoring to assess risk factors for recurrent cytomegalovirus reactivation and reconstitution of antiviral immunity post allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.Transpl Infect Dis. 2011;13(3):222-236. [6]赵晓甦,刘代红,许兰平,等.异基因造血干细胞移植后巨细胞病毒肺炎临床特点分析[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2009,41(5): 548-553. [7]Torres HA, Aguilera E, Safdar A,et al. Fatal cytomegalovirus pneumonia in patients with haematological malignancies: an autopsy-based case-control study.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2008; 14(12):1160-1166. [8]Leruez-Ville M, Ouachée M, Delarue R, et al.Monitoring cytomegalovirus infection in adult and pediatric bone marrow transplant recipients by a real-time PCR assay performed with blood plasma.J Clin Microbiol. 2003;41(5):2040-2046. [9]张之南,沈悌.血液病诊断及疗效标准[M].3版.北京:科学出版社, 2007. [10]Muñoz-Cobo B, Solano C, Costa E,et al. Dynamics of cytomegalovirus (CMV) plasma DNAemia in initial and recurrent episodes of active CMV infection in the allogeneic stem cell transplantation setting: implications for designing preemptive antiviral therapy strategies.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2011;17(11):1602-1611. [11]Kekik C, Besisik SK, Seyhun Y,et al. Relationship between HLA tissue type, CMV infection, and acute graft-vs-host disease after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: single-center experience.Transplant Proc. 2009;41(9):3859-3862. [12]Jang JE, Hyun SY, Kim YD,et al. Risk factors for progression from cytomegalovirus viremia to cytomegalovirus disease after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2012;18(6):881-886. [13]van der Bij W, Speich R. Management of cytomegalovirus infection and disease after solid-organ transplantation.Clin Infect Dis. 2001;33 Suppl 1:S32-37. [14]陈育红,赵晓生,刘开彦,等.造血干细胞移植后患者血浆巨细胞病毒DNA拷贝数与巨细胞病毒病的关系[J].中华医学杂志,2009, 89(22): 1540-1543. [15]Eid AJ, Razonable RR.New developments in the management of cytomegalovirus infection after solid organ transplantation.Drugs. 2010;70(8):965-981. [16]Ariza-Heredia EJ, Nesher L, Chemaly RF.Cytomegalovirus diseases after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a mini-review.Cancer Lett. 2014 ;342(1):1-8. [17]金欣,陈建魁,于农,等.血液系统恶性肿瘤患者巨细胞病毒和EB病毒定量检测的临床价值[J].国际检验医学杂志, 2011,32(7): 793-794. [18]谢卫民,张曦,彭贵华,等.造血干细胞移植受者免疫抑制治疗与巨细胞病毒感染的关系[J].中南大学学报(医学版), 2010,35(11): 1162-1166. [19]刘开彦.造血干细胞移植患者巨细胞病毒感染的诊治进展[J].中国实用内科杂志,2007,27(20):1597-1598. [20]Ruiz-Camps I, Len O, de la Cámara R, et al.Valganciclovir as pre-emptive therapy for cytomegalovirus infection in allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. Antivir Ther. 2011;16(7):951-957. [21]Boeckh M, Boivin G.Quantitation of cytomegalovirus: methodologic aspects and clinical applications.Clin Microbiol Rev. 1998;11(3):533-554. [22]SY Y, YP C. The development of laboratory diagnosis of human cytomegalovirus infection. Foreign Medical Sciences Section of Pediatric. 2005; 32: 284-287. [23]Bhatia J, Shah BV, Mehta AP,et al. Comparing serology, antigenemia assay and polymerase chain reaction for the diagnosis of cytomegalovirus infection in renal transplant patients.J Assoc Physicians India. 2004;52:297-300. [24]Griscelli F, Barrois M, Chauvin S,et al.Quantification of human cytomegalovirus DNA in bone marrow transplant recipients by real-time PCR.J Clin Microbiol. 2001;39(12):4362-4369. [25]翟文静,魏嘉琳,赵明峰,等.巨细胞病毒定量PCR与pp65抗原测定监测异基因造血干细胞移植巨细胞病毒感染的比较[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2009,17(6):1522-1526. [26]Boeckh M, Gooley TA, Myerson D,et al.Cytomegalovirus pp65 antigenemia-guided early treatment with ganciclovir versus ganciclovir at engraftment after allogeneic marrow transplantation: a randomized double-blind study.Blood. 1996;88(10):4063-4071. [27]Gerna G, Baldanti F, Middeldorp J, et al. Use of CMV transcripts for monitoring of CMV infections in transplant recipients.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2000;16(4):455-460. [28]Einsele H, Ehninger G, Hebart H,et al.Polymerase chain reaction monitoring reduces the incidence of cytomegalovirus disease and the duration and side effects of antiviral therapy after bone marrow transplantation.Blood. 1995;86(7): 2815-2820. [29]Lu SC, Chin LT, Wu FM,et al. Seroprevalence of CMV antibodies in a blood donor population and premature neonates in the south-central Taiwan.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 1999;15(10):603-610. [30]张晓艳,李建勇,吴汉新,等.造血干细胞移植后对人巨细胞病毒感染病毒载量的检测[J].中华传染病杂志,2006,24(6):401-405. [31]邱志祥,王茫佶,王莉红,等.异基因造血干细胞移植后血巨细胞病毒定量监测及临床意义[J].中华内科杂志,2012,51(5):371-375. [32]陈欢,刘开彦,许兰平,等.异基因造血干细胞移植后实时定量聚合酶链反应在巨细胞病毒感染诊断和治疗中的应用[J].中华血液学杂志,2009,30(2): 77-81. [33]Winston DJ, Ho WG, Bartoni K,et al.Ganciclovir prophylaxis of cytomegalovirus infection and disease in allogeneic bone marrow transplant recipients. Results of a placebo-controlled, double-blind trial.Ann Intern Med. 1993;118(3):179-184. [34]Crumpacker CS.Ganciclovir. N Engl J Med. 1996;335(10): 721-729. [35]李春元,陈本川.更昔洛韦的临床应用进展[J].国外医药:合成药生化药制剂分册,1998,19(3):172. [36]胡增建,蒋华良,杨玉社.抗病毒药物研究新进展[J].中国药理学通报,1996,12(5):385. [37]Tokimasa S, Hara J, Osugi Y, et al. Ganciclovir is effective for prophylaxis and treatment of human herpesvirus-6 in allogeneic stem cell transplantation.Bone Marrow Transplant. 2002;29(7):595-598. [38]刘鑫荣.更昔洛韦对巨细胞病毒感染的治疗应用[J].国外医药:抗生素分册,1996,17(1):66. [39]Henkin CC, Griener JC, Ten Eick AP. Stability of valganciclovir in extemporaneously compounded liquid formulations. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2003;60(7):687-690. [40]Emery VC, Hassan-Walker AF. Focus on new drugs in development against human cytomegalovirus. Drugs. 2002; 62(13):1853-1858. [41]Weiskittel P.Valganciclovir hydrochloride (Valcyte): a new antiviral agent.Nephrol Nurs J. 2003;30(1):93-95. [42]Bozkaya H, Yurdaydin C, Bozdayi AM,et al. Oral ganciclovir for treatment of lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B virus infection: a pilot study.Clin Infect Dis. 2002;35(8):960-965. [43]Griffiths P, Whitley R, Snydman DR,et al.Contemporary management of cytomegalovirus infection in transplant recipients: guidelines from an IHMF workshop, 2007.Herpes. 2008;15(1):4-12. [44]Winston DJ, Yeager AM, Chandrasekar PH,et al. Randomized comparison of oral valacyclovir and intravenous ganciclovir for prevention of cytomegalovirus disease after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation.Clin Infect Dis. 2003;36(6): 749-758. [45]Meyers JD, Reed EC, Shepp DH,et al.Acyclovir for prevention of cytomegalovirus infection and disease after allogeneic marrow transplantation.N Engl J Med. 1988;318(2):70-75. |
| [1] | Chen Xiao, Guo Zhi, Chen Lina, Liu Xuanyong, Zhang Yihuizhi, Li Xumian, Wang Yueqiao, Wei Liya, Xie Jing, Lin Li. Factors affecting the mobilization and collection of autologous peripheral blood hematopoietic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2958-2962. |
| [2] | Cao Linlin, Ding Kaiyang, Song Hao, Wu Guolin, Hu Maogui, Fan Dandan, Zhou Chenyang, Wang Cuicui, Feng Yuanyuan. Efficacy and influencing factors of autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in the treatment of malignant lymphoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 1993-1998. |
| [3] | Zhang Suping, Sun Ling, Wan Dingming, Cao Weijie, Li Li, Liu Changfeng, Liu Yufeng, Wang Dao, Guo Rong, Jiang Zhongxing, Xie Xinsheng. Effectiveness of unrelated peripheral blood stem cell transplantation in the treatment of severe aplastic anemia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(31): 4994-5001. |
| [4] | Wei Yuanfeng, Huang Dongping. Current status of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in the treatment of aplastic anemia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(19): 3093-3100. |
| [5] | Zhang Ling, Sun Yanling, Wang Xiaozhen, Long Bing , Liu Jiajun. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of refractory chronic graft-versus-host disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(13): 2034-2038. |
| [6] | Zhong Yanping, Zou Hongyan, Quan Zhanrou, Deng Zhihui, Hong Wenxu. Analysis of full-length sequence and 18 point mutations of HLA-B in a leukemia patient and her family [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(1): 77-82. |
| [7] | Xue Hui, Feng Shuqing, Hu Yongchao, Liu Zhibin, Li Xiaoyu, Gao Feng. Stratification therapy for cytomegalovirus infection after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(5): 756-760. |
| [8] | Chen Xiaoling, Deng Huilan, Lu Quanyi, Hong Xiuli, Hu Jiasheng. Pure red cell aplasia follows allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a two-case report and literature review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(5): 761-766. |
| [9] | Guo Zhi, Ren Hua, Ji Yong, Chen Liping, Chen Lina, Liu Xuanyong, Zheng Shanshan, Liu Xiaodong, Chen Huiren. Thrombopoietin improves platelet recovery after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for severe aplastic anemia: an assessment of safety and efficacy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(33): 5269-5274. |
| [10] | Liu Jiao, Wang Daming, An Taixue, Hu Xuesong, Li Nankai, Wang Hongfu, Ma Wen, Nie-He Zhongrong, Xiao Lijia, Zhou Yiwen, Zheng Lei. Expression profile analysis of miRNAs in serumal exosomes as sensitive biomarkers in patients with graft-versus-host disease following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(21): 3418-3425. |
| [11] | Wang Xiaoning, Chen Ying, Zhu Huachao, Zhang Mei, He Pengcheng. Protective effect of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on acute drug-induced liver injury after conditioning in haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(17): 2690-2695. |
| [12] | Wei Yuanfeng, Wei Zhongling, Yang Yuqiong, Qi Jing, Yan Jiawei, Huang Dongping. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for severe aplastic anemia in 10 cases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(13): 2042-2048. |
| [13] | Wan Ding-ming, Sun Lin-lin, Xie Xin-sheng, Guo Rong, Cao Wei-jie, Zhang Su-ping, Li Li, Chen Xiao-na, Liu Yu-ye. Peripheral blood haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in adults: monitoring minimal residual diseases to intervene recurrence [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(9): 1413-1418. |
| [14] | Wan Ding-ming, Liu Yu-ye, Cao Wei-jie, Xing Hai-zhou, Xie Xin-sheng, Wang Dao, Zhang Su-ping, Li Li, Chen Xiao-na, Sun Lin-lin. Genetic haploidentical peripheral blood stem cell transplantation for treatment of myelodysplastic syndrome: a 2-year follow-up visit of 21 cases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(5): 662-668. |
| [15] | Ren Juan, Zhao Juan, Wang Xiao-ning. Co-transplantation of umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells and haploidentical hematopoietic stem cells for treatment of severe aplastic anemia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(33): 5297-5302. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||