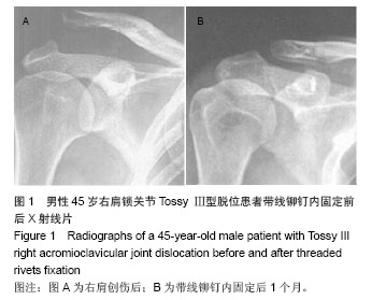
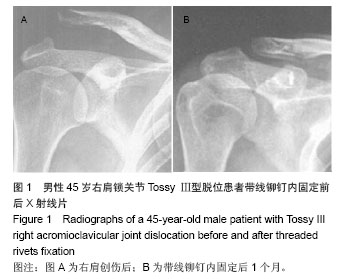
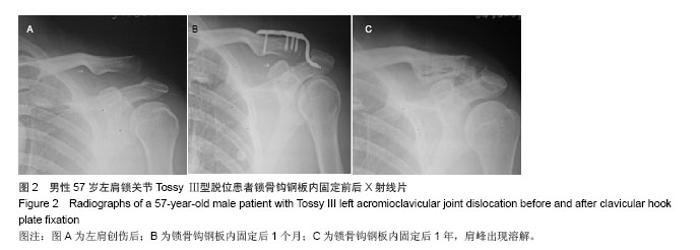
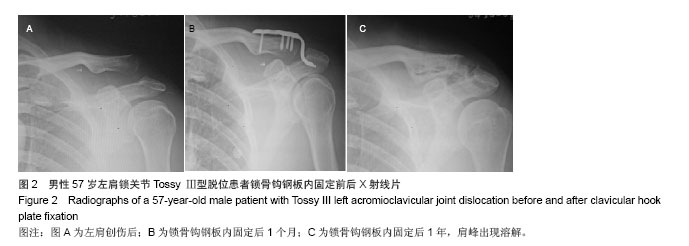
| [1]Li X, Ma R, Bedi A, et al. Management of acromioclavicular joint injuries. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96(1):73-84.
[2]吕书军,曹勇,周广鉴,等.三重固定纽扣钢板肩锁关节脱位的生物力学[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(9):1675-1679.
[3]Beitzel K, Cote MP, Apostolakos J, et al. Current concepts in the treatment of acromioclavicular joint dislocations. Arthroscopy. 2013;29(2):387-397.
[4]Flinkkila T, Ristiniemi J. Surgical treatment of unstable fractures of the distal clavicle: a comparative study of Kirschner Wire and clavicular hook plate fixation.Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica. 2002;73(1):50-53.
[5]Wojtys EM, Nelson G. Conservative treatment of grade III acromioclavicular dislocations. Clin Orthop. 1991;268:112-119.
[6]Tossy JD, Mead ND. Acromioclavicular Seperation,useful and practical classification for treatment. Clin Orthop. 1963;28: 111-119.
[7]Dumonski M, Mazzocca AD, Rios C, et al. Evaluation and management of acromioclavicular joint injuries. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2004;33(10):526-532.
[8]Nasca RJ,Salter EG,Weil CE. Current concepts review:subacromial impingement syndrome.J Bone Joint Surg(Am). 1998;80(12):1852-1853.
[9]姜从玉,李骥耀,张鹏,等.本体感觉训练治疗肩峰下撞击综合征研究进展[J].中国运动医学杂志,2013,32(7):637-3645.
[10]Scott J, Huskisson EC.Vertical or horizontal visual analogue scales. Ann Rheum Dis. 1979;38(6):560.
[11]Huskisson EC.Measurement of pain. J Rheumatol. 1982; 9(5): 768-769.
[12]Takagishi N,Nobuhara K,Fukuda H. Shoulder evaluation sheet. J Jpn Orthop Assoc. 1987;61(2):623-629。
[13]Bhangal KK,Evans SC,Gibbons CE. Treatment of displaced lateral clavicle fractures with the AO hook plate.Eur J Trauma. 2006;32:468-470.
[14]陈新,王佳,闫旭,等.钩钢板治疗肩锁关节脱位术后肩峰下撞击综合征与第二肩关节间隙的关系[J].中华骨科杂志,2010,30(7): 654-657.
[15]Cote MP, Wojcik KE, Gomlinski G, et al. Rehabilitation of acromioclavicular joint separations: operative and nonoperative considerations. Clin Sports Med. 2010;29(2): 213-228.
[16]郑冲,瞿玉兴,蒋涛,等.肩峰下撞击综合征肩峰下滑囊骨形态发生蛋白-2及7表达及意义[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志, 2012,26(3): 245-246.
[17]翟艳斌,张永红,王东. AO锁骨钩钢板中长期留置对肩锁关节脱位术后肩关节功能的影响[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2013,15(4): 288-292.
[18]EIMaraghy AW,Devereaux MW,Ravichandiran K,et al. Subacromial morphometric assessment of the clavicle hook plate. Injury. 2010;41:613-619.
[19]杨成林,毕郑钢,邵国君,等.应用缝合锚钉急诊修复四肢腱性组织止点区断裂伤的研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2007,9(11):1038-1041.
[20]张克刚,陆芸.带线铆钉治疗TossyII、Ⅲ型肩锁关节脱位[J].中华骨科杂志,2011,31(7):744-748.
[21]Harris RI,Wallace AL,Happer GD,et al. Structural properties of the intact and the reconstructed coracoclavicular ligament complex. Am J Sports Med. 2000;28:103.
[22]Nüchtern JV, Sellenschloh K, Bishop N, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of 3 stabilization methods on acromioclavicular joint dislocations.Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(6):1387-1394. |